Author's rating
Author of the article
Yakov Pavlovich
Professor, Head of the Department of Vegetable Growing
Articles written
153
Quite often, gardeners are faced with the problem of drying and yellowing of the crown of the fruit tree. One of the most popular crops in the garden are apple trees. This is a rather unpretentious tree, but it is important to know the basic nuances of caring for it. There are several reasons why an apple tree sometimes dries out in the summer. Among the main negative factors are harmful insects, as well as diseases of fruit crops.
Fruit rot - apple moniliosis
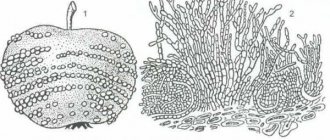
The causative agents of the disease “practice” their activity mainly on apple fruits. Drying of branches is already a side effect, because an unhealthy tree’s natural life processes are disrupted.
In humid summers, moniliosis spreads throughout the garden very quickly and causes the death of 80% of the fruit crop. The worst outcome of the disease will be the death of the trees themselves if treatment and prevention measures are not taken.
Infection carriers include insects, raindrops, and wind. Infection occurs as follows:
- The first to be affected are fruits with damage from birds, insects, and cracks on the surface.
- The pathogens of moniliosis spend the winter in rotten fruits remaining on the branches after harvesting. They pose a danger for 2 years.
- By the end of the winter period, the fungus penetrates through the stalk into the fruit branches and waits out the remnants of the cold there. In spring it moves to flowers, then to fruit ovaries.
- When warm, humid weather sets in, spores spread throughout the garden from one tree to another, causing more and more lesions. The development of the disease is rapid: the fruits rot in 3–5 days, and after 8–10 days the fungus begins sporulation.
- The second wave of the disease occurs in mid-July. Apple trees begin to dry from the top down the branches.
Treatment of moniliosis is complex, costly and time-consuming. It is carried out according to plan:
- Treat the garden with Fitosporin-M according to the instructions 1 month before harvest. An alternative is an iodine solution (10 ml per 10 liters of water).
- Spray again after 3 days.
- Check plants for signs of scab. Moniliosis spores penetrate inside through spots on fruits. Pick damaged apples immediately.
- In early spring, when green leaves just appear, treat the trees along the branches with 3% Bordeaux mixture. Treatment at a later date is carried out at the beginning of the formation of buds (use a 1% solution).
- As soon as the apple trees finish blooming, apply a second treatment with 1% Bordeaux.
- After 2-3 weeks, go through the trees again with Bordeaux mixture (1% solution) or replace it with a solution of copper oxychloride (40 g - per 10 liters of water).
For any treatment, the solution consumption will be 2 liters per 1 tree.
Preventive measures to combat fruit rot:
- Remove damaged fruits - eaten by wasps, beaten by hail, pecked by birds, etc.
- From the beginning of leaf fall until the end, remove fallen leaves and burn them.
- In summer, collect carrion.
- Cut off dried branches, taking 10–15 cm of healthy tissue. They are subject to burning.
- Plant disease-resistant varieties (Uralets, Kandil Sinap, Idared, Slavyanka, Babushkino, etc.).
If the apple tree dries out, how to save it?
Saving dying trees is urgent and important. But the methods of rescue will depend on the reasons that caused the problems. If you find out why the apple tree is drying up, then what to do and how to save it will be easier to solve:
- It is very difficult to save a variety planted in a place where groundwater is too close. The only thing that can help them is to form a small apple tree.
- If a plant is grown in poor or depleted soil, then gradually adding organic matter can help.
- Diseases and pests can quickly cause irreparable damage. Therefore, they must be destroyed immediately after they are discovered. If this is not done immediately, then very soon only a dried apple tree will remain on the site.
- In the spring, it is easiest to determine why the branches on an apple tree are drying. In most cases, this is the cause of freezing. Damaged branches will remain dry in the spring, while others will begin to wake up.
Dried branch on an apple tree.
Chemicals are used only as directed. They are toxic and are not used for processing during fruit ripening.
Young apple trees
There are a number of reasons why a young apple tree dries out. And while it is not yet too rooted, something can be done:
- If the reason is that the location is unsuitable, the young tree can be replanted.
- If the cause is infection or parasites, then a quick response will be required so that the small apple tree is not completely damaged.
Young plantings are easier to care for and there are more ways to resuscitate them. At the stage of initial growth, it is easier for the tree to recover.
Other diseases
Some diseases are less common than fruit rot, but cause no less damage to apple trees. Among them are especially distinguished:
- Common cancer. It begins its action by damaging skeletal branches, then moves on to second-order branches and bark.
- Black cancer. The disease begins on the forks of skeletal branches. Then it appears on the leaves in the form of reddish spots (they quickly increase in size). The damage extends to the cortex. It gradually turns black, begins to crack and peel off.
The causes of diseases are:
- unfavorable weather conditions (extreme heat or frost);
- injuries caused to the tree during rough pruning of branches, fractures, lack of treatment for wounds, etc.
Mostly old apple tree specimens are susceptible to common and black cancer. Diseases cannot be cured. All that remains is to destroy the trees.
High location of groundwater
Apple trees need water for growth and development, but excess moisture leads to rotting of the roots. This happens when groundwater levels are high.
When the root system stops working, the plant begins to suffer from “hunger.” Old branches are the first to react to lack of nutrition. They dry out quickly. The same fate will soon befall the young shoots. If rescue efforts are not carried out, the tree will die.
The optimal groundwater level for apple trees is:
- on vigorous rootstocks - 3 m;
- for medium heights - 2.5 m;
- for dwarf forms - 1.5 m.
If it is known that the waters lie above the permissible limit, make mounds of fertile soil:
- Pour the soil mixture in layers. Tread the embankment well for strength when it reaches a thickness of 15–20 cm. The result should be a structure 1.5–2 m in diameter and 0.5–1 m high.
- Make hills in the fall so that the soil settles and becomes compacted over the winter. Plant apple trees on them in the spring so that the roots in the ground do not freeze.
- Tie the trunk of the seedling to a strong stake so that it does not break in the wind.
- Apple trees on hills need frequent and abundant watering, especially if the first 2-3 months after planting are hot and dry.
- During the first 2 years, apple trees planted on hills will lag behind their relatives planted in the traditional way. But then their development will accelerate significantly.
If the location of groundwater was unknown during planting, the problem goes unnoticed at first. The trees develop normally, but after 10–15 years they begin to wither.
Symptoms of roots reaching groundwater:
- the tree stops growing;
- leaves quickly turn yellow or brown;
- frequent infections with fungal diseases;
- When the summer heat sets in, the leaves begin to fall en masse.
There is only one way to correct the situation - by radically pruning the apple tree. When the height of a tree is no more than 2–2.5 m, it will not require deep roots to obtain water.
How to revive a tree
Depending on the cause, gardeners use different methods of prevention and resuscitation of a drying tree:
- The crop should be planted in a sunny area with deep groundwater. When planting, drainage is added to the holes (pebbles, crushed stone, broken brick), which will prevent root rot and moisture stagnation. To deoxidize the soil, dolomite flour, slaked lime or powdered chalk are added to the site.
- To increase the nutritional value of the soil, the area for planting apple trees is fertilized with rotted manure, wood ash, potassium nitrate and superphosphate. These components increase the tree’s immunity from various diseases and eliminate the risk of drying out of the underground and above-ground parts.
- In the regions of the Middle, Central and Northern zones, where there is a high risk of freezing of the roots and near-trunk zones, it is necessary to add mulch from peat, humus and garden soil, as well as provide the trees with good cover from spruce spruce branches or roofing material.
- To protect trees from black cancer, it is necessary to keep the area clean, remove the affected parts in a timely manner and treat the tree with copper sulfate. In the fight against scab, the drug Topaz or Hom is used, and against powdery mildew - Skor. Traditional methods for spraying sick specimens include a copper-soap solution, soda solution, and 1% boric acid solution.
- To destroy aphids, gardeners use special pesticides - Aktaru, Aktellik or folk remedies - ash-soap, tobacco-soap, garlic or pepper infusions. Treating the crown with karbofos will help get rid of caterpillars, and Nitrofen, Karbofos or Chlorophos will help exterminate spider mites, leaf rollers and moths. Special pesticides and traps are used against rodents.
- At an advanced stage, when the tree or seedling is half dried, the tree is radically pruned to healthy tissue, then the crowns are treated with copper sulfate and fertilized with a complex composition (superphosphate, potassium salt and azofoska). Such a tree will survive if you regularly care for it - water, fertilize, loosen the soil, mulch and provide good protection for the winter.
- If the reason lies in damage to the root system, the tree is dug up, the damaged parts are removed, sprayed with copper sulfate, allowed to dry slightly and planted in a new place with fertile, loose soil and deep groundwater in the area.
Poor planting site
For an apple tree, planting in lowlands is not a suitable option. In such a place in the spring, water from melted snow accumulates, and after rains, puddles remain for a long time. Stagnant moisture deprives the roots of oxygen. The tree begins to suffer from a lack of the element, reacting by drying out the branches.
Melt water is especially dangerous. In spring, the fruit plant begins to grow root hairs. They especially need oxygen to develop. After a day without air, they die. After another 3 days, the death of larger roots begins.
Symptoms for determining the location of an apple tree in a bad place with frequent stagnation of water:
- the leaves become brown and begin to fall off;
- the growth of new shoots stops;
- Over time, the tree dries out completely.
Transplanting apple trees to solve the problem is difficult. Only preventive measures are effective: planting trees on high ground or on embankment hills.
Poor soil on the site
Drying branches may be a signal of unsuitable soil type in the area. Apple trees do not like calcium-poor clay, loamy and swampy soils. They will need to be diluted by adding lime, chalk, dolomite flour, peat, and river sand.
Some wild cereal grasses pull the nutrients the apple tree needs from the ground, causing it to become significantly depleted. Then the drying of the branches is provoked by a lack of certain nutritional components in the soil:
- potassium;
- boron;
- zinc;
- manganese;
- magnesium;
- nitrogen.
Special fertilizers will help make the soil more nutritious:
- Superphosphate is a complex mineral preparation;
- Calcium nitrate;
- Pixa Super Compost is a product containing beneficial microorganisms;
- Kemira-Lux is a substance containing 20% phosphorus, 27% potassium, 16% nitrogen.
No watering
Many inexperienced gardeners believe that it is necessary to water an apple tree only in the first year of growth. This statement is relevant for northern regions with wet soils and cool summers. But in the southern regions, even mature trees require watering.
A lack of moisture is indicated by:
- uniform drying of branches;
- wilting of leaves.
During the summer, in the absence of rain, it is enough to water the apple trees twice: 2–3 weeks after flowering and 3 weeks before harvest. In regions with frequent long-term droughts, another watering is done in the spring before flowering begins.
The water consumption for each tree is as follows:
- 50–80 liters of water for a seedling 3–5 years old;
- 120–150 l for an apple tree 7–10 years old;
- up to 200 l for older specimens.
Compliance with irrigation rules increases yield by 25–40%.
Prevention measures
In order to prevent future problems with the apple tree, it is recommended to periodically carry out preventive measures. It is easier to prevent any troubles with a fruit tree than to then eliminate the consequences.
Choosing the right landing site
To plant a young seedling, you need to choose the right place. The area for the apple tree should be closed from drafts and well lit. The main thing is that the soil in this place is breathable. If the apple tree is planted in a lowland where water stagnates, it is necessary to first make drainage. However, in areas that do not need drainage, it is also necessary to prepare the soil in advance. When digging, add humus, compost or peat to the loamy soil. Experienced gardeners recommend placing the fruit tree along the perimeter of the plot, while retreating from the boundaries of the neighboring plot by at least three meters. Also, when planting an apple tree, it is recommended to maintain a distance of four meters between powerful shrubs.
Treatment against insects and diseases
To combat insects and various diseases, gardeners use both specialized preparations and folk remedies. To prevent fungal diseases, it is necessary to treat with fungicides. The scab pathogen spends the winter in fallen leaves and bark, so leaves and other debris should be burned. To eliminate harmful insects, various herbal infusions and decoctions are used. The following recipes are considered the most effective: tobacco infusion, mustard solution with laundry soap, infusion of wormwood, garlic and onion leaves. The following drugs are also used to fight infections: Decis, Karate, Iskra, Fufafon. Treatments begin in the spring and end two weeks before harvest.
Timely watering and fertilization
Proper care, which includes timely watering and the application of fertilizer mixtures, is important. Proper care of the apple tree helps to increase its immunity and prevents infection and insects. Fertilizer compositions are applied three times per season. The first application of fertilizing is carried out in early spring, before buds form. The second time the apple tree is fed during flowering and budding. Then, in July–August, organic compounds are used. During the second stage, mineral supplements are used. The most suitable fertilizers for a fruit tree are: chicken droppings, compost, manure, humus and mineral compounds with potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus. Watering is regulated depending on the variety. On average, irrigation is carried out every two weeks. For one tree, 30-40 liters are enough. At the time of watering, the water should be warm.
Previous
Apple treeHow to spray apple trees against pests and diseases: effective folk remedies and chemicals
Next
Apple tree Brown rusty spots on apple leaves: causes of appearance and methods of control
Errors during landing
Drying of branches occurs when a young seedling does not take root in a timely manner. Some gardeners make the mistake of planting trees in the summer. The plant simply does not have time to adapt to a new place and grow a sufficient root system and branches before the fall.
According to the rules, apple trees are planted in spring or autumn. In the first case, the seedling will take root well over the summer, in the second, it will adapt and harden over the winter.
Another mistake when planting a seedling is the close placement of large perennial plants with a wide root system. This happens when the plot is small, and the owner tries to place fruit trees and berry bushes on it as much as possible.
Improper pruning and grafting
For pruning, there are certain rules aimed at choosing an unnecessary branch, the method and timing of the procedure, etc. Violations of the procedure sometimes affect the drying out of previously healthy shoots.
Pruning is carried out in spring or autumn. In summer - only if absolutely necessary. Winter pruning is contraindicated. Frosts will cause drying out not only of the branches, but also of the tree as a whole. A “sleeping” apple tree will not be able to regenerate exposed tissue.
An unsuccessful grafting will, at best, lead to drying out and rejection of the scion, and at worst, the death of the rootstock. A sign of incompatibility of a shoot with a tree is an influx at the grafting site. The same factor indicates that the apple tree is infected with a viral disease due to violation of hygiene rules.
Presence of pests
Often the cause of drying out apple tree branches is exposure to pests. The most common insect is the larva of the May beetle. It is found in almost all regions.
The larvae are based in the soil of the root zone of the plant. They harm young seedlings up to 5 years old. Their roots are shallow and do not stick well to the ground. Disruption of the process of nutrition and absorption of oxygen from the soil affects initially the branches (they begin to dry), and then the tree as a whole.
The pest is not accessible to insecticides because it penetrates a meter deep into the soil.
To get rid of cockchafer larvae, use a solution of ammonia (50 g per 10 liters of water). Consumption for each tree is 10 liters of solution. Trees are watered in mid-May. The larvae cannot stand the smell of ammonia, and for the apple tree the drug will be a good nitrogen supplement.
In addition to insects, rodents harm the apple tree:
- field mice;
- moles;
- shrews.
They build homes in the ground, disturbing the location of the roots (sometimes they gnaw them). The branches are the first to react to the presence of rodents, gradually losing their elasticity and drying out due to a decrease in the level of nutrition.
Causes
As practice shows, dwarf, semi-dwarf and columnar varieties are more susceptible to this phenomenon. Vigorous (seed) rootstocks are more resistant to drying out.
There are many reasons why this process occurs.
Climatic conditions
Freezing of fruit crops is a common occurrence caused by sudden temperature changes in winter. This usually happens in early spring.
As a rule, the bark freezes on the south side, becomes covered with black cancer, and after a couple of years the tree dies. This is typical for apple trees grown in regions with harsh climatic conditions.
In summer, during the season of prolonged rains, a process of partial peeling of the bark on the trunk occurs, which leads to drying out of individual parts. This process is typical for the regions of the southern strip.
With severe or complete freezing of the root system in the regions of the Middle, Central and Northern zones, the crop dries out completely.
Errors during landing
The reason for the drying out of young apple trees is failure to comply with planting dates - this procedure is usually carried out in spring or autumn.
Some gardeners do this in the summer, making a big mistake, because the seedling has less chance of survival. In summer, the plant runs the risk of dying from lack of moisture and sunburn.
You should not plant plants such as foxtail, wheatgrass, timothy grass nearby - they negatively affect the health of apple trees and have a poisonous effect on them.
Soil features
Planting young plants on acidified loamy, sandy soil leads to their drying out. The soil should be loose, slightly acidic, enriched with organic and mineral components.
Plants planted in areas with close groundwater often suffer from waterlogging. The root system does not receive the required amount of oxygen, which causes it to suffocate and begin to rot. After some time, the foliage on the tree turns yellow, the shoots wither, dry out and the tree dies.
Young apple trees dry out due to lack of good drainage in the soil. In too heavy and clogged soil, the same process of suffocation of roots and drying out of the above-ground part occurs.
The cause of drying out after flowering may be damage and rotting of the roots in soil that is too waterlogged or waterlogged. Without access to oxygen, the roots begin to die, the plant forms flower buds, but in small quantities, and the harvest is not so tasty and rich.
Malnutrition
If there is a lack of nutrients, the leaves may dry out.
Lack of nutrients in the soil is another reason. There are several types of fasting:
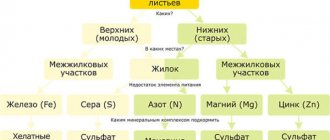
- Nitrogen. The foliage turns yellow and dries out, and eventually falls off.
- Potassium. The leaf blade has a characteristic yellow border that covers the entire leaf. The crown of the central conductor may also dry out in columnar and dwarf varieties.
- Magnesium. Yellowing and drying of the leaves occurs between the veins.
- Iron (chlorosis). The tops of the shoots and the surface of the leaves acquire a yellowish tint. The same phenomenon is typical with a lack of nitrogen, potassium, manganese and with an excess of lime in the soil.
Incorrect grafting and pruning
When buying a seedling for planting, you should carefully inspect the grafting site - there should be no swelling or growths in it, otherwise it will not be suitable for the future rootstock. Such a tree has a high risk of contracting a viral infection during grafting, which can lead to its drying out.
There is a high risk of drying out if pruned incorrectly in cold regions of the country. Due to inexperience, some gardeners prune on the eve of the upcoming frost - the tree does not have time to recover, freezes slightly, and with the arrival of spring begins to dry out.
A dried apple tree branch must be trimmed to healthy tissue, and the cut areas should be treated with copper sulfate and covered with garden varnish. Branches that have dried out are burned, because they are a source of development of pathogenic microflora in the area.
Diseases
Shoots, leaves, and buds dry out in spring or autumn due to infection with various diseases.
- Black cancer. First, brown spots appear on the leaves, over time they turn black and turn into sores. The infection quickly spreads to other organs - skeletal branches, trunk. Over time, the apple tree is completely covered with a black coating. To avoid further infection, it is necessary to remove the infected parts on the tree and treat the cut areas with copper sulfate. Often only the central conductor dries out, and after that the process spreads to all other organs.
- Scab. With this disease, the leaves are primarily affected - they turn brown, dry out and fall off en masse.
- When affected by powdery mildew, a whitish coating appears, which darkens over time and takes on a brownish color. At an advanced stage, the tree stops bearing fruit and dries out completely.
- Drying of the tops of shoots can be caused by a fungal disease - cytosporosis or black cancer. At the same time, the crown of the central conductor also dries out.
- When a tree is infected with fruit brown rot, the apples dry out. First, the fruits become covered with brown spots, then with a white coating in the form of warts. Over time they fall off.
Pests
Sometimes the apple tree dries out due to the invasion of parasites.
Insects can destroy a tree
- Ants and aphids. Small parasites, which reproduce at a galloping pace, suck the juices from leaves, flower and vegetative buds, which leads to their drying out. At the affected sites, the insect leaves sticky excrement, which serves as an excellent environment for the development of sooty fungus. This infection affects all organs of the plant and at an advanced stage the tree dries out and dies.
- Caterpillars. They chew out leaf tissue, causing it to curl and dry out.
- The same phenomenon occurs on trees that are affected by spider mites, leaf rollers and codling moths.
- The apple tree often suffers from an invasion of rodents - field mice, shrews and moles. These pests chew out roots and bark on the trunk.
- May beetle larvae are the most dangerous pests of young apple trees. They gnaw out young roots, as a result of which the entire above-ground part withers and then dries out.
Drying out on one side
This phenomenon is possible due to improper care. A tree that partially dries has weak immunity, grows in clogged soil with poor moisture and air permeability, or suffers from a lack of space on the site (dense plantings, close proximity of shrubs and other fruit crops).
In such conditions, the apple tree rations its nutrition, depriving the weakest and most underdeveloped branches of nutrients. Gradually these parts die and dry out.
Causes of drying out in different months
Branches can dry out at any time of the year. Monitoring the condition of the tree should begin immediately after the snow melts and until the apple tree goes into hibernation.
After wintering, the apple tree is able to bloom normally, and then begin to quickly “lose” shoots. Causes:
- severe wetness in early spring;
- mold damage;
- water rat damage;
- in steppe areas - winter-spring drying out.
Most often in such cases the tree is incurable. But, if there are visible wounds, burns on the trunk and branches, the damaged areas must be cleaned to healthy tissue, sealed with varnish or red lead.
With the onset of summer, the bark of apple trees warps until it separates. The reason for this is prolonged rains and excess moisture. This year this does not affect the general condition of the tree in any way. But with such damage, the apple tree will have a hard time surviving the winter, and already next season the branches will begin to dry out.
In summer (especially in July), problems with branches can be caused by:
- cytosporosis;
- black and common crayfish;
- bacterial burn;
- rust in disrepair;
- sensitivity to waterlogging;
- pests;
- bark and root diseases;
- consequences of the frost experienced.
Nuances and questions
There are some subtleties regarding individual parts of the apple tree. Although there can be many reasons for drying out, they can be easily found and stopped in a timely manner.
A young apple tree is drying up: what to do
If the tree has only recently grown, and yellowing and drying out are already noticeable, then you need to find the cause. When it lies in improper care, then it needs to be returned to normal. And if the reason is in the wrong place or mistakes made during the planting process, then it will be easier to plant them correctly in a new place, observing all the requirements.
Branches
Individual shoots may dry out if they do not have enough nutrition. The tree cannot evenly distribute useful substances and partially does not release them into some shoots. So the dried parts need to be cut off and the areas covered with garden varnish. But this is not enough; it is necessary to correctly distribute the fertilizers and form the crown.
Top
If the apple tree begins to dry from the central conductor, then it needs to be cut back to the living one. The cut area is painted over. After this, the cut part needs to be burned and the growing tree fertilized.
Trunk
Treatment methods for the trunk depend on the cause of damage and drying. If parts of the shoots and large branches are dry, they are cut off and the cut areas are painted over.
The trunk of an apple tree is in the process of drying.
It’s another matter when the cause of drying is a tinder fungus, sooty fungus or cancer. With such damage, the apple tree most often dies. It is best to cut it down so as not to infect neighboring trees.
If part of the trunk is simply frozen, then you can cut off the central conductor and form a crown in a slate shape. Most often, this is the only way to revive the crown.
Bark
Very often, the cause of dry spots on the bark of an apple tree is the appearance of fungi or mold. To prevent the damage from spreading further, you need to remove as much of the damaged parts as possible and whitewash the trunk. Sometimes it is better to cover them first with garden varnish or paint over them. When the damage is very large, the apple tree most likely cannot be saved.
in spring
If at the beginning of the season it is noticeable that the apple trees began to bloom and then dried up, then most likely they:
- suffered from rodents;
- got too wet;
- became infected with mold;
- frozen.
In most cases, the apple tree can still be saved if treatment is started in a timely manner.
What are foliar feedings?
If the yellowing is only partial and some young parts curl, turn yellow and dry out, this may be due to a lack of certain nutrients: sulfur, magnesium or iron.
Foliar feeding of apple trees.
Spraying the leaves with special solutions will help solve problems with the lack of these substances. There are a large number of them on sale, you can choose according to your needs.
How to revive a tree
If a problem has just been discovered, you can immediately begin resuscitation. There are several ways to do this:
- apply fertilizer on the leaf or at the root;
- if the problem is temperature, then insulate and cover the apple tree;
- if fungal diseases appear, immediately use a solution of copper-containing preparations;
- if the problem appears due to pests or diseases, immediately begin the fight;
- if the problem comes from the ground or from damage or rot of the roots, then you can try to revive them, partially remove the rot;
- young seedlings can be transplanted to a new location.
However, it is best to avoid emergency resuscitation. To do this, you just need to properly plant and care for the apple tree.
Reasons for drying of tree branches of different ages
The problem arises at any stage of the development and growth of an apple tree - from a seedling to an already mature tree. For each specific case, there are certain methods of salvation.
In seedlings
The most common cause of drying of seedlings is damage by cytosporosis. The disease also manifests itself in the form of reddish spots with yellow areas on the surface of the trunk. If detected, use a complex of drugs Insecticide and Fungicide Rescuer.
Young plants often lack minerals, especially nitrogen. Feeding with complex fertilizers will help.
Young apple trees
Drying of branches is caused by parasites on the roots, rodents, and fungal infections. The problem is solved by using chemicals.
To combat diseases, the following drugs are used:
- Trifloxystrobin;
- Copper sulfate + calcium hydroxide;
- Difenoconazole + 1/2 flutriafol.
For insect pests, medications are recommended according to the instructions:
- Pyriproxyfen;
- Aversectin S;
- Malathion.
Another reason for the drying out of young apple trees is an unsuccessful choice of rooting site. At an early age of a tree, the problem is not difficult to eliminate by moving it to a new site suitable for growth and development.
By old trees
The first reason for the drying of the branches of an old apple tree is natural aging. Upon reaching the age of 10 years, the plant enters the completion phase of its life cycle.
Old trees also have weak immunity. Various “sores” “stick” to them. Dry branches may indicate damage to common, black and root canker. In this case, the tree will no longer be able to be helped, and it is better to destroy it in order to save younger seedlings.
Often the gardener himself is to blame for the drying of apple tree branches. His inattention or negligence when planting a tree and further caring for it will certainly have consequences. If you catch it in time, the problem can be solved, and the plant will only get away with the loss of a few branches. Otherwise, you will have to forget about developing the apple orchard.
0
0
Copy link
Apple trees are drying up: what to do?
If it turns out that the groundwater does not lie deep enough, then nothing can be done about it; replanting an adult tree is very risky, it will most likely die. Therefore, you will have to prune and further maintain the size of the apple tree, preventing it from growing. If the soil around the apple tree is depleted, the situation can be improved by regular fertilizing with organic matter. The main thing is not to use fresh manure for this, as it can “burn” the roots of the apple tree.
If the reason that the apple trees are drying is due to disease or pests that are localized in the roots of the apple tree, then chemical treatment will be required. But it must be carried out very carefully, observing the prescribed dosage and taking all precautions. If the winter was very frosty and as a result some shoots were damaged, then they must be carefully trimmed using very sharp and disinfected garden tools. After pruning, treat the crown with Heteroauxin, diluting it in the required dosage - this will help the tree heal wounds faster and stimulate the growth of new branches.
Apple tree branches drying out: photo of the problem
If the reason that apple trees are drying up lies in pests that have settled on the branches and leaves (for example, aphids), then in case of severe damage, part of the branches should be cut off and burned, and the rest should be treated with some means prepared according to folk recipes (soap -soda solution, tincture of pepper or cinnamon). During the flowering and fruiting period, it is not recommended to use chemicals, as this can negatively affect the harvest.
If the problem of drying branches affects a young, recently planted tree, and the reason lies in an inappropriate planting site, then in this case you can carefully and carefully replant the apple tree. This will delay fruiting for some time, but you will be able to save the tree.
If a disease is detected on young trees, for example, scab, you can use drugs such as Trifloxystrobin, Difenoconazole with flutriafol. If bark beetles and other bark pests are detected, you can use Aversectin C, Piripsoxifene or Malathion.