Caring for fruit crops involves a whole range of measures, including the fight against various diseases. Scab on apple trees is one of the most common and dangerous diseases, leading to significant crop losses. To protect trees, you need to understand the causes and identify the initial symptoms of fungal infection, treat plants in a timely manner, and also carry out preventive measures.
The disease affects the leaves and fruits of the plant, in some years it manifests itself en masse and has the character of epiphytoties
Characteristics of the disease, description of scab symptoms
Scab is a fungal disease caused by the marsupial microorganism Venturia inaequalis. The course of the disease is accompanied by damage to the leaves, their petioles, inflorescences, stalks and the fruits themselves. Scab cannot cause the death of a tree, but it significantly harms the future harvest: it impairs the taste and appearance of the fruit, and shortens the duration of their storage. In central Russia, losses from scab amount to approximately 40% of the crop, and in years with unfavorable climatic conditions - up to 80%.
The fungus overwinters in damaged tree bark and fallen leaves, and in the spring, during the period of bud formation, it begins to disperse spores throughout the orchard. The spread of spores is facilitated by rain, wind and insects flying from tree to tree.
Favorable conditions for the activation of the fungus Venturia inaequalis are created on rainy days with air temperatures from +18 to +20 ° C and humidity up to 80%.
Scab is common in areas characterized by rainy summers. In regions with hot and dry climates, this disease is much less common.
Signs of defeat
Once on young foliage, the spores germinate.
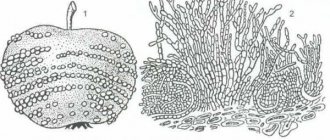
In early June, yellow spots appear on the outside of the leaf blades, gradually becoming overgrown with a velvety brown coating. Severely affected leaves dry out and fly off, infecting the stalks, ovaries and fruits that have already grown. The apples are covered with gray-black round dots, which also initially have a velvety coating. Gradually, these spots increase in size, and growths covered with cracks form on their surface. As a result, the apples become deformed, slow down in growth and become small.
Apples affected by scab are not suitable for consumption; they are used only for processing.
Causes
In addition to weather conditions, the active development of the disease is due to several other factors:
- excess soil moisture as a result of excessive watering;
- thickening of tree crowns due to non-compliance with the required interval when planting seedlings;
- ignoring the autumn cleaning of plant debris;
- susceptibility of a particular variety to the disease;
- lack of sanitary pruning or non-compliance with its standards;
- insufficient air circulation in the garden.
The recommended distance between seedlings, which prevents excessive crown thickening, is from 3 to 10 m, depending on the variety and size of the future tree.
Most often, scab affects old apple trees; young specimens are more resistant to this disease.
Why does it appear on an apple tree?
Long-term observations of plants have shown that the main reason for the appearance of the fungus on apple trees is high humidity. During particularly rainy seasons, 90–100% of farms are affected by scab.
The fungus survives the winter on the remains of apple fruits and fallen leaves in the form of immature fruiting bodies. When spring comes, in conditions of high humidity and air warming up to temperatures up to +18 + 20 degrees Celsius, fruiting bodies appear and spores ripen. They have a mucous membrane that helps them attach to the leaves and shoots of the plant.
Active ejection of spores is observed in April – June. The latent period lasts on average 10–20 days. In addition to high humidity, this is facilitated by densely thickened plantings and the cultivation of varieties with low scab tolerance.
Ways to combat the disease
There are a number of measures through which you can not only get rid of this problem, but also prevent its occurrence on fruit crops. The set of measures consists of direct treatment and preventive procedures. At each time of the year, characteristic manipulations are performed.
How to get rid of scab in spring
The sanitary and preventive measures taken at this time in the fight against scab are considered especially important.
They begin before the buds begin to swell and the juice begins to flow. Just like in the fall, sanitary pruning is carried out in the spring, eliminating dry and diseased shoots. After the procedure, the instruments must be treated with antifungal agents, for example, a solution of potassium permanganate or copper sulfate. Before and after flowering, trees in the garden are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture (1%), as well as one of the fungicides:
- "Abiga Peak";
- "Horus";
- "Skor."
Before sap flow begins, apple trees are treated with preparations diluted in 10 liters of water:
- "DNOC" 100 g;
- "Nitrafen" 200 g.
In the spring, you shouldn’t forget about fertilizing, but you shouldn’t overuse it either. A lack of nutrients, as well as their overdose, contributes to a decrease in immunity, which increases the vulnerability of trees to various diseases, including fungal attack.
If signs of scab are detected, a number of actions are taken to eliminate it:
- The above-ground part of the apple tree is treated with a urea solution diluted with water in a ratio of 500 g / 10 l. This product not only helps fight fungus, but also saturates the tree with nitrogen, which is necessary during the period of awakening and intensive growth.
- In the phase of the pink, unopened bud, the apple tree is sprayed again using one of the preparations diluted in 10 liters of water: “Skor” (2 ml), “Chorus” (2 g), “Fitolavin” (20 ml), “Gamair” (10 tablets).
- The trees are treated the third time after flowering has ended. During this period, “HOM” or Bordeaux mixture (1%) is recommended for use.
Traditional methods
The fight against scab in spring can be carried out not only with the help of chemicals, but also with the use of products prepared according to folk recipes. Such options are not highly effective, but are safe for human health.
- Spraying with salt water (1 kg salt / 10 liters of water). The composition is relevant during the period of spring frosts, as it slows down the process of awakening apple trees, thereby reducing the likelihood of them becoming infected with scab. When processing, it is worth considering that salt reduces the rate of absorption of micronutrients, and therefore the immunity of trees.
- Spraying with horsetail infusion.
- Treating the crown of apple trees with a solution of mustard powder (100 g / 10 l of water).
After the snow melts, it is necessary to somehow remove the foliage and mummified fruits remaining from the fall.
How to treat apple trees for scab in summer
If small olive spots are detected on the leaves in the summer, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment, for which you can use fungicides, biological preparations and folk remedies.
“Fitosporin” can be used in any phase of the growing season: it effectively blocks the spread of the fungus to other parts of the tree and at the same time does not accumulate in already formed fruits. The drug does not pose a risk to the health of people and domestic animals and can be used at any temperature. To prepare the working solution, it is recommended to add Zircon to Fitosporin, which stimulates plant growth.
In the process of fighting scab, copper-containing preparations are used to suppress the development of all fungal diseases. During the summer, apple trees are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture; its use is stopped 2 weeks before harvest. To prevent leaf burns, treatment is carried out with a weak solution (1%) prepared from 200 g of lime, 100 g of copper sulfate and 10 liters of water.
For summer spraying, the composition “HOM” is well suited, containing copper oxychloride, which is practically not dangerous to bees and is not phytotoxic. The use of the drug "Strobi" with a frequency of up to 3 times every 10 days is also effective. During the summer, it is necessary to periodically rid the garden of weeds and other plant debris.
If the disease is difficult to treat and reappears, it is worth checking the acidity of the soil.
Scab especially often affects trees growing in acidic soils with low nitrogen content. The lack of this substance contributes to stunted growth and decreased immunity in the apple tree.
Features of the fight in July
In July, due to the active growth of tops, the apple tree experiences a strong thickening of the crown, regardless of the autumn and summer pruning.
At this time, the tops need to be broken out, since they no longer participate in the further formation of the crown and ovaries do not appear on them. By increasing the green mass with their presence, the tops prevent proper ventilation. To treat trees from scab in July, chemicals belonging to hazard class 3 and below are used. If at this time the fungus has infected early varieties of apple trees, then chemicals are no longer used. Treatment is carried out with folk remedies or biological products.
How to deal with scab in the fall
Autumn prevention is especially important in the fight against fungal diseases. It includes a number of the following activities:
- Collection of weeds, leaves, mummified fruits and other plant debris. Destruction outside the garden area. In this case, it is possible to further use the ash remaining after the fire.
- Carrying out sanitary pruning after the end of sap flow. Cut branches should also be burned.
- Stripping the bark of various bulges and roughness - ideal places for overwintering fungal spores.
- Digging the soil in tree trunk circles.
- Treatment of the crown and soil with a solution of copper sulfate (3%) or Bordeaux mixture.
- Whitewashing the trunk and main branches with a composition prepared from slaked lime, PVA glue and copper sulfate (1%).
Preventive actions
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to choose the right variety and the appropriate planting location.
To avoid disease, you should follow several rules of agricultural technology:
- Do not plant fruit trees densely.
- Select the right variety for planting, which is less susceptible to the disease (Antonovka, Topaz, etc.).
- Regularly treat the tree crown with garlic infusion.
- Promptly cut and burn affected leaves and branches.
- Use new generation fertilizers that contain silicon.
It is worth noting that urea and treatments based on it are perfect for preventing and treating apple trees from scab in the fall. Refers to mineral supplements and is absolutely safe for humans. After the leaves fall, the apple tree is sprayed with a 10% urea solution.
Scab-resistant varieties
Domestic breeders have managed to develop more than 20 varieties of apple trees that are resistant to this disease. The most popular of them:
- Alexander Boyko;
- Health;
- Bolotovskoe;
- Ivanovskoe;
- Aphrodite;
- Oryol Polesie;
- Kandil Orlovsky;
- Apple saved;
- Venyaminovskoe.
Growing immune varieties helps prevent the occurrence of scab and many other diseases. Thus, gardeners manage to avoid the use of chemicals, which has a beneficial effect on the environmental friendliness of the future harvest.
Advice from experienced gardeners
The disease can be cured, but it is better to prevent fungal infection in advance than to fight it later. To avoid pathology, it is enough to do the following correctly:
- watering;
- processing in June, July;
- fertilization;
- landing;
- pruning
General rules for growing and caring for apple or pear trees will help reduce the risk of infection. Regular inspection of the orchard will help to catch the disease in the early stages of development and provide timely therapy.
Basic drugs for treating the disease
Fungal diseases are controlled using fungicides. Before using them, you need to familiarize yourself with several nuances:
- With repeated use of the same drug, the fungus develops immunity to its components, which reduces the effectiveness to zero.
- When purchasing a chemical, it is important to pay attention to its main active ingredient, since the same components may be hidden under different names.
- Each drug has a specific waiting period until the fruit can be eaten. Shortly before harvest, it is recommended to use formulations with short waiting periods.
Popular fungicides for scab control
There are several types of fungicidal preparations, differing in certain characteristics and application features.
| Drug name | Active substance | Terms of use | Duration of therapeutic effect (in days) | Dosage | Treatment frequency |
| Copper-containing preparations | |||||
| Bordeaux mixture | Lime, copper sulfate | Spring, autumn | 20 | 100 g / 10 l (1% solution) | 1 |
| Copper sulfate | Copper sulfate | Autumn, spring | 20 | 100 g / 10 l (1% solution) | 1 |
| "Abiga Peak" | Copper oxychloride | The entire growing season | 15 | 50 ml / 10 l water | 4 |
| "Oxyhom" | Oxadixil, copper oxychloride | Growing season | 15 | 20 g / 10 l | 3 |
| Systemic drugs | |||||
| "Horus" | Cyprodinil | Formation of a green cone before flowering begins | 7–10 | 3 g / 10 l | 2 |
| "Switch" | Ciprodil, fludioxonil | Growing season | 20 | 2 g / 10 l | 2 |
| "Skor" | Difenoconazole | Ovary formation phase | 5–7 | 2 ml / 10 l | 3 |
| "Embrelia" | Isopyrazam, difenoconazole | Flowering period until harvest | 7–10 | N/A | 3 |
| Biofungicides | |||||
| "Fitosporin-M" | Soil bacteria Bacillus subtilis (bacillus subtilis) | Growing season | 7–14 | 5 ml / 10 l | Not limited |
| Other drugs | |||||
| inkstone | Ferrous sulfate | Late fall | 20 | 50 g / 10 l | 1 |
Use of iron sulfate
Iron sulfate to combat scab.
Iron sulfate helps against scab on apple trees.
It is low toxic to humans. To combat scab, it is used in the fall after the leaves fall or in the spring before the buds open.
For autumn use, prepare a 7% solution : 700 grams of iron sulfate are diluted in 10 liters of water.
In the spring you can use a 1% mixture, for this: dissolve 100 grams of powder in a 10 liter bucket.
Important! Do not use a metal bucket.
Foliar treatment not only destroys fungal spores, but also improves fruiting of old apple trees.
Signs of infection
The owner of the plot most often finds out that there is scab on an apple tree in the spring, at the conidial stage of development of the fungus, when its spores, under the influence of humidity and heat, germinate into the epidermis of the leaves. These lesions become the first signs of the disease.
Symptoms of leaf damage:
- oily light olive spots of a round shape are formed, clearly visible and gradually growing;
- they are covered with a dense gray-green coating;
- the middle of the spot turns brown over time, cracks and rots;
- yellowing of the entire plate occurs;
- the leaf falls off.
After conidia germinate on the leaves, the spores actively spread to young shoots, flowers and fruit ovaries. For example, spots form on the petals, similar to those that affect the foliage. They rot and fall off quickly. On infected apples, dots with a grayish halo appear, which gradually grow. At this point the pulp corks, becomes dense to the touch and hardens. As a result, the fruits become severely deformed, do not grow in size, and develop cracks. In rare cases, dark olive spots form on the tree trunk. Then the bark swells, cracks and peels.
Note. Ascospores of Venturia inaequalis can germinate not only in spring, but also in summer, if it turns out to be cool and rainy. In different regions, the fungus awakens in different phenophases of the plant - the gardener needs to know about this in order to have time to treat the apple trees in a timely manner.
Development of scab in different regions of Russia:
When to treat trees
Treatment of apple trees against scab should begin as early as possible. When the first yellow-green spots appear, you must immediately spray the trunk, branches and leaves so that the spores do not spread further and damage the remaining healthy part of the apple tree.
Therefore, the first treatment is carried out when the air temperature warms up above 10 °C. Before the beginning of the growing season, they are sprayed with fungicides and preparations that contain copper. The most experienced gardeners use a rather bold method - burning the skeletal branches and trunk with a gas burner.
Before flowering begins, when young leaves have already begun to bloom, re-treatment with fungicides or whey is carried out. During the flowering period, any treatment is not recommended. And the use of chemical fungicides should be stopped a month before fruiting.
Consequences
First of all, scab poses a danger both to an individual infected apple tree and to the entire garden. Among the consequences:
- frost resistance decreases - the risk that the tree will not survive the winter increases;
- the quality of apples deteriorates - they become tasteless and dry;
- neighboring fruit and berry crops become infected;
- leaves fall en masse - up to the complete baldness of the tree;
- overall yield decreases;
- if no measures are taken for 2-3 years, the apple tree will die.
Is scab harmful to humans and is it possible to eat apples from an infected tree?
In Russia, the relevant stations (Rospotrebnadzor, WHO) do not give any recommendations on this matter. However, it must be borne in mind that in some European countries their sale is prohibited at the legislative level and this is due precisely to the danger of eating contaminated fruits.
The harm lies in the fact that infected apples contain toxic substances. Penetrating into the body, they:
- reduce immunity;
- destroy tooth enamel;
- lead to inflammation of the gums;
- cause intoxication - if you eat such apples in large quantities, you can become seriously poisoned.
They pose a particular danger to children and the elderly, whose immunity is already reduced due to age. To be poisoned, it is enough for them to eat 2-3 pieces.
Treatment of the garden in the fall from pests and diseases. Preparatory stage
In order for the autumn treatment of the garden to be effective, it is necessary to first perform the following work.
Cleaning leaves
To do this, you need to use a rake to remove all the leaves that have fallen to the ground. If no pests or diseases were observed on the fruit trees last season, then the foliage is quite healthy and can be used for composting in a special heap, for making warm beds or as mulch for perennial wintering flowers. It is important to remove or burn all fallen leaves from the area if they are affected by powdery mildew, scab or other diseases - such leaves are not only unsuitable for use, but also dangerous for trees.
Abundant watering
Fruit trees should not be allowed to remain with dry soil before a long winter. When there was a dry autumn, you need to thoroughly water the trunk circle near each fruit tree with a large amount of water. To do this, one adult tree should require about 50 liters of water.
This type of irrigation is called moisture-charging. This does not mean that you need to immediately pour the entire required volume under the root. This will be of little use, because the water will spread far beyond the tree trunk circle and will not be absorbed exactly where it is needed. It is necessary to water the tree in stages: 12-15 liters are poured in one hour. With this method of watering, the soil will be thoroughly saturated to a depth of approximately 1 m.
It is not recommended to use ice-cold tap water. It should be about 5 degrees warmer than the air temperature. After all these manipulations, the tree trunk circles are mulched. The most suitable material is spruce branches (it will protect against rodents), peat, humus or compost. This way, you can be sure that moisture will remain in the ground.
Preparing fruit bushes
Just like trees, fruit bushes also need autumn preparation. All unnecessary branches are removed from them - this way young shoots will begin to grow faster in the spring. For the best wintering, the bushes are fertilized with potassium phosphate fertilizers (1 tbsp for each bush).
Raspberries are cut at the root: all fruit-bearing bushes affected by diseases or those that create a strong thickening of the plantings must be removed. Organic matter is added to the remaining raspberry bushes: manure (6 kg per 1 sq.m.) or chicken droppings (with water 1:12).