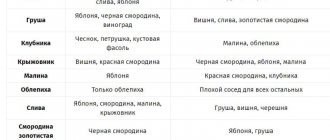
The same crops cannot grow in a vegetable garden all the time - this leads to a reduction in yield and depletion of the soil. Proper rotation helps to increase annual yields, and also allows you to preserve in the soil a full set of nutrients and microelements necessary for plants. Let's take a closer look at what can be planted after onions and what not.
Causes of soil fatigue
Each vegetable feeds on the same substances; if they are constantly planted in last year’s place, this will lead to depletion of the soil. Consequently, in a couple of years the area will become unsuitable for growing other crops due to the lack of any minerals.
In addition, when planting a plant in the same place, pathogenic bacteria and pest larvae that specialize in this vegetable begin to accumulate in the soil. They are capable of infecting a garden bed and remaining in it for several years in a row. Naturally, the source of fire will not have the best effect on the planted vegetables, which will lead to the instant death of the root system and fruits.
How does crop rotation occur in the field?
The only thing we know about growing bulbs in an open field is that it is a troublesome business. However, there are such craftsmen who are not afraid of difficulties and soon, onions begin to appear on the field. Careful care of the plants leads to the fact that in the fall the crop is harvested and the field is plowed. Further actions depend on the owner; if he wants to plant carrots in an open area, then use a cultivator to cut the ridges, plant winter carrots and cover with mulch. If the next planting is intended for beets, then after plowing, the area is leveled and left untouched until spring. In early spring, beet seeds are sown.
Does the earth need to rest after the bow?
Planting vegetables in one place leads to soil depletion, a deficiency of mineral components, and a decrease in harvest volumes. Fertilizing will not change the structure of depleted land, which needs restoration for at least 2 years. Soil depletion will prevent crop changes. Other vegetables will not be damaged by onion diseases and will help even out the soil microflora. To increase soil fertility, it is necessary to apply mineral-based fertilizers and organic beneficial components.
What should you not plant?
After harvesting the bulbs, experts do not recommend placing plants of the bulbous family (vegetable crops and ornamental varieties) on the beds.
Landing prohibited:
- leek;
- garlic;
- daffodils;
- gladioli;
- wild garlic;
- chives;
- shallots, etc.
After onions, similar plants are susceptible to insect pests. Bulbous crops can be planned in the same area only after 2 years of idleness, subject to soil cultivation, weeding and growing another vegetable crop. In addition to humus compounds and organic components, it is necessary to saturate the soil with fertilizers containing potassium.
Some types of flowers (hyacinth, amaryllis) after onion crops can be crushed or bloom for a long time. It is forbidden to occupy a bed with garlic due to the similar characteristics of the variety. Experts do not recommend sowing physalis after bulbous varieties. Ornamental plants (tulips, hazel grouse) are not suitable for planting. To quickly restore the soil layer, it is optimal to plant green manure, such as mustard and clover.
Compliance with crop rotation rules
Growing the same plants in one place for several years has a big impact on the soil.
- The most obvious thing is that the roots of any plants loosen the soil at different depths, and can even compact it.
- By absorbing a different set of nutrients, the roots change the chemical composition of the soil and are even able to influence the pH of the soil liquid, acidifying or, conversely, alkalizing the soil.
- As plants grow and develop, they can attract a variety of parasites, the larvae and spores of which remain in the ground after harvest.
- Plants release a wide variety of organic substances into the soil, the effects of which can be positive, neutral, and even toxic to other representatives of the plant kingdom.
Attention! Most often, toxic compounds released have the greatest effect on plants of the same genus or family.
It is for this reason that it is not recommended to plant plants of the same genus or even belonging to the same family in one place in a row.
On the other hand, diseases and pests remaining in the soil can have a negative impact specifically on crops from the same family. While other vegetables will be immune to their influence. And in a few years they will leave on their own, not finding a suitable food supply for their existence.
Growing the same crops in the same place, or even those belonging to the same family, necessitates mandatory additional feedings and treatments, otherwise you can completely forget about yield.
Since ancient times, so much knowledge has been accumulated on the interaction and influence of plants on each other that not everyone is able to keep all this information in their head. The most basic principle of crop rotation is to alternate the so-called tops with roots. That is, plants in which a person uses mainly their above-ground part (cucumbers, lettuce, cabbage, tomatoes) with root vegetables (carrots, beets, potatoes). Onions in this sense are a universal plant, since both the above-ground part (feather) and the bulb growing underground are equally suitable for food. This means that after onions, you can plant almost any vegetable or herb the next year.
What soil and growing conditions do cucumbers need?
Cucumbers love fertile soil. This should not be forgotten when growing them both in open ground and in a greenhouse. It is best if the soil composition is loamy or sandy loam. Heavy and acidic soils are not suitable for cucumbers. The acid reaction must be neutral or slightly alkaline. The optimal indicator would be a pH of 7.
Soil acidity can be determined by using litmus paper or by observing weed growth. If horsetail, plantain, horse sorrel and heather grow on the site, it means that the acidity is high and it needs to be reduced artificially.
You don’t need to do anything if you encounter weeds such as wheatgrass, clover, common chamomile, coltsfoot, and field bindweed. These plants are an indicator of weak soil acidity. Such land is quite suitable for growing cucumbers. The beds are prepared in the fall.
Acidic soil is limed using ash, lime, and dolomite flour. For low-acid soil, alkaline liquid fertilizers are used. In spring, the surface of the soil is dug up deeply, after which humus is added. Then the bed is watered abundantly and covered with film for 2-3 days. It doesn’t matter whether you are going to sow seeds or plant seedlings - the bed is prepared after the threat of frost has passed.
Helpful advice! It is recommended to grow cucumbers in raised beds. In this case, the harvest will be significantly greater.
7 days after preparation, you can plant cucumbers.
Recommendations for planting cucumbers
Since cucumbers are one of the most favorite vegetable crops, many would like to know whether it is possible to plant cucumbers after onions or is it better to plant them? Let's try to take a closer look at what the pattern is of alternating planting of cultural crops in the same beds, in particular cucumbers.
Experts unanimously claim that plants of the same type can be planted in the same place for 3 years. In order to get an excellent harvest and give, as they say, the fertile soil the opportunity to “rest” after three years of planting the same type of planting group, they must be replaced with another.
In the beds in which onions previously grew, according to experienced gardeners, any crops, including cucumbers, grow and develop well.
You can also safely plant cucumbers in beds in which the following predecessors previously grew:
- early variety of both cauliflower and white cabbage;
- legumes and potatoes;
- tomatoes and beets.
And instead of carrots, experts recommend planting onions or garlic.
The question of the proximity of tomatoes to cucumbers has remained completely unanswered. One group of gardeners is convinced that these two crops go well together, while the other is convinced that they are completely incompatible. Whether it is worth planting the most popular vegetables in our region in the neighborhood, gardeners will have to decide on their own, after weighing all the pros and cons. However, when making a decision on this issue, it should be understood that the analyzed cultural plantings require different watering regimes, since the cucumber crop is much more moisture-loving than the tomato.
How onions affect culture
Is it possible to plant cucumbers after tomatoes?
The root system of onions is located very close to the soil surface. For this reason, it is recommended to plant vegetables with significantly deeper roots after it. For example, you cannot plant garlic after onions, since both of these crops belong to the same species. Their roots have the same structure. For this reason, soil depletion occurs at one level. Therefore, after onions, you need to plant those plants whose roots go deep into the soil.
Plants whose roots go deep into the soil
In addition, do not forget about the pests and diseases that affect both of these plants. If the onion in the area has a nematode, then before sowing another plant, you need to disinfect the area, and then plant a vegetable with immunity to such a disease.
Planting cucumbers in “hot beds”
Cucumbers can be planted not only in open ground, but also in so-called hot beds, which home craftsmen can make on their own, following certain steps:
- a small ditch is prepared, approximately 70-75 cm deep;
- any branches, shavings and other wood waste are placed at the bottom of the trench;
- on top the wood backfill is covered with a fertile layer of soil;
- A so-called border, at least 30 cm high, is laid around the perimeter of the bed. Wooden boards or ordinary bricks can be used as a base. It is imperative to take care of the presence of drains to drain excess moisture;
- the upper part of the bed is formed using compost, the layer of which should be 20 cm or higher, depending on the height of the structure being created;
- It is recommended to plant cucumber seedlings in prepared beds directly in plastic cups, making sure that there is a hole at the bottom so as not to harm the delicate root system.
The best neighbors - what to plant nearby?
Crops successfully located in the neighborhood will help each other grow, produce substances necessary for neighbors, and jointly repel pests. Therefore, it is important to select vegetables in the garden so that they do not compete for a “place in the sun”, but interact successfully. It is not recommended to plant cucumbers near potato, salad and herb plantings. The exception is dill.
The proximity to tomatoes is controversial, although some grow them in the same greenhouse.
- Firstly, these vegetables have different microclimate requirements.
- Secondly, as tomatoes grow, they will inhibit cucumber plants.
- They also have differences in watering.
Radishes, beets, corn, and peas get along well next to cucumbers. Due to their agricultural technology, these crops do not compete with cucumbers for nutrients.
Eggplants will be good neighbors for cucumbers. They can be grown side by side both in open ground and in a greenhouse. Growing cucumbers and peppers at the same time is also quite acceptable. It is only necessary to observe the conditions under which the cucumber vines will not obscure the pepper, so take into account the direction of growth of the lashes. The proximity to zucchini can also be called good. Just make sure that their leaves do not drown out the cucumber specimens.
A suitable neighbor for cucumbers is sunflower. The powerful stems of this plant provide support for vines with green foliage.
Is it possible to grow cucumbers and tomatoes in the same greenhouse: video
What can you plant after onions?
Onions can easily be considered one of the most popular vegetables grown in gardens. Although its perennial green forms are more likely to be classified as herbs and spices. There are many varieties of onions, each of which has its own growing characteristics. But all onions have one thing in common - amazing healing bactericidal properties, which are widely used by people to this day. It was its bactericidal properties that created a real miracle in gardens - after onions, almost all planted plants feel excellent in the beds.
Onion itself is a crop that is moderately demanding in terms of nutrients. After onions, a significant amount of organic matter always remains in the ground, and the soil itself acquires a slightly alkaline reaction. Most of all, it takes nitrogen from the soil, but phosphorus and calcium remain in reasonable quantities. Therefore, after onions, crops that require a slightly alkaline soil reaction and the presence of phosphorus and calcium (cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, beets, carrots) will grow best.
For other crops, the most important will be its bactericidal and soil disinfecting properties (strawberries).
You can plant after onions next year in a greenhouse or open ground:
- pumpkin (zucchini, pumpkins);
- melons (watermelons, melons);
- turnip;
- cucumbers;
- carrot;
- beets;
- tomatoes;
- pepper;
- squash;
- legumes (peas, chickpeas, beans, soybeans);
- potato;
- green manure (gentian, clover, mustard).
Experts recommend preparing a layout of plantings in the garden, taking into account the periods of planting vegetables and herbs. It is prohibited to grow plants belonging to the same family as successors due to the presence of similar diseases. When drawing up a planting scheme, it is necessary to take into account harvest periods and replace free areas with quickly ripening crops.
Predecessors of the bow
So, we figured out what to plant after the onions. It's time to talk about what predecessors are welcome for this culture. Initially, it is worth considering that the place for the bow should be well lit. It is important that the soil is saturated and not deficient in potassium and phosphorus.
It is best to plant onions in a bed that was previously occupied by peas, pumpkin, tomato, cabbage, and green manure. As a rule, onion planting begins at the end of April or at the beginning of May. Ideally, sow in the place from which the potato crop was harvested. Substances left in the soil after carrots, garlic, and cucumbers can have a negative effect on onions.
Good neighbors for onions will be lettuce, radishes, strawberries, spinach, cabbage, and carrots. It is not recommended to plant turnips near beans, as they will negatively affect the composition and development of the vegetable. It is also undesirable for onions to be in company with sage and chamomile. Many inexperienced gardeners often ask whether it is possible to plant onions near garlic. Some people believe that the smell of garlic protects the bulbs and repels onion flies and weevils. Others are sure that this will not lead to anything good, since garlic absorbs the same substances as onions, therefore, a lack of fertilizer will cause early yellowing of feathers and small fruits.
What not to plant after onions
The list of what not to plant after onions is not very long. A noticeable effect of this plant on the soil is the extraction of potassium. Therefore, after harvesting, it is worth feeding it with potassium fertilizers. There are several garden crops that are best not planted after onions. Here is a list of unwanted followers:
- Garlic. It is not recommended to plant it after onions next year, because these plants are from the same family, which means they have common diseases and pests.
- Beans. However, many gardeners do not agree with the opinion that this legume plant should not be planted in an onion bed. It grows well in soil from which its predecessor has taken nitrogen, and can even enrich it. You just need to take care of feeding with potassium.
- Leeks, chives and other onions. These vegetables take minerals from the soil, and after them you can not expect a good harvest.
The list is small, so planning spring plantings is not difficult. Most cultivated plants planted in the same bed produce rich harvests. Properly organized crop rotation can be a significant help in the fight against soil depletion. But in order to get the maximum effect from changing crops in your garden beds, you should carefully consider all the nuances of changing plants and draw up a crop rotation plan for several years in advance.
Green manure
If mid-season or late-season onions were grown at the dacha, harvesting can begin at the end of August or beginning of September. The period of night frosts will soon begin, so it will not be possible to plant a new crop after the onions are harvested. To saturate the soil with useful substances and establish crop rotation, you can use green manure, which in everyday life is called “green doctors”. Their planting will allow:
- prevent weeds from appearing;
- fertilize the soil;
- fight pest larvae and pathogenic bacteria, which in turn will ensure cleansing and disinfection of the soil;
- carry out good loosening of the soil due to strong roots.
For each site you need to select a specific green manure. This plant is classified into 5 varieties. The cruciferous family saturates the soil with phosphorus, sulfur, and organic matter, and protects plant crops from wireworms, root rot, and nematodes.
The Asteraceae family is a source of complex, difficult to decompose organic fibers. Cereals will help fill the soil with potassium, nitrogen and organic matter. Buckwheat will saturate the soil with the same microelements as cereals.
Important! When choosing green manure for onions, special attention should be paid to the cabbage family.
Which beds are better not to use?
It was said above that when alternating crops, you should not use plants of the same type. Cucumbers belong to the pumpkin family, so all representatives of this family - pumpkins, zucchini, zucchini, squash, melons, watermelons - are undesirable predecessors. There are several arguments against it.
- If pumpkin plants were sick or were attacked by pests last year, then cucumbers have a risk of experiencing these problems themselves. Larvae of harmful insects and pathogenic microbes that are dangerous for this group of vegetables may remain in the ground.
- Sometimes it is difficult to find areas with low acidity for pumpkin plants, so you have to neutralize the existing soil by liming. If you subject the bed to such a procedure every year, then alkali will accumulate in the soil and in large quantities will only interfere with the development of the crop.
- The roots of pumpkin plants “suck” microelements from the soil that are necessary for development, thereby depleting the soil. Cucumbers will not develop in such a bed, but this is not a hindrance for weeds, and they can clog weak cucumber sprouts with their active growth.
Pumpkin crops are bad predecessors for their own kind, but after them other vegetables (nightshades, root vegetables, tubers, onions, garlic, herbs) develop well. This is facilitated by the influence of the root system on the looseness of the soil.