Young cherries do not take root very well and overwinter in the middle zone. Therefore, if you decide to plant this tree in your garden, you will have to regularly feed it, prune it, and protect it from frost and sunburn.
The root system of the cherry tree is usually located horizontally, but at the same time it is capable of going deep into the ground by almost 2 m. Therefore, you cannot plant a cherry orchard in areas with high groundwater, as well as in lowlands. Cherries like loam and sandy loam soil the most. If the soil is acidic, then it will need liming about a week before applying fertilizers (in sandy loam soil - 400 g of lime per 1 sq.m, in loam - about 600 g).
Cherry varieties
There are a huge number of varieties and types of cherries. They are classified:
- by the color of the berries (yellow, yellow with a red side, pink, dark red);
- to taste (sweet, sweet with sourness);
- according to the density of the pulp (tender, soft or dense crispy).
Early ripening
Their fragrant and juicy berries with excellent taste reach maturity in the 2-3rd decade of June. The best among the early varieties are:
Valery Chkalov . A productive, frost-resistant variety. It has a dessert purpose and is suitable for canning. Large fruits (7-9) g, collected on a small stalk, are heart-shaped with a dark red color. Berries with a large, semi-separable seed. Has average resistance to fungal diseases.
And the way . Frost-resistant, partially self-fertile, medium early-fruiting variety has an average yield and early ripening. The fruits are average 5-7 g, heart-shaped with roundness and a white point at the top. The color changes as it ripens from dark red to almost black. The stone is light brown, slightly pointed at the top, and sticks slightly to the pulp with medium density. If there is excess moisture, the fruits crack. The Iput cherry is resistant to fungal diseases. It begins to bear fruit in the 5th year.
Raditsa . The variety tolerates winter frosts well. High-yielding, but self-sterile, so a pollinator variety should grow nearby. The fruits are dark red in color. The tree is low-growing with a compact crown.
Orlovskaya amber . A variety of medium winter hardiness with good yield. The berries are average 5-6 g, with good taste, yellow-pink in color.
Mid-season
After the early varieties, the turn of the middle ones gradually comes:
Bull's heart . A variety with large pomegranate-colored fruits with hard-to-pull heart-shaped fruits weighing 8-10 g. Ripening occurs in the second half of June. The variety tolerates cold well and is resistant to diseases.
Fatezh . A medium-sized plant with small berries up to 5 g, but a stable yield. The variety is resistant to diseases. The fruits are pale scarlet in color and have slightly sour flesh.
Vasilisa . A low tree with mixed fruiting. The berries are large, up to 15 g, sweet with dense pulp. With good resistance to frost. It begins to bear fruit 3 years after planting.
Surprise . A variety with average frost resistance. Low damage from disease. Tolerates drought and heat well, but can get sunburn. Large berries 10 g dark red with sour pulp. Pollinators required.
Late
These varieties require more heat and time to ripen the fruit. They are finishing the cherry season:
Tyutchevka . Medium height. The harvest is stable. The berries are medium scarlet 6-7 g with red pulp. They tolerate transportation well. The plant is resistant to moniliosis. Ripens in early July.
Record holder . The tree is tall and productive. The berries are large, 8-10 g, creamy with a pink tint, the flesh is elastic, sweet, and has a medium seed. It is resistant to frost.
Regina . A low tree that begins to bear fruit in the 3rd year after planting. The fruits are dark red, large, 8-10 g, with a rich taste, suitable for transportation. They begin to ripen in mid-July. The plant is frost-resistant.
Napoleon . Tall tree. The fruits are large, 6-8 g, slightly oblong, heart-shaped, dark red (almost black) with dense pulp, which has a sweet taste with a barely noticeable sourness. Transported without compromising quality. Cherries are ready for harvest in early July.
By correctly comparing the characteristics of varieties, such as their flowering time, yield, winter hardiness, disease resistance, and soil requirements, you can grow an excellent harvest with a minimum of effort.
Preparing berries for planting
More than three thousand varieties of this tree are known in the modern world. Some long-lived varieties have a lifespan of more than a hundred years. Many novice gardeners do not know which variety to choose when choosing a seedling for their plot.
Variety selection
When choosing a type of wood, you should pay attention to the following characteristics:
- pollination - self-fertile; partially self-fertile; pollinated by insects and wind;
- time of flowering of the tree and timing of fruit formation - early, middle, late;
- trunk height and crown shape - vigorous, medium-sized, low-growing;
- taste, color and shape of berries - yellow, with a pink side, red;
- fleshiness and juiciness of the fruits – juicy, fleshy;
- berry size – large, medium, small;
- frost resistance – frost-resistant, medium-resistant, heat-loving.
Beginning amateur gardeners planning to plant cherries on their property should get recommendations in advance on choosing a variety from the city garden society, where they will tell you all the intricacies of tree care and help you choose a seedling.
Requirements for soil and planting site
This tree prefers neutral soil. Considering that sod-podzolic soils with high acidity are more typical for central Russia, it is recommended to improve its properties by liming. Lime application rates depend on the severity of the soil and are (in grams per square meter):
- light sandy loam - up to four hundred;
- heavy loamy - up to eight hundred.
Liming promotes better absorption of nutrients and is involved in the formation of fruit seeds. It is better to carry it out on the site in the fall or early spring, by evenly distributing lime over the top of the soil or by burying it to the depth of a spade bayonet (about twenty centimeters).
Another important circumstance that must be observed is that for cherries you need soil that is not waterlogged, loose and freely allowing air to pass through. The close occurrence of groundwater leads to a slowdown in the development of young shoots and drying out of the tree, starting from the top.
Light mode
This tree loves warmth very much, so abundant sunlight is a prerequisite for successful growth. The place for planting a seedling should not be shaded by other trees or buildings.
In order to increase productivity, it is recommended to plant at least two trees of different varieties not too far from one another to ensure cross-pollination of the trees.
Choosing a cherry seedling
The choice of seedling determines how the tree will grow and how it will bear fruit. For planting, 1-2 year old trees with a mandatory graft mark are selected; this will be a partial guarantee of the varietal tree. The roots should not have growths or damage. A trunk with a diameter of at least 17 cm with good branching of branches - at least 3-4, ~ 40 cm long, the bark is smooth.
Of particular importance when choosing a planting plant is the good condition of the central wire trunk. He must be alone - straight and strong. With 2 trunks, an adult cherry tree is likely to break due to the severity of the harvest, and therefore, the death of the tree.
A broken wire trunk will contribute to the development of competitors, which will have a bad effect on the development of cherries.
Description of the garden tree Cherry
The deciduous tree Cherry (Prunus avium) is a species of the genus Prunus (Prunus). It is a genus of fruit trees and shrubs that includes Plums, Cherries, Peaches, Nectarines, Apricots and Almonds. In Western sources, Cherry and Cherry are often described as one species, although they have many differences. The first mentions of Cherry came to us from ancient times. By 800 BC. E. this crop was already actively grown in Asia Minor, although varieties of Prunus avium were also found in central and northern Europe.
The tree's lifespan is from 15 to 30 years or more, growing to 15–32 m in height. The bark of a young tree is smooth purple-brown, becoming harder and dark brown with many cracks with age.
The leaves are green, oval to spear-shaped, pointed, with serrated edges. Leaves appear after or during flowering, which lasts from early spring to mid-spring. The flowers are white, five-petaled, fragrant, collected in clusters of 3-5 pieces. At the end of May, at the beginning of summer, Cherry fruits ripen (it all depends on the varieties and climatic conditions).
The hard, reddish-brown wood is valued as a quality material for making furniture and musical instruments. Cherry wood is also used for smoking as it imparts a distinct and pleasant flavor to the product.
There are more than 1000 varieties of Cherries. But they are divided into three groups:
- "Bigarro" - fruits with dense, crispy pulp, medium and late ripening. Ideal for storing for the winter and for transportation.
- "Gini" - early varieties with juicy, loose pulp. Ideal for eating fresh.
- “Dukes” are hybrids of cherries and sweet cherries, incorporating the properties of both parents.
The Cherry tree is a self-sterile crop. To pollinate flowers, you need to plant several more Sweet Cherry or Cherry trees nearby (it is also a pollinator). Although there are self-fertile varieties of Prunus avium, the proximity of other plantings will only benefit.
Landing dates
Depending on the region, cherries can be planted in spring and autumn. It is important that this happens during the plant’s rest period. In the south, seedlings are planted in the fall in September-October, the main thing is that rooting occurs before the first frost. In the northern regions in the spring before the onset of kidney swelling. It is important to create an adaptation period before the onset of heat.
Mistakes gardeners make when planting and growing cherries
Mistakes when caring for cherries will, at best, result in loss of harvest. In the worst case, crown growth will slow down, foliage, ovary and color will begin to fall off, and the tree will die. A list of common mistakes when caring for crops is shown in the table.
Preparing the planting hole
The most suitable place for the growth and fruiting of cherries will be sunny southern or southwestern areas of the garden with loam or sandy loam soil. Thanks to its air and moisture permeability, quick access of fertilizers to the root system of the tree will be ensured. This crop does not tolerate stagnant water.
During autumn planting, the following work is expected to be carried out:
- Site preparation. To do this, fertilizers are applied per square meter. m – compost (10 kg), superphosphate (180 g), potash fertilizer (100 g). It can be replaced with a special complex fertilizer, then the soil is dug up. Acidic soil is limed a week before applying fertilizer;
- In the prepared area, dig a hole with a diameter of ~100 cm and a depth of at least 70 cm, while the earth is divided into upper and lower layers and folded in different directions.
- A rod is driven into the middle of the hole. Its purpose is to fix the seedling in a vertical position, so it should be ~0.5 m above the ground.
- The deposited top layer of soil is mixed with superphosphate (200 g), potassium sulfur (60 g), ash (500 g) and compost. Part of this mixture is poured into the hole, lightly tamped, sprinkled with earth from the bottom layer, watered and left for 2 weeks to shrink.
Lime and nitrogen fertilizers are not applied during planting of cherry seedlings, as during this period they will cause burns to the roots.
In the case of spring planting, the prepared hole at the end of October and November remains open for the winter. After the snow melts, mineral fertilizers are added to this pit in the spring, and nitrogen fertilizers, which are prohibited in the fall, can also be applied. After 7-10 days, you can begin planting the cherry seedling. It is produced in spring and autumn according to the same scheme:
What problems arise
During the development of a tree, some troubles are possible that interfere with normal growth and fruiting. Learn more about possible problems and ways to solve them.
Doesn't grow
Poor seedling growth can be caused by high acidity of the soil or lack of nutritional components. If liming is not carried out in a timely manner, it is recommended to apply lime mortar to the area around the trunk; form holes in the ground up to twenty centimeters deep. If there is a lack of nutrients, it is necessary to fertilize with nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers.
Doesn't bloom
The absence of flowers is due to the following possible reasons:
- incorrect choice of landing site - lack of sunlight;
- insufficient development of the seedling - for some varieties it takes about five years before the first flowers appear;
- excessive soil moisture or close groundwater.
If the conditions for planting a tree are chosen poorly, it is necessary to replant it, otherwise the seedling will suffer for a long time, and it will not be possible to wait for the harvest for a long time.
Doesn't produce a harvest
Lack of harvest may be due to the following circumstances:
- improper pollination;
- bad weather;
- low-quality fertilizer;
- excessive soil moisture;
- soil clogging, leading to insufficient oxygen supply to the root system;
- high acidity of the earth;
- excessive crown density.
By eliminating these problems, the gardener will achieve the long-awaited harvest.
Spend more time on your garden, and the trees will delight you with spring blossoms and abundant fruiting.
Planting seedlings in open ground
The prepared seedling is soaked in the root solution for 8-10 hours. Next, the seedling is inspected, damage is removed, and all roots are lightly pruned. Landing is carried out according to the rules:
- The seedling is placed in a prepared hole with the south side facing the peg. The roots are carefully laid out on the soil with fertilizer. The root collar should rise above ground level up to 7 cm;
- the roots are covered with soil from the bottom layer;
- pour in a bucket of water;
- the pit is completely filled up;
- compact the earth around the tree and pour out 1 more bucket of water;
- Make a roller from the remaining soil to the diameter of the hole.
When planting several cherries, given the large size of mature trees, seedlings should be planted on the site at a distance of up to 5 meters from each other.
How to grow cherries without hassle
In order for the fruit tree to actively develop and bear fruit well, a sunny place is chosen for it, which is not blown by cold northern winds. A good option would be to plant a seedling on the southwest or south side of a building. Cherry loves fertile light loams, sandy loam soils, and feels absolutely uncomfortable on poor sandstones, heavy peat and clay soils.
You only need to plant zoned seedlings that are sold in specialized nurseries. In addition, they will definitely tell you how to grow cherries without unnecessary hassle. To improve pollination, experts advise planting two or three trees on a plot, but if there is not enough space, growing cherries from your neighbors will save the situation.
The main, beloved varieties:
- very early - “Ruby early”, juicy “Skorospelka”;
- early ones - the unsurpassed “Valery Chkalov”, delicate “Priusadennaya” and “Zhabulet”;
- medium - “Pink Pearl”, “Adeline” and dark red “Veda”;
- late ones - “Leningradskaya black”, sweet “Drogana yellow” and “Bryanskaya pink”.
In the middle zone, spring planting of cherries is practiced, since this is a heat-loving species that can freeze out in the first winter.
Planting correctly
You can plant a cherry orchard in the spring from April until the second ten days of May, provided that the seedlings have unblown leaves. The most favorable months for planting in autumn are September and October, because the young tree will have time to take root before the onset of frost (applicable only to the southern regions).
Planting a tree:
- Planting holes must be prepared in advance. If you plant in the spring, prepare it in the fall, and for planting in the fall, approximately in August. It is best to make the holes round, so the roots will develop well, filling the space evenly. The optimal diameter of the hole is about a meter, the depth is about 80 cm. We pour two buckets of good soil and 12 kg of manure, which must be rotted, into the hole. Mix everything thoroughly and leave for the earth to settle and settle;
- At the time of planting, we dig a hole, leaving a small mound in the middle. We drive a strong stake 5 cm from the center, which will initially protect the trunk of a fragile tree from strong winds and sunburn;
- We examine the root system for damaged roots and cut them back to healthy tissue. In addition, do not forget to place the seedling in water a day before planting so that it is well saturated with moisture;
- We place the young tree on a mound and carefully place the roots, while monitoring the position of the root collar, which must not be buried;
- We tie the seedling to the stake and fill the hole with earth, compacting it with our feet perpendicular to the trunk (heel to the edge of the hole);
- Create a hole around the stem and pour out 3 buckets of water.
Planted young cherry trees are subsequently watered at least 4 times.
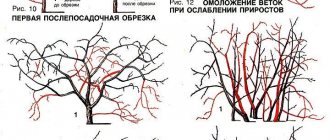
Making the cut
Young trees grow very intensively, so for the first 6 years before the leaves bloom, formative pruning is done. The tree must be kept within certain limits to make harvesting convenient.
The most common types of crowns are:
- sparsely tiered. A total of three tiers are laid, leaving 4 skeletal branches in the bottom (3 are possible), on average 50 cm apart - 3 branches, and in the top, at the same distance - 2 more branches.
- flattened. The principle of pruning is based on the formation of three tiers: in each of them two branches are placed perpendicular to each other. After laying the last tier above the weak side branch, the main conductor is cut off. Subsequently, the branches in tiers are pruned, adhering to the sparse-tiered principle;
- cupped. Such a crown consists of mainly four or five strong branches that form something like a bowl. Thanks to good lighting, fruit branches will live for more than ten years.
Upon completion of formation, pruning is done moderately for ten years, removing all broken, unnecessary shoots and shoots growing towards the conductor. So, the time for the first rejuvenating pruning is imperceptibly coming: you need to shorten all two- and three-year-old branches. Three years later, they make another one, cutting out branches with five- and six-year-old wood. Between “rejuvenation” trees continue to be thinned out annually.
Water and fertilize
In the year of planting, it is very important to destroy weeds in the circle of cherry trees and subsequently continue to carefully monitor this. The ground around the tree can be mulched to retain moisture as much as possible.
Experts recommend the first watering only after flowering, the next one in mid-June and then in July. During the flowering period, do not water; the tree may react by completely dropping the ovary. Water-charging irrigation is carried out in October - up to 100 liters per adult tree. For good harvests, the tree will need a lot of nutrients, which means it can’t do without fertilizing.
Once every three years, 8 kg of organic matter is dug up with soil per square meter according to the projection of the crown. Nitrogen fertilizers are applied in early spring and in July under loosening in liquid or dry form. The tree is treated with phosphorus and potassium fertilizers in September so that it has time to prepare for the winter cold. In addition, growing cherries requires whitewashing the trunk and skeletal branches in autumn and spring to prevent sunburn and frost damage.
Proper care of cherries
In order for cherries to enjoy a good and tasty harvest, they need care. They need a sunny place without drafts, properly fertilized soil. The basis of care is proper planting, timely watering, digging, fertilizing, pest control and pruning.
Watering and fertilizing
Cherry is a moisture-loving plant. Active, deep watering is applied to it - the moisture should reach the location of the main mass of roots ~ 40cm. Watering is required in June - this is the period of tree and fruit growth, during severe drought, in the fall before cold weather, no more than once a week. During fruit ripening, cherries are not watered to prevent cracking of the berries. Watering also stops in the 3rd decade of July and August, so as not to delay the growth of shoots.
In order for the cherry tree to withstand the freezing of moisture from the crown and not freeze in windy and frosty weather, it is necessary to remember about autumn watering.
Whether feeding is necessary or not is decided individually depending on the appearance of the tree and the condition of the soil. Cherries in the fourth year and older can be fed in the 1st decade of May with the following composition: superphosphate, potassium sulfate, urea, 20 g of each per 1 sq. m. m. After harvesting, foliar fertilizing with mineral fertilizers is carried out and organic fertilizers are added.
Crown formation and pruning in two stages
A mandatory step in caring for cherries is pruning. With its help, a tiered crown is formed that can withstand the mass of a huge harvest. The pruning process should begin with the formation of a skeleton of the correct shape. It is held from 1st to 5th year. Gradually forming several tiers:
- In the first year, the height of the trunk is adjusted: it is measured to 60 cm, 4-6 buds are counted up, and a cut is made.
- In the second spring, the base of the first tier is formed. They will be 3-4 shoots located in different directions from the central trunk, and this is done by pruning them leaving 0.5 m. The trunk is measured 70 cm long from this mark, counted up to 6 buds, the rest is cut off.
- In the third spring, branches growing inside the crown or vertically are removed. The second tier is formed and their length is adjusted. It should be up to 15 cm shorter than the branches of the 1st tier and 20 cm below the main trunk. It is measured from the beginning of the second tier at 0.5 m and cut off behind the 6th bud.
- In the fourth spring, the formation of the first two tiers is completed; if higher branches appear on the tree, then the third tier is formed. To do this, cut branches to 20 cm less than the length of the central trunk.
- In the fifth spring, work on the formation of cherries is completed - they bear fruit.
Pruning cherries in two stages
Summer pruning is carried out in 2 stages. The first after flowering, but before fruiting. To provoke the growth of new horizontal branches, young shoots growing in the wrong direction are shortened. The second stage occurs at the end of fruit harvesting. It involves removing weak, broken, misdirected branches.
Harvesting and subsequent care of cherries
Harvesting begins as the berries ripen. They can be collected in several ways - by cutting the berries with scissors along with part of the cuttings, or by picking them by hand with or without cuttings. For safety, devices are used on a telescopic handle; they can be collet with a grip or wire, pneumatic fruit pickers, and a tulip fruit picker.
When the fruits are collected, the trees are treated with insecticides and fungicides or Bordeaux mixture. Pruning and fertilizing with organic and mineral fertilizers are carried out.
Forming and pruning cherries
Without spring pruning, cherry trees become longer and their yield decreases. It is better to prune before the sap begins to flow, and it is advisable to choose a period with relatively warm weather. Immediately after planting, the tree is pruned at a level of 50-70 cm so that the fruiting zone is not laid too high.
The central conductor (the part of the trunk from the lower skeletal branch to the top of the tree) should not be more than 15 cm higher than the tops of the skeletal branches.
In the second year, the skeletal branches are cut to the outer bud, shortened by 1/3.
Branches that compete with the central conductor are cut into a ring.
Usually 3 branches are left in the first tier. In subsequent years, side shoots and too long skeletal branches are shortened by a third, preventing exposure. As a rule, the second tier is formed from two branches. The third tier in one skeletal branch is the final one in the formation of the crown. Subsequently, lateral shoots develop on each skeletal branch. Those of them that do not participate in the formation of the crown are cut to 30 cm.
- Pruning fruit trees in spring - tips for beginners and more
Schemes, photos and videos of spring pruning of garden trees.
At the age of 2-3 years in May, the cherry branches are bent horizontally using spacers or weights. This accelerates the formation of fruit buds. In this case, you cannot bend the branches by the tops, because in case of bending, vertical shoots will begin to form on the branch. In the fall, the spacers and weights can be removed, by which time the branches should already be fixed in their new position.
Fruit-bearing trees are subjected only to sanitary and thinning pruning. At the same time, branches directed into the crown are removed. Dry and diseased branches are pruned without stumps. The cut areas are treated with garden varnish.
If the tree is grafted, then the root shoots of the rootstock must also be removed at the very base.
There is no consensus on autumn pruning. Some gardeners believe that it cannot be done. Others, on the contrary, consider the removal of weak and damaged shoots, as well as shortening of second-order branches to 30 cm, as one of the mandatory elements of preparing a tree for wintering. Both of them agree on only one thing: one-year-old seedlings cannot be pruned in the fall.
- Preparing the garden for winter: what work to do in the fall
We tell you what the autumn preparation of the garden for winter involves.
Cherry propagation
Cherries can be propagated by grafting, seeds and cuttings.
The most effective method of propagating cherries is the grafting method. This method requires cuttings and rootstock. Cuttings of several varieties are cut in the fall and stored in a cool place. The rootstock is shoots and seedlings. 1-2 weeks before the start of active sap flow, copulation is carried out - oblique cuts of up to 5 cm are made on the rootstock and scion, an additional cut of up to 1 cm is made on both sections. The scion and rootstock are connected to each other in a lock, creating immobility, and wrapped with a special tape or tape.
To improve the engraftment process, cuttings are taken with 2 buds, which must be of the same diameter as the rootstock at the grafting site.
To propagate cherries by cuttings, it is necessary to prepare planting material - shoots with growth buds ~ 30 cm long and a substrate of peat and sand 1:1. Prepared cuttings with the lower cut parts are kept in a growth stimulator for about 12 hours. Then they are planted in a greenhouse, with the prepared substrate deepened to 3 cm with an interval of 5 cm. Caring for them consists of frequent watering and maintaining a temperature of 25-300 C. The roots appear after 3 weeks.
Propagation by cherry seeds most often results in trees with inedible berries. This type of propagation is used to grow rootstocks compatible with any variety.
Fertilizing cherries in spring in the Moscow region
Peach care
If a tree grows in the Moscow region, it can be fed with inorganic fertilizers, which include the following components:
- Phosphorus stimulates the formation of flowers. If there is not enough of it in the soil, the leaves become gray.
- Magnesium promotes the formation of shoots and foliage. You cannot overdo it with adding the substance to the soil, otherwise the leaves will turn brown.
- Fertilizer with potassium increases the immunity of the shoot. It will not suffer from frost and other negative external influences.
- Nitrogen will help speed up the growth of the seedling. It is necessary for the formation of a good crown. Against the background of a lack of substance, the number of fatty shoots will actively increase.
- Potassium helps the tree to bloom and form a sufficient number of buds. Additionally, the tree will have fairly strong and powerful branches.
If the question arises about how to feed cherries in the spring, attention should be paid to organic fertilizers. Among them, humus, slurry from manure, compost and herbal solution are very popular. In the Moscow region they also practice growing special crops under trees. To increase the nitrogen content in the soil, it is recommended to plant legumes.
Diseases and pests
Cherry trees are susceptible to fungal diseases: clasterosporiasis, monoliosis, coccomycosis. Methods to combat them involve cutting out the infected parts and burning them. The cleaned wound is treated.
Dangerous enemies of cherries are aphids: black cherry and apple-plantain. To get rid of it, herbal preparations are used. Insecticides are used if necessary.
Caterpillars of the Pentecostal plant, cherry blossomworms, and leaf rollers cause harm. It is better to carry out preventive treatment against them in the spring.
Cherry berries have excellent taste and are a storehouse of nutrients; there is nothing more beautiful than a blooming cherry tree. And to have all this you need to put in a little effort and patience.
What trees can I plant cherries with?
A cherry tree bears fruit only if it is in a favorable neighborhood. In addition, if trees are planted nearby that are interfered with by cherries, there may be no harvest.
Cherry is a cross-pollinating tree, so two or more seedlings should be planted at once.
Favorable neighborhood for cherries:
- plums
- Cherry tree;
- Apple tree;
Cherry trees are undesirable nearby:
- black currant;
- peach;
- Rowan.
- nut;
- pear trees;
How to treat cherries against diseases?
Among the many diseases that affect fruit trees, there are those that pose the greatest threat to cherries. And the point is not only in their danger, but also in their prevalence. Spring preventative spraying allows you to prevent the development of these diseases in time.
Scab
A common fungal disease that affects leaves and fruits. The result of infection is loss of yield. When affected, the leaves become covered with brown-olive spots with a velvety structure. Yellowish circles appear around the spots.
Later, fungal spores migrate to the fruits, causing them to crack before they ripen. The disease especially often appears after heavy rainfall.
How to fight:
- In the spring, before the buds open, the tree trunk circles are treated with Nitrophen.
- The second stage is treatment with 1% Bordeaux mixture. The first time the cherries are sprayed is when the buds begin to bloom, then after flowering.
To prevent scab infection from recurring next year, treatment with Bordeaux mixture is carried out in the summer, after harvesting the fruits.
Brown spot
This fungal disease is also called phyllostictosis. Small brown spots with dark rims and black dots appear on the leaves. With severe damage, the leaves dry out and fall off.
How to fight:
- Spray the tree with 1% copper sulfate until the buds open.
- In the “green cone” phase or during budding, apply Bordeaux mixture.
- After flowering, re-treat the trees with 1% Bordeaux mixture, and two weeks after flowering, spray again.
Clusterosporiasis
The second name for this fungal disease is perforated spotting. The microorganism affects almost all above-ground parts of the plant - buds, leaves, flowers, ovaries, fruits and even woody shoots.
The disease is easily recognized by multiple holes in the leaves. First, small red-brown and crimson spots appear on them, which enlarge and become perforated. The fruits become stained and mummified. The bark of the affected tree cracks and gum flows from it.
How to fight:
- In the spring, before the leaves bloom, spray the cherries with a 3% solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture. Treat not only the crown, but also the tree trunk, as well as the soil underneath it.
- When the cherry blossoms, spray it with Horus, Captan, Signum or Topaz, and after a couple of weeks, repeat the treatment with Bordeaux mixture.
Coccomycosis
This is a dangerous fungal disease in which the leaves of the tree first become covered with red-brown spots and then die. The foliage of diseased trees falls off long before autumn. The fruits, even if they ripen, become covered with brown spots and become mummified.
How to fight:
- First, before the buds swell, spray the cherries with copper-containing preparations - Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate.
- At the “green cone” stage, re-spray the tree with copper preparations, or even better, copper oxychloride.
- During the budding period, use more serious drugs - for example, Topaz, Chorus, etc.
Moniliosis
This disease, more commonly known as fruit rot, is caused by a fungus. Symptoms: leaves dry out, fruits do not ripen and become mummified, softened areas appear on the shoots, and the bark cracks. On large trees, affected and healthy parts can be clearly distinguished.
Branches infected with moniliosis dry out. Some even turn black. When the berries ripen, they rot and become covered with a whitish-gray coating.
How to fight:
- Before the buds swell, spray the cherries with 3% Bordeaux mixture.
- Before flowering, treat the tree with a 4% Zineba solution. If you were unable to spray the cherries before flowering, do it at the budding stage. Use 1% Topsin for this purpose. It can also be used for subsequent spraying.
- Immediately after dropping the petals, treat the tree with Horus.
If the cherry variety is resistant to moniliosis, then no more spraying will be needed during the season.