Not every gardener knows which vegetable crops have a beneficial effect on the growth and taste of peppers, whether it is possible to plant sweet and bitter peppers next to each other, which they cannot tolerate at all, and why they grow poorly. It is necessary to know this, because sometimes it is those plants that are nearby that affect the yield. Some help growth and development, others destroy, transmit pests and take away vitamins. Sometimes it is necessary to plant some crops at a very large distance from each other.
Many gardeners dream of growing hot peppers, but they doubt the right choice of place for them. There are several nuances that help you determine exactly where hot peppers can be planted next to so that they do not harm other crops. Everything that we plant and grow in our dachas should yield good yields.
Features of growing hot peppers
We noticed that some gardeners, with the same care, have completely different yields and the quality of the crops they grow; the same applies to hot peppers. Often this depends on the fact that not everyone knows and adheres to the rules of crop rotation.
These rules include the importance of what you grow nearby, because some crops have a positive effect on the development, quality and taste of hot peppers, while others, on the contrary, have a very negative effect on these characteristics, carrying insect pests and selecting those that are extremely important for the development of peppers nutritional elements. It is also very important after which you plant hot pepper on the site, and there are a number of crops after which it is strictly forbidden to plant it.
Since each gardener dreams of a good, tasty, high-quality harvest of chili peppers, today we will analyze in detail next to what plants it needs to be planted so that neither they harm it, and also indicate which predecessors in the garden will be ideal for growing peppers and raising the level of harvest.
Advantages and disadvantages of combined plantings
The method of mixed cultivation of garden crops is not a tribute to a fashionable trend. This planting method was known to the ancient Slavs and Indian tribes.
Gardeners who practice growing vegetables together see considerable benefits in this:
- Economical use of site area. A reasonable choice of crop compatibility, taking into account different nutritional needs and ripening periods, will ensure the production of up to 15 kg of vegetables and herbs per 1 m2 per summer season.
- Eliminating land depletion. Combined planting of crops, the growth of which requires different nutrients, not only prevents the same microelements from being drawn out of the soil, but also saturates the soil with certain components. A well-thought-out planting scheme will free you from the use of fertilizers or reduce the volume of application.
- Harm from insects and diseases is minimal. Because some plants “share” phytoncidal properties (similar to antibiotics), which destroy bacteria and pathogens. Others attract birds, worms, and some, on the contrary, drive away harmful insects.
- Organization of a fertile environment on the ridge. Strong tall crops protect and shade low, fragile plants from the scorching sun and wind, reducing the frequency of their watering.
- Mixed cultivation affects the taste of the fruit.
Increased yields and plant health are the result of combined plantings.
The only negative, according to gardeners, is that it is more difficult to cultivate the beds, especially loosening them, since the approach to the plants is limited by the density of the plantings.
Choosing a place and soil
Before planting peppers, it is imperative to choose the right place and appropriate soil. Pepper is a heat-loving plant, so the area must be sunny and at the same time free from drafts. Temperature changes have a very negative impact on the growth, development and, as a result, on the yield of hot peppers. In hot weather, and especially at its peak, plants need to create shade, since the sun's rays can cause burns on the foliage.
For growing peppers, the ideal place is a greenhouse or greenhouse rather than open ground. Since it is in the greenhouse and greenhouse that the regular levels of temperature and humidity are maintained, which are so important for the development of peppers, even minimal temperature changes can slow down growth. It is impossible to create such conditions on open ground, but at the same time, with proper and proper care, you can grow a fruitful crop on it.
The soil for hot peppers should be loose, fertile, moist and non-acidic. Do not allow water to stagnate or become waterlogged - the roots may rot. If the soil is acidic, it needs to be “deacidified”; the most popular means for this is dolomite flour.
The area must be dug up and fertilized before planting.
Features of the location of the beds
For joint cultivation, you need to choose varieties with the same microclimate and care requirements. But do not forget that pepper is considered a more heat-loving crop, and tomato prefers active ventilation.
Tomatoes and peppers in greenhouses can be placed as follows:
- Typical chess order. First, seedlings of tall varieties of tomatoes are planted, and beds with peppers are formed between them. Please note that there must be free space between crops. Otherwise, intertwining of root systems and shoots is possible.
- Dividing a greenhouse into two or more greenhouse zones. In this case, the central part, where fresh air enters, must be given over to planting tomatoes. It is better to plant peppers along the walls of the greenhouse structure.
- General planting divided into linear rows. Tomatoes are planted in long, even rows, followed by beds with peppers. Thanks to the use of this scheme, pepper bushes are protected from aphid invasions. Harmful insects will be repelled by the characteristic smell of tomatoes.
How to plant peppers
You can plant peppers either as seedlings or as seeds in open ground. The first method is the most popular, it is used by the northern regions, and the second - by the southern regions.
For seedlings, depending on the region, the sowing time will be different, since ready-made seedlings are also planted in open ground at different times. For the southern regions, seeds for seedlings are sown approximately from January to February, while in the northern regions - from the second half of February to March. It is most convenient to grow chili pepper seedlings in wooden boxes. After planting, the boxes are covered with film to maintain the required humidity and temperature conditions.
Hot pepper seedlings are planted in open ground when an average of 45 days have passed since the seeds were planted. At this moment, the seedlings have already grown by 15 cm, and about 6 leaves have formed on the plant.
Mutually beneficial partnership
By combining “neighbors” by ripening period, you can organize an uninterrupted conveyor of fresh fruits for your table, collecting several harvests throughout the entire growing season.
Creating a favorable environment with proper placement of plants promotes stronger immunity and healthy growth
of peanuts nearby will significantly improve the stability and productivity of tomato bushes. Bacteria living on the roots of groundnuts will generously endow the soil with “living” nitrogen, enriching the nutrition of vegetables directly in the garden.
Herbs with a pronounced smell go well with tomatoes - mint, oregano, sage, parsley, oregano, lovage, rosemary, thyme, marjoram, tarragon . Scented companions enhance biocontrol by masking the scent of the main plant they are growing with, making it more difficult for pests to find their favorite food. You can additionally spray cultivated plantings with infusions of these aromatic herbs, scaring away uninvited guests.
The taste of tomatoes is far from an idle question. It has been noted that it depends to a certain extent on what spices grow nearby. Compactly planted fragrant herbs will harmoniously resist aggressors, and at the same time change for the better the ratio of acids and sugars accumulated by fruits during the ripening process. For example, basil has a very positive effect on this characteristic. There are suggestions that essential oils stimulate increased formation of fructose and sucrose in fruits.
The “vegetable trio” of tomatoes, garlic and basil works seamlessly together to benefit each other, not only in the garden. They harmonize wonderfully in dishes of the usual seasonal menu and in various preparations for the winter.
Interesting recipes for tomato preparations with basil can be found in the article on our website
Onions, sweet potato , shallots , mustard greens, chard, salad greens, spinach are good compactors for vegetable crops. Sown along the edges or between rows, they together form a pleasant, cool microclimate, covering the lower part of the bushes and the root zone, preventing the soil surface from drying out.
Annual flowers, which have disinfectant and antibacterial properties, are not without reason called “plant repellents.” Marigolds, nasturtium, pyrethrum, calendula, tansy are distinguished by such qualities . In addition to their protective functions, framing borders made of low-growing annuals are also useful because they actively attract helper insects - pollinators and entomophages. And visually mixed plantings of vegetables with decorative flowers (zinnias, daisies) look more picturesque and aesthetically pleasing than ordinary, standard beds with monocultures.
Many gardeners believe that tomatoes do not get along well with representatives of the umbelliferae - dill, fennel, cumin, parsley, coriander, anise . However, according to experts, such proximity in open ground is completely justified, since herbs repel ticks, slugs and snails, which interfere with obtaining a decent harvest of your favorite vegetables.
How to care for peppers
After the seedlings have hatched, the film must be removed. The seedlings are transferred to a bright, warm place until the seedlings are transplanted into the ground. When 2 full-fledged leaves appear on the plants, the seedlings are picked. Before picking, be sure to moisten the soil a couple of hours. Next, each seedling is moved into a separate container; peat pots are best suited for this.
For pepper, it is necessary to create proper lighting - at least 12 hours a day. If natural lighting is not possible, you should resort to artificial lighting - using a lamp.
Move the seedlings to the beds when the air warms up steadily to +14 degrees, then the risk of frost will be reduced to zero.
When growing hot peppers, be it in open ground or in boxes with seedlings, it is necessary to maintain soil moisture and in no case allow it to dry out. You cannot water pepper using sprinkling methods. Also, the soil must be loosened, ensuring oxygen supply to the roots. Hot pepper responds very positively to fertilizing; it needs to be done a couple of times a month. Do not forget to remove weeds, as they can negatively affect the harvest.
The hot pepper harvest is harvested from mid-summer to autumn - the timing directly depends on the planting method and the region. It is recommended not to wait until the peppers are overripe, but to pick them when the fruits are still green.
Hot pepper stores very well; it is used as a seasoning, added to various dishes and canned food. It is very healthy, contains many vitamins and microelements (for example, vitamins of groups A, B, C, etc.). Pepper perfectly boosts the immune system and speeds up metabolism.
Care instructions
As already mentioned, in some aspects the care of the two plants will be different. The gardener must remember this.
Feeding and watering
You only need to water tomatoes once every five days, a little more often in hot weather. Peppers, on the contrary, love more moisture.
The first fertilizing is carried out 2 weeks after planting. Phosphate fertilizers, nitrogen, potassium, and additional nutritional supplements are used.
Pinching and pinching
Peppers are pruned after they reach 15 cm. The first buds, top and side shoots are removed. This way you can achieve the formation of a strong stem and fruit.
Excess leaves on tomatoes are also removed. This helps the proper distribution of nutrients throughout the plant. Pinching is carried out when the top flowers have already opened.
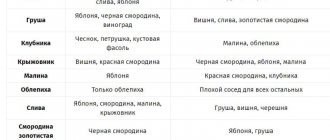
Favorable neighbors in the garden
When growing any vegetables, it is very important to know which crops are recommended to be grown next to them in order to speed up their growth, and which should be planted at the other end of the garden. Let's talk about which crops are the most favorable neighbors for hot peppers.
Surprisingly, herbs will be positive neighbors for peppers; this does not mean that the entire garden bed should be covered with it - there should be grass in moderation. Chamomile, coltsfoot, etc. are ideal for proximity to chili peppers - they significantly accelerate the growth of fruit ripening. Grass can be planted along the edge or between the rows. An excess of grass will take away all the useful elements from the soil.
We must be removed, as they carry destructive diseases and insect pests.
Cilantro, dill, and basil will also go well with pepper - they will add more flavor to the pepper. Please ensure that there is no shading; pepper may have a negative effect on this.
According to the crop rotation table, the proximity of hot peppers to tomatoes will affect the rapid growth of both crops; eggplants, carrots, cabbage and onions are also perfect for proximity.
If you plant garlic next to hot peppers, the second one will repel all insect pests.
Pest and disease control
Dangerous parasites and diseases can interfere with the normal growth and development of vegetable crops. Therefore, you should know what problems may arise during cultivation and how to properly deal with them.
You may be interested in:
Growing tomatoes, peppers and eggplants together For some reason, not all gardeners think about how to properly place beds in a garden or greenhouse. Meanwhile,…Read more…
Aphid damage
These pests love succulent bushes that contain a lot of water. Aphids begin to cause damage at the end of summer. It sucks out all the beneficial juices from the plant, stops their growth, which leads to withering and death of the seedlings. In addition, aphids attract ants and can infect the bushes with a virus.
If you carefully inspect the seedlings, you can detect the pest in time and get rid of it. Aphids live on the underside of leaves, on young stems or on the tops of a bush.
Effective drugs for pest control are “Healthy Garden” or “Fitoverm”. Instructions for use are written on the packaging. The drugs take effect on the second day. “Fitoverm” is also capable of increasing the immunity of the crop due to the absorption of the drug into the plant juice. Using the drug you can destroy other pests. Valid for up to three weeks.
Slug attack
Comfortable conditions for breeding slugs and snails are a moist, shaded environment in a greenhouse. Insects spoil stems, leaves and fruits, and carry various fungal and infectious diseases.
You can prevent the appearance of slugs using slate, which is installed between the beds. Over the course of the entire day, a sufficient number of parasites will accumulate on it, which can be easily destroyed by turning the slate upside down. There is no need to remove dead slugs, since after them other slugs will come and eat them and will not have time to get to the leaves of the crop.
You may be interested in:
About growing cucumbers, peppers and tomatoes together in a greenhouse It is known that the growth of a vegetable crop is influenced by those neighbors who are nearby. There is even a separate gardening science...Read more...
What should you not plant peppers next to?
In addition to favorable neighbors, there are also, on the contrary, unfavorable ones, which should be planted away from hot peppers, and better yet, at the other end of the garden. Moreover, it can harm not only hot peppers, but also vice versa - a “hot” plant can negatively affect the taste of vegetables planted nearby, so be extremely careful.
Let's start with the fact that proximity to fennel is unfavorable for hot pepper. This is expressed by the fact that the pepper can get sick, which will lead to wilting of the foliage, the fruits themselves will develop poorly, which will certainly affect the level of yield, since fennel takes away all the useful microelements necessary for development.
The next vegetable with which it is not recommended to plant peppers or keep a sufficient distance is beets. Since beets grow and develop quite quickly, the root system with its rapid growth suppresses the roots of its neighbors.
Also, peppers cannot be planted with potatoes, since the latter takes away all the microelements, vitamins and other beneficial substances from other vegetables. Therefore, it is better to choose a place for potatoes away from other vegetables.
Also, the proximity of bitter and sweet peppers is not allowed. When placed next to each other, two peppers will pollinate each other, this will lead to bitterness in the sweet pepper, while at the same time, unfavorable taste changes and loss of beneficial microelements are noticed in the hot pepper. When two peppers are adjacent, the heat will be of a completely different variety, all thanks to pollination. It follows that bitter and sweet peppers must be planted in different places, in this case the bitter pepper will not lose its quality and taste characteristics.
Formation of bushes and harvesting
Proper plant formation increases yield. To do this, you need to remove all the stepsons, as well as the leaves located below the fork. Leaves that look inside the bush and greatly thicken the plantings must also be removed. After the bulk of the fruit has formed, the top of each bush needs to be pinched. The peppers will stop growing, but all efforts will be directed towards the fruits that have already set.
Most varieties ripen in late August or early September. Peppers acquire a characteristic color. Hot peppers come not only red, but also yellow, purple, and green. Due to the high content of natural preservatives, the fruits practically do not spoil. Over time they only dry out. You can tie them into bundles and store them hanging in a warm and dry room. When the pods are dry, they should be crushed and then used as a seasoning.
After what crops are hot peppers planted?
When planting pepper, it is very important what grew before it in this place, since past “tenants” can negatively affect the harvest, so the land must be rested.
You will get an even, delicious crop if you plant hot peppers in the place where melons (watermelon, melon, pumpkin, etc.) and also herbs previously grew.
The next favorable predecessor is cucumbers, after which the soil is very favorable for the growth of hot peppers. If there are two or more greenhouses on the site, the plantings in them should be changed annually.
Also, beans, peas, etc. are excellent precursors - they saturate the soil with potassium and phosphorus minerals, which are very important and necessary for pepper. It is from them, as well as from magnesium and humus, that hot pepper grows very well.
Do not plant peppers after other nightshades (for example, tomatoes, potatoes and others), this can be very detrimental to the growth of hot peppers and the harvest as a whole. All nightshades have absolutely the same ailments, in the form of diseases and pests, which will not make it difficult for our “burning” plant to adopt these “misfortunes”.
When growing hot peppers, it is extremely important to respect the proximity. For a fruitful, tasty, high-quality pepper harvest, you need to choose the right “neighbors” in the garden who will not harm its growth and development, but, on the contrary, will accelerate its growth, protect it from pests and diseases, and generally have a positive effect on all the characteristics of hot pepper. Do not forget that the pepper itself can cause harm - do not allow this to happen. Before planting, it is recommended to draw up a scheme for planting vegetables, this will allow you to avoid mistakes in the neighborhood. Follow our recommendations and advice and you will be guaranteed a wonderful harvest.
Other useful and unwanted "neighbors"
Other crops can be grown next to the beds of tomatoes and peppers. Excellent neighbors for tomatoes include carrots, radishes, radishes, beets, celery, garlic, green onions, cabbage, corn, basil, spinach, lemon balm, mint and sage. Next to the peppers you can plant eggplants, carrots, onions, coriander, basil, and marjoram.
The close placement of potatoes, kohlrabi cabbage, cucumbers, fennel, dill and peas is considered not the best solution. As for the predecessors, tomatoes and peppers grow well and bear fruit in beds where cucumbers, cabbage, bulbous and annual legumes were previously grown.
Features and characteristics of tomato culture
The tomato belongs to the nightshade family along with potatoes, eggplant, tobacco, peppers and a number of other plants. They are distinguished by serrated lobed leaves arranged in pairs, flowers that are collected in inflorescences, and a taproot system. Flowering nightshades can occur from spring to summer, and harvesting occurs from summer to autumn. The resulting fruits will be berries or capsules.
Tomatoes are grown in greenhouses all over the world. Thanks to this growing method, its fruits can be consumed fresh all year round. Most greenhouse varieties are indeterminate, so vertical or horizontal trellises are used to support them. The height of the plants reaches 3 m. Determinate or bush tomatoes can also be planted in a greenhouse, but such planting is carried out much less frequently.
Did you know? Red tomatoes have more nutrients than yellow ones.
Tomatoes are inherently perennials, but are usually grown as annuals. Tomato fruits are multi-locular berries. Often they are collected in brushes. The range of fruit sizes is quite wide - from 1.3 to 10 cm. In addition, the fruits are characterized by a wide range of colors.
The nuances of placing plants in one area
Growing several crops in one bed that have different ripening periods, and therefore harvesting, can also be considered joint planting.
Pepper is a late crop, and it is planted in the ground at the beginning of summer, when the weather is warm enough. Therefore, early, quickly ripening crops such as lettuce, onions, and peas were widely planted before him.
This alternation will not only allow you to collect several harvests from one plot per year, but will also increase the overall productivity per square meter.
On a note! Leaf lettuce also prevents the soil from drying out.
Why does hot pepper stop being bitter?
First, let's consider a situation where a hot pepper for some reason loses its pungency. In the vast majority of cases, hot peppers grow insufficiently hot or even bland due to the fact that the “parent” plant was a hybrid, and, as is known, experiments with obtaining seeds from hybrids lead to the most unexpected results. It cannot be ruled out that the new bush was grown from seeds obtained as a result of cross-pollination with other varieties, i.e. you have come across that very second generation, about which it is unknown whether it inherited the burning sensation of one of its ancestors or not.
Someone becomes a victim of completely sincere misconceptions spread by experienced gardeners who continue to believe that the variety has lost its qualities solely due to “cross-pollination”, and not due to mistakes made during the growing process. A special role in the popularization of the myth was played by the fact that some industrial producers, for some reason, do not follow the technique of growing crops to obtain seeds, which is why seed material with “loose” characteristics is put on sale. This explains the fact that the varieties grown on your site acquired qualities that are not very typical for them already in the first year.