Author: Elena N. https://floristics.info/ru/index.php?option=com_contact&view=contact&id=19 Category: Garden plants Published: September 04, 2016Last edits: January 06, 2021
- How to grow peanuts
- Spanish group (Spanish varieties)
- Beneficial properties of peanuts
Cultivated peanuts (lat. Arachis hypogaea), or underground peanuts, or groundnuts , are a popular earthen crop that belongs to the genus Peanuts of the Legume family. From a botanical point of view, the peanut nut is not a nut, but a legume. The homeland of the plant is South America, where it already had value in those days when the mainland had not yet been discovered by Columbus. Peanuts came to Europe thanks to the Spanish conquistadors, and later the Portuguese brought this crop to Africa, where the nutritional properties of peanuts and their ability to grow on poor soils were highly appreciated. And after a while, slave traders brought peanuts to North America. In the 30s of the 16th century, Portuguese sailors brought peanuts to Macau and India, and Spanish sailors brought them to the Philippines. Then the culture came to China and became a salvation from hunger for the local population. In the early 19th century, commercial peanut farming began in South Carolina, and the crop fed both armies during the North-South War. Since peanuts were considered the food of the poor, farmers were not eager to grow this crop, but in 1903, American agricultural chemist George Washington Carver invented more than 300 products from peanuts - drinks, cosmetics, medicines, dyes, printing ink, laundry soap and even an insect killer... And Since the boll weevil was massively destroying cotton crops in those years, Carver was able to persuade farmers to alternate growing soil-depleting cotton with cultivating peanuts. As a result, peanuts became the main cash crop of the southern states, and in the city of Dothan, Alabama, grateful Americans erected a monument to Carver. Today, peanuts in Ukraine, Transcaucasia and other regions of the former USSR with a warm climate are grown on an industrial scale.
Planting and caring for peanuts
- Planting: sowing seeds in open ground - in mid-May.
- Lighting: bright light.
- Soil: moist, light, containing humus, calcium and magnesium, sandy loam or chernozem neutral reaction.
- Watering: after the top layer of soil has dried. During flowering - 1-2 times a week in the mornings; after flowering, watering is moderate, but it is necessary to spray the peanuts with warm water in the evening. During drought, sprinkling or watering along furrows between rows is advisable. In a season with normal rainfall, 4-5 waterings will be needed.
- Fertilizing: complete mineral fertilizer: 1st – when the seedlings reach a height of 10 cm; 2nd – at the beginning of fruiting.
- Reproduction: seed.
- Pests: thrips, aphids, caterpillars and wireworms.
- Diseases: affected by powdery mildew, phyllostictosis, Alternaria blight, Fusarium wilt and gray mold.
Read more about growing peanuts below.
Varieties for the middle zone, Siberia, the Urals, the Volga region
Russian farmers love everything exotic. This desire pushed breeders to develop new varieties of peanuts that could adapt to the climate of central Russia.
Here are proven varieties with positive reviews:
- Adyg.
- Accordion.
- Stepnyak.
- Klinsky.
They show good results and are excellent as further own seeds. The third generation fully adapts to Siberia, the Volga region and the Urals.
Read how to grow peanuts in the middle zone here.
Methods for growing cultivated groundnuts
There are two ways to grow peanuts:
- Sowing seeds in open ground.
- Preparing seedlings at home, followed by replanting in greenhouses or for growing plants in warm beds.
Attention! Each method has its own characteristics and is selected based on the desired result.
So the seedling method helps to harvest before the onset of autumn frosts, and the seed method - in early August. Read about how and where peanuts grow here, and this article tells you how to grow groundnuts at home in a pot.
Peanut plant - description
Cultivated peanut is an annual plant up to 70 cm high with highly branched shoots. Its root is also branched, taprooted, its stems are erect, pubescent or bare, slightly faceted, with recumbent or upwardly directed lateral branches. Peanut leaves are pubescent, alternate, from 3 to 11 cm long, pair-pinnate, with a grooved petiole and two pairs of pointed elliptical leaflets. Peanuts bloom with whitish or yellow-red flowers, collected in 4-7 pieces in short axillary inflorescences. Although each peanut flower blooms for only one day and fades by evening, the entire plant blooms from late June or early July until late autumn.
Peanut fruits are oval, swollen two- to four-seeded beans, one and a half to six centimeters long, with a cobwebby pattern. When they mature, they bend down to the ground, dive into it, and mature there. Peanut seeds are oblong, the size of a bean, covered with dark red, light pink, cream or grayish-yellow skin. Peanut fruits ripen in September-October.
Which plot to choose in the garden?
Peanut is a light-loving crop, but is tolerant of slight shade. The area at the dacha should be free of snow and well dried. It is better to choose a windless area: in Siberia, the Urals and the Volga region, cold winds negatively affect seedlings at the end of spring. Here are the answers to the main questions about the technology of growing groundnuts and the nuances of caring for them in open ground:
- How to prepare the soil for planting? A favorable environment for groundnuts is soil with a neutral pH, rich in calcium and magnesium, loose, well permeable to air and water. Before planting seedlings in open ground, the soil is enriched with natural organic matter.
- When to sow and how to transplant seedlings into open ground? Plants are planted in early June. The planting pattern is 60x60 cm. It can be planted in another way - wide-row, when the width between plants is 65 cm and the distance is 20 cm.
- When is the best time to plant seedlings in open ground? Peanuts are planted in warm, windless weather until June 25. Otherwise, the seedlings will be cramped in the container and the roots will stop developing normally.
Water the seedlings lightly before planting in open ground. Wait until the soil softens completely. Otherwise, the root system will be damaged and the groundnut will become unsuitable for further growth.
Planting peanuts in open ground
How do peanuts grow?
Peanuts are grown in open areas with intense light without the slightest hint of shadow from buildings or other plants. Peanuts grow at temperatures above 20 ºC - if the temperature drops literally two degrees, the plant stops growing. The easiest way to grow peanuts in Ukraine and other warm regions is to sow its seeds in the ground at the time when acacia is blooming. Peanuts in Russia, especially in areas with a cool climate, are best grown by seedlings.
- Marking F1 on a package of seeds - what does it mean?
When to plant peanuts in the ground
Since peanuts can only be planted in warm soil, this is done after sowing melons, when the soil warms up to 12-14 ºC, which means not earlier than mid-May. Keep in mind that returning spring frosts are detrimental to peanuts. Peanuts purchased in a store or market can be used as seed material, but not fried, candied or salted.
Then you can plant peanuts
When growing peanuts, it is very important to observe crop rotation. It grows best after crops such as cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes and potatoes, especially if organic fertilizers were applied to these crops. But after legumes (beans, peas, beans, lentils), peanuts are not grown, because the plant can develop root rot.
Soil for peanuts
The soil for peanuts should be moist, light and neutral, with a high content of humus, magnesium and calcium - black soil or sandy loam. The crop does not tolerate saline soils, and acidic soils must be limed before planting peanuts.
The area for planting peanuts is prepared in advance: during the autumn digging of the soil, 1 to 3 kg of humus is added to a depth of 25-30 cm for each m² of area. In the spring, the soil is dug up again, but not so deeply, and 50 g of Nitrophoska is added to the soil for each m² of plot.
How to plant peanuts
How to plant peanuts? Peanuts are planted in holes 10 cm deep, located in a checkerboard pattern at a distance of 50 cm from one another. The gap between the rows is left within 25-30 cm. You can sow peanuts in the garden using a square-cluster method according to the 60x60 or 70x70 cm pattern. Peanuts can also be planted in a wide row, maintaining a row spacing of 60-70 cm and a distance between plants in a row of 15- 20 cm. Place 3 large seeds in each hole, since small ones may not sprout. After sowing the seeds, water the bed generously with a hose through a shower head under low pressure so as not to wash away the soil.
Optimal timing for planting
Peanuts are a heat-loving legume that quickly begins to grow. It is planted depending on the climatic characteristics of the region and weather conditions. The crop can be grown in different ways:
- Sowing seeds directly into the garden bed.
- Growing seedlings in an apartment and planting planting material in the soil.
- Growing in a greenhouse, greenhouse, under agrofibre.
Seeds are planted in the garden after the soil has warmed up to 15 degrees and the threat of spring frosts has passed: low temperatures are destructive for the crop. Optimal temperature indicators for full growth are 22-28 degrees. If the temperature drops below 15 degrees Celsius or rises above 30 degrees, the bushes will stop growing and developing. Since groundnuts prefer warmth, in regions with a cold climate and the likelihood of frost returning (Ural, Moscow region, Black Earth Region), the plant is planted in wide peat pots.
It is better to sow peanut seeds in separate peat cups in April and transfer them to open soil in June.
Growing peanuts in the garden
How to grow peanuts
How to grow peanuts in the garden? Caring for peanuts consists of watering the bed during drought, weeding, loosening the soil and fertilizing. Young low seedlings must be protected from weeds. Weeding can be combined with loosening the soil, and vice versa. At the end of flowering, 1.5-2 months after sowing, the expanding ovaries will begin to descend to the ground and grow into the soil, where the ripening of peanuts will occur. As soon as the ovaries begin to bend to the ground, the bushes are covered with moist, loose soil, like potatoes, so that the receptacle can quickly reach the nutrient medium. Instead of hilling, you can add a layer of mulch from humus, sawdust, sand or peat at least 5 cm thick to the bed. On average, 30-50 beans ripen under each bush, each of which has from 1 to 7 seeds.
Watering peanuts
Groundnuts like moist but not wet soil. It needs to be watered when the top layer of soil dries out. During flowering, it is watered abundantly, once or twice a week in the morning; after flowering, it does not need watering as much as spraying in the evening every other day or two. If it rains during the ripening period of peanuts, cover the bed with polyethylene. And during a drought, it is best to sprinkle peanuts, but if this is not possible, then water the peanuts along the furrows between the rows. In total, 4-5 waterings are carried out per season.
Peanut feeding
The first time peanuts are fed with a solution of 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 45 g of potassium salt and 70 g of superphosphate in 10 liters of water, when the seedlings reach 10 cm in height. The second time is at the beginning of fruiting, although this feeding is optional.
Peanuts at home
Select strong and healthy peanut seeds and soak them overnight in a bowl with water and a drop of Epin. The next morning they should have small white sprouts. Plant the seeds in loose soil placed in a wide container. Peanuts germinate very quickly, and immediately after flowering, hypophores are formed in place of the flowers, which, bending, go into the ground, where peanut beans develop. Did you know that peanuts develop underground?
Keep peanut crops away from drafts, on a southern windowsill, but in the midday hours the plant needs shading. Water your peanuts regularly, but try not to allow water to stagnate in the roots. On hot days, spray your peanuts to prevent spider mites from infesting them. Two and a half to three months after germination, the peanut leaves begin to turn red, and this is a sign to you that the peanut fruits in the soil are already ripe.
Preparing the site before planting
It is worth preparing the area for sowing peanuts in the autumn. Preparatory activities are:
- Digging the area with a spade bayonet.
- Application of organic fertilizers (2 kg of compost, humus or charcoal per 1 sq. m.),
- Cultivating the beds and removing emerging weeds along with the root system.
- Application of nitrophoska (50 g of the drug per 1 sq. m. of soil).
Peanuts prefer light soil that easily absorbs moisture. Groundnuts do not develop well on heavy soils and clayey soil, which retard the penetration of water to the root system. The best soil mixture is sand and humus, taken in equal parts.
Peanut pests and diseases
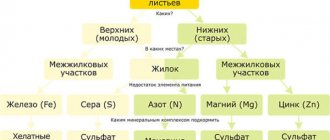
Peanuts can be susceptible to powdery mildew, phyllostictosis, Alternaria blight, Fusarium wilt and gray mold.
Powdery mildew - the first signs of this disease look like single spots of powdery plaque on both sides of the leaves, which grow over the course of the disease and cover the entire leaf, causing it to turn yellow and dry out. The disease affects both stems and even embryos. In case of severe infection, in the fight against powdery mildew, they resort to treating peanuts with systemic fungicides - Bravo, Quadris, Ridomil, Switch, Skor, Topaz or Horus.
Phyllosticosis, or leaf spot, is not such a harmful disease, but it is necessary to combat it. The onset of the disease can be recognized by small brown spots growing up to 6 mm in diameter. Gradually, their middle fades, the tissue in it dies, and the border becomes brownish-violet. Phyllostictosis progresses during periods of high air humidity. Treatment of plants with broad-spectrum fungicides is effective in combating disease.
- Sweet peas: growing from seeds in the garden
Alternaria blight, or black leaf spot, appears in years when wet and warm weather sets in for a long time at the end of the growing season. Black spots up to 15 cm in diameter form on the edges of the leaves, which grow and merge as the disease progresses, causing the edges of the leaves to die. On the spots you can see a dense black coating of fungus. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to follow the agricultural practices of the species, which serve to increase the plant’s resistance to the pathogen.
Fusarium wilt manifests itself in the form of root rot, causing a cessation of plant growth and development, yellowing of its above-ground parts and rapid death. The danger of the disease is that it may subside for a while, but during the period of flowering and fruit set it develops with renewed vigor, which leads to the death of plants even before harvesting. Fusarium wilt can be prevented by following agricultural practices and timely harvesting.
Gray rot usually occurs at the end of peanut flowering and is manifested by rusty-brown spots that move from the leaves along the petioles to the stems, causing their upper part to wither and die. Fruits do not form on affected plants, and those that have already formed become deformed. Active development of the disease is observed at the end of summer in humid and warm weather. The only way to prevent the appearance of gray rot is by growing peanuts in a high agricultural environment.
Sometimes peanuts can also suffer from dwarfism, dry rot, ramularia and cercospora.
Among the pests that can annoy peanuts are thrips, aphids and caterpillars, which can be gotten rid of by sprinkling the garden bed with a mixture of wood ash and tobacco dust, and against thrips peanuts are treated with insectoacaricides. The worst thing is if the peanuts start to be eaten by wireworms - the larvae of the click beetle living in the soil. Their destructive activity is not prevented even by the fact that the peanuts are in shells - they easily gnaw through them and feed on peanut seeds.
To destroy wireworms, pit traps are dug in several places, into which pieces of beets, carrots or potatoes are placed. The traps are covered with boards, pieces of slate or metal, and after a while they are opened and the larvae that crawl in to feed are destroyed.
In order to minimize the risk of pests appearing in the garden, follow crop rotation and agricultural practices of the species, and remove weeds from the area in a timely manner.
Harvesting and storage, drying of fruits
Harvesting begins in mid to late September. You need to have time to remove it before daytime temperatures drop below +8...+10 °C. Then the quality of the harvest will not decrease. To clean, you need to dig up the root part with a fork. This article will tell you about treating tomato seeds before planting seedlings.
You need to dig up the bush on both sides of the bed. After carefully shaking it off, it is taken out and placed on a garden cart. They are taken to the site, under a canopy, where the beans can be separated from the stems.
Drying of beans is necessary. Use household dryers in which the temperature is maintained at no more than +45...+48 °C. For large volumes of grown peanuts, heliofruit dryers are used. Enterprises where the area under this crop amounts to tens of hectares use industrial belt dryers.
Dried fruits are stored in bags or craft bags, boxes that protect the collected beans from rodents.
Harvesting and storing peanuts
As soon as the peanut leaves turn yellow, dig up a couple of beans and if the seeds come out easily, be ready to harvest. Peanuts are usually harvested when the air temperature remains stable around 10 ºC. Do not delay harvesting until the cold weather, because after the soil freezes, the seeds become bitter and become unsuitable for food. Wait for a nice sunny day and start cleaning.
A pitchfork is used to dig up fruits. After being removed from the ground, the beans are separated from the stems and dried in the fresh air in the shade. When the shells are dry, pour the beans into fabric bags and store them in a dry place with good ventilation and a temperature not exceeding 10 ºC.
Video of growing groundnuts from planting in the ground to harvesting
In a video clip from the YouTube channel, an experienced gardener shows and tells:
- how to plant groundnut beans in the garden;
- flowering and hilling of peanuts;
- harvesting (digging).
You might be interested to know: Is it necessary and how to soak pea seeds before planting?
It is clearly not possible to grow peanuts on an industrial scale in Russia. We don’t eat groundnuts like Americans, but the harvest we get from our garden is enough for our personal needs. Surprise your dacha neighbors and delight yourself with a hand-grown product that is atypical for our climate - groundnuts.
Types and varieties of peanuts
There are more than 70 types of peanuts in the Legume family. Several species are grown in South America, but only two species are cultivated outside of this continent - cultivated peanuts and Pinto peanuts. A huge number of cultivated varieties of peanuts are divided into four groups:
Spanish group (Spanish varieties)
These small peanuts are grown in South Africa and the southeastern and southwestern United States. The Spanish type of peanuts is characterized by a higher oil content than in varieties of other types. Spanish peanuts have small kernels in a pink-brown shell, which are used mainly for the production of peanut butter, candied and salted nuts. The largest suppliers of Spanish peanuts are Texas and Oklahoma.
The best varieties of Spanish-type peanuts include Dixie Spanish, Spentex, Argentine, Spanet, Natal common, Star, Comet, Spankhoma, Florispan, Spankromm, Tamspan 90, O'Lean, Spanko, Wilko, White Kernel, Shafer's Spanish and others.
Valencia Group
Represents varieties mostly with large kernels. These are tall plants, reaching a height of 125 cm, with three-seeded smooth fruits. The seeds are oval, in a bright red shell, for which they are often called redskin. This group is a subgroup of Spanish.
Group Runner
The varieties of this group are superior in taste to the varieties of the Spanish type; in addition, Runner is better fried and produces higher yields. The kernels of Runner varieties are large and oblong. They are used to produce peanut butter and salted nuts for beer. The best varieties of the Runner group are Dixie Runner, Early Runner, Virginia Bunch 67, Bradford Runner, Egyptian Giant, North Carolina Runner 56-15, Georgia green, Fragrant Runner 458, Southeast Runner 56-15 and others.
- Which pepper to sow: we recommend TWO hybrids for soil and greenhouse – it doesn’t get any sweeter!
Virginia Group
These selected, large peanuts are roasted in the shell and used for confectionery. The best varieties of the Virginia group are Shulamit, Gull, Wilson, Gregory, Virginia 98R, Perry, Virginia 92R, North Carolina 7, North Carolina 9 and others.
How to get seedlings at home - step-by-step instructions
When is the best time to sow?
When to plant depends, first of all, on how many days it takes for the groundnut seed to germinate. The right time for planting seeds using the seedling method is mid-May ; Germination will last for 10 days. Here are detailed instructions and answers to the most important questions.
- Where to get seeds and how to prepare them for planting? Do I need to soak it, how?
Seeds can be purchased at a specialized seed store, or you can buy them at a regular store. It is important that they are not fried, salted, or processed by other methods. So, if you are thinking about whether you can plant store-bought nuts in your garden, alas, it won’t work. If you come across a nut in the beans, the chance of success increases. In order for the nuts to sprout, they are soaked for 5 hours in warm water. The seeds are pre-treated in a solution of potassium permanganate to reduce the risk of any diseases during plant development. It is recommended to add a growth stimulator. - What soil should I choose and how should I prepare it to successfully germinate grains? The culture prefers light, nutrient-rich soils. A good soil will be soil mixed with sand and manure in equal proportions.
- Which container should you choose? The container can be anything from plastic cups to wide boxes. The latter contribute to the favorable development of radicular nodules.
- How to sow seeds? The nuts are deepened into the soil by 3 cm, then the container is covered with glass or film.
Important! The planting material must have its original red shell and be intact. Peeled and half-grown ones will not sprout.
Care
The environment is the main factor influencing the speedy germination of seeds. Here are some recommendations.
- Light mode . Peanuts love light. Some gardeners create artificial lighting. If it is not enough, then the growth of the plant slows down significantly. But extreme heat is not acceptable either. It is better to remove the sprouts in partial shade for a while.
- Temperature regime . The temperature in the room should be between +20 and +25°C, otherwise the peanuts will go into the sleep stage.
- Watering . Plants are watered when dry soil crust is observed.
- Do I need to feed seedlings? You can feed peanuts with fertilizer in the form of ash. Bird droppings should not be added to the soil.
After each watering it is necessary to loosen the soil. This will improve the aeration of the root system and the plant will develop faster.
Properties of peanuts - harm and benefit
Beneficial properties of peanuts
What are the benefits of peanuts? To understand the benefits of peanuts, you need to study its composition. Peanuts contain linoleic, pantothenic and folic acids, vegetable fats, glutenins, easily digestible proteins, starch, sugars, vitamins A, E, D, PP, B1 and B2, iron, macroelements magnesium, phosphorus and potassium. Its fruits contain antioxidants, and this makes peanuts, along with strawberries, pomegranates, blackberries and red wine, one of the most effective means of preventing cardiovascular diseases.
Peanut proteins have an optimal ratio of amino acids, and this is the reason for their excellent digestibility by the human body. The fats contained in peanuts have a slight choleretic effect, which is useful for gastritis and gastric ulcers. Folic acid promotes cell renewal in the body, and a large number of antioxidants protect cells from free radicals and prevent vascular ischemia, heart disease, early aging, atherosclerosis and the formation of cancer cells.
Peanuts have a calming effect on people with increased excitability, help to quickly restore strength, improve memory, increase potency, enhance sexual desire, and eliminate insomnia.
Due to their high protein content, peanuts increase the feeling of fullness, which is why nutritionists often use them as the basis of weight loss diets. But what peanuts do not contain is cholesterol.
Peanuts - contraindications
Any, even the most healthy product, if used in exorbitant quantities, can be harmful, therefore, when consuming peanuts, you need to observe moderation, especially for those who are overweight. Peanuts can be harmful to people who are prone to allergies, especially if the kernels are consumed along with the skin, which contains strong allergens.
Arthritis and arthrosis are also contraindications to eating peanuts. We recommend that you monitor the quality of the product, since moldy or rancid peanuts can lead to poisoning.
Aftercare
To care for peanuts, it is necessary to periodically perform the following procedures:
- Perform regular loosening of the soil.
- Weed the rows to remove weeds.
- Water the plant at least once a week.
During the flowering period of the crop, the rules of care become more complicated. The plant needs to be watered more often and fed with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers.
To form nuts and obtain a harvest, you must do the following:
- Raise small mounds 5 cm high.
- After a week of flowering, increase the hills to a height of 13-15 cm.
- After the flowering of the crop is completed, the last hilling is carried out to a height of 25 cm.
- Reduce watering to once a week.
- By mid-August, gradually reduce watering until it stops completely.
- During cold weather, it is recommended to cover peanut plantings with thick cloth.
Protection of plantings from pests
Potential threats to peanuts include rodents and mole crickets.
To avoid damage, it is recommended:
- Install the mesh fence at a depth of 5-8 cm underground.
- Collect the grain and dig it into the garden bed.
- Cover it with roofing felt.
- Cover with manure and plant debris.
Disease Control
Common diseases for peanuts are:
- cercospora;
- fusarium;
- powdery mildew;
- Alternaria blight;
- phyllosticosis;
- gray rot.
To prevent these diseases, you must do the following:
- Monitor crop rotation.
- Isolate last year's crops from new ones.
- Treat the area with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture.
- Treat crops with fungicides.
- Sprinkle the plants with ash and tobacco.
How to plant peanuts correctly?
In order for peanuts to grow and produce a harvest, it is necessary to strictly follow the instructions for processing seeds and soil. Some diseases cannot be cured. They must be excluded at the stage of preparing seeds for planting.
Planting in open ground
Seeds are planted in the ground when the weather reaches 20 degrees Celsius, and the temperature at night does not drop below 5 degrees. In the prepared area, it is necessary to make grooves, as for planting legumes, to a depth of 8 centimeters. The distance between the bushes should be 15 centimeters so that they do not shade each other. The interval between grooves should be half a meter.
Peanuts can be planted in separate holes. Then they should be arranged in a checkerboard pattern.
Gardeners plant nuts and beans. Peanut skins provide additional fertilizer.
Planting by seedling method
By growing seeds in this way, you can grow strong seedlings at home, immediately identifying the best bushes. They are planted in the garden plot. The time for growing seedlings is April - May.
After the seeds germinate, you need to plant them in pots or boxes. Convenient to plant in peat pots and tablets. This allows you to plant the plant in the ground without damaging its roots. Pots with seedlings are placed in a bright place. In spring, the days are cloudy; the plant needs to be illuminated up to 12 hours of daylight.
When the sprouts become stronger and 4–5 leaves appear on them, they can be transplanted into open ground. Before this, the soil should be moistened and mineral fertilizers applied. Typically, seedlings are transplanted at the end of May or June.
The Gnomvolga channel tells how to grow peanuts correctly and what mistakes should not be made.
Features of peanuts
Cultivated peanut is an annual plant that reaches a height of 0.7 m. Its shoots are highly branched. The tap root is also branched. Bare or pubescent, erect shoots are slightly faceted, side branches are directed upward or recumbent. There is pubescence on the surface of the alternately arranged pair-pinnate leaf plates; they reach 3–11 centimeters in length, their petiole is grooved and there are two pairs of pointed leaves of an elliptical shape. Short axillary inflorescences consist of 4–7 flowers of red-yellow or whitish color. The life of each individual flower is only about 24 hours, but the flowering of peanuts is long, it begins in the last days of June or the first days of July, and ends in late autumn. The fruits are swollen two- to four-seeded oval-shaped beans, they reach a length of 15–60 mm, and there is a cobweb pattern on their surface. During ripening, the fruits bend towards the surface of the soil and then sink into it. It is in the ground that they ripen. The seeds of this plant are the size of a bean, they have an oblong shape, and the top is covered with pinkish, dark red, yellow-gray or cream-colored skin. Fruit ripening is observed in September or October.
Peanuts in the country - the complete process from planting to harvesting
Requirements for growing peanuts in a summer cottage
To grow peanuts you need fertile, black soil. If peanuts are planted to obtain oil, then you need to pay attention to the shade of the soil: seeds planted in light soil will produce light peanut oil, and seeds planted in dark soil will produce dark oil. Bushes love warmth, at temperatures below 0 degrees, they stop developing and die.
In the middle zone, only certain varieties of peanuts can be grown:
- Steplyak;
- Klin peanuts;
- Krasnodarets 13 and 14;
- Runner;
- Valencia.
What do peanuts require?
For successful cultivation it is necessary to create suitable conditions for it. Observe crop rotation, choose suitable soil and location, monitor light, humidity and air temperature.
Temperature, humidity and light
Germination of peanut seed material begins at a temperature of 14-16 ° C; the plant will not survive frosts and a sharp drop in temperature. Therefore, before planting, you need to make sure that the night frosts have subsided.
Peanuts require high soil moisture. To do this, follow the watering rules, sprinkling and spraying the seedlings. With insufficient moisture, the bushes begin to die, the leaves dry out and fall off.
Important! Excessive watering of peanuts leads to the development of root rot.
Lighting at the seat must be at least 8 hours a day. Shading or partial shade has a detrimental effect on the development of the plant. He will not have enough strength to form an ovary.
Required soil composition
Peanuts are unpretentious in choosing soil composition. It grows well in sandy soil and black soil. But it requires certain conditions to be met:
- neutral earth environment;
- enrichment with magnesium, potassium, manganese, nitrogen, calcium;
- good breathability and drainage of excess water;
- sufficient soil moisture.
Favorable and Undesirable Neighbors
When planting, the crop requires crop rotation. Peanuts should not be planted on the site after cultivation and next to the following plants:
- beans;
- peas;
- beans;
- lentils.
These crops are close relatives of the nut, and therefore have common diseases and pests. The risk of developing root rot increases.
Favorable neighbors and predecessors for peanuts are:
- potato;
- cabbage;
- cucumber;
- tomato.
Peanut Spread
In recent years, the production of peanut beans in the world has been constantly increasing due to an increase in acreage, the use of high-yielding varieties, fertilizers, chemicals, irrigation, and the improvement of harvesting machines. Peanut crops in the world occupy about 19 million hectares.
Leading countries for peanut production: India (approximately 7.2 million hectares), China, Indonesia, Myanmar. The second place in world peanut production belongs to African countries (approximately 6 million hectares). In the economies of Senegal, Nigeria, Tanzania, Mozambique, Uganda, Niger and several other countries, peanuts are of paramount importance. On the American continent, the largest areas are in Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, and the USA.
Peanut Growing Tips for Beginner Gardeners
Tips for beginner gardeners:
- In the garden, it is better to immediately, without waiting for problems, cover the plant with film or grow it in a greenhouse. This will solve the problem with pests and some diseases.
- The plant suffers from waterlogging of the soil.
- There is no need to pour several seeds into one hole. If more than two shoots emerge from the hole, you need to leave one and remove the rest. Otherwise, all the bushes will have small nuts.
- To get a rich harvest of nuts every year, you need to change the planting location. It is convenient to alternate planting tomatoes with peanuts.
When to Harvest
Peanut harvesting begins when the tops turn yellow and dry out. First, they make a dig, remove 2-3 seeds and check their condition for maturation. If the nuts are easily separated from the shell, they are ripe, and it’s time to harvest. The nut usually ripens at the end of September or beginning of October.
Digging up peanuts using a pitchfork. Then all the fruits are collected, transferred to a dry place under a canopy, and left to dry. When the shells are dry, the nuts are cleaned from the soil with a brush and packaged in bags.
Important! Only breathable materials are used for storage.
How to choose peanut seeds for growing: popular varieties
To figure out what the growing conditions should be, you first need to choose the right variety. The most common include Spanish, Virginia, Runner and Valencia. Now let's find out the intricacies of growing individual varieties:
- The Spanish variety is a low-growing plant. Characterized by a high content of oils in the composition. The variety has separate subspecies: Dixie Spanish, Argentine, Spanko or Natal.
- Runner has good yield. The nuts have an excellent taste and roast perfectly. This variety is prized by peanut butter producers. Subspecies include Georgia green, Bradford and Fragrant runner.
- The Virginia variety is in demand among producers of salted nuts. These peanuts grow in bunches or shoots and are distinguished by a rich harvest. Subspecies include the Gul, Shulamit, Wilson or Gregory variety.
- The Valencia variety grows into a tall bush with large leaves and heavy stems. Used to prepare boiled peanuts.
- The fruits of the Tennessee variety are small in size.
The fruits of the varieties differ from each other, but they all have nutritional properties and health benefits.