Why did garlic grow in one head? Why didn't the garlic split into cloves?
Find out why the garlic did not split into cloves or slices - we will give two main reasons. In other cases, the landing technique is to blame.
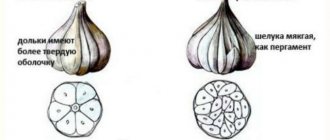
You can tell if garlic is ripe by looking at the head of garlic. We dig out one head of garlic and try to press it a little; if the head of garlic does not separate into cloves, then the garlic is not yet ripe. Therefore, the conclusion is clear:
- The head of garlic has not separated into cloves because it is still early.
- Unripe garlic is divided into slices only with the use of human effort.
Why did garlic grow without cloves?
Here are two main reasons:
- he is not ripe;
- did not dry after collection.
Why did the garlic not form a head?
There are several reasons why the garlic did not form a head:
- The most obvious one is that it “went into the arrow”; to prevent this, you need to remove the arrows in time. Many people tie a feather in a knot for this, but it’s better to just pinch it while it’s just starting to rise. In addition, young garlic shoots are very tasty.
- In addition, the problem with head formation may arise due to lack of feeding. in the ground. Make sure there is enough nitrogen fertilizer and soil looseness.
Review from Maria, an amateur gardener
Last June there was very hot, dry weather for almost three weeks. In those areas where garlic was watered rarely and irregularly, its “neck” began to dry out (people say “the neck has dried up”). As a result, the plants sharply slowed down their growth and development. Rainy weather in July partially saved it: excess moisture in the air and soil allowed the garlic, albeit slowly, to continue its growing season throughout the month. Although the heads turned out to be solid, they were quite large. The growing season of spring garlic stopped almost a month and a half earlier than usual.
Nowadays, too, there is clearly not enough moisture. Dear gardeners, do not repeat last year’s mistake!
Garlic, like onions, has a fibrous root system that is located in the surface layer and cannot draw water and nutrients from the deeper layers of the soil.
And a few more tips. Garlic requires early planting. In the last decade, weather conditions have been such that garlic could and should have been planted in April, or at most on May 1-2. Do not skimp on fertilizers for your garlic!
A few words about winter garlic. Break out the arrow on it (and repeatedly), then the head will be twice as large. Well, if you need to collect seeds, leave the arrows of a few of the strongest plants.
Necessary measures to enhance growth
Vegetable growers have several methods in their arsenal that are used if garlic grows poorly and the leaves turn yellow and dry. This problem often occurs due to a lack of nutrients, especially nitrogen and potassium.
You can feed vegetable beds with urea. It is more effective to carry out foliar spraying with a liquid solution. To prepare the solution, you will need to dilute 25 g of urea in 10 liters of water.
Feeding with potassium sulfate is useful. For foliar feeding, you will need 5 g of the drug, which is diluted in one liter of water. You can water the beds with a liquid solution, in this case you will need to dilute 20 g in 10 liters of water.
If a spicy vegetable grows poorly due to an increased acid reaction, it is useful to treat the area with dolomite flour in the fall or spring. You can sprinkle a little ash or make a liquid solution. It is useful to add organic fertilizers.
Plant garlic heads. How to plant garlic heads and get a wonderful harvest
Almost every home garden owner grows garlic. It is an integral component of summer and autumn preparations, helps improve the taste characteristics of various dishes, is used in folk medicine, and also as a protection for cultivated plants from attacks by insect pests. Basically, individual cloves (of all varieties) and aerial bulbs (winter, bolting varieties) are used for sowing. For planting with whole heads, a slightly different technique is used. In this article you will learn whether garlic can be planted in heads.
Planting garlic heads
Is it possible to plant garlic heads?
Planting of spring varieties with heads begins after the snow cover has melted and the soil has thawed. The soil is first fertilized with a complete mineral complex. The planting material is buried at least 10 cm. The interval between planting holes is maintained at 25-30 cm. A handful of rotted compost and a teaspoon of garden diatomaceous earth are added to each hole. A head of garlic is placed at the bottom of the fertilized hole, slightly pressed into the soil, and sprinkled with soil on top. If there is poor soil on the site, it is recommended to add compost on top, which will serve as a source of additional nutrition.
Further care measures are no different from caring for conventional vegetable crops. The main recommendations are:
- Mandatory adherence to planting deadlines;
- Growing crops on well-drained, moisture- and breathable soils;
- Carrying out several loosenings per season (at least 2-3 times);
- Feeding with mineral complexes (at least once);
- Breaking out the arrows that weaken the underground part of the plant.
You should also be careful when choosing a landing site. The best proximity to strawberries and fruit trees. It is not recommended to grow garlic in beds where garlic, onions, and bulbous flowers previously grew.
The crop does not tolerate excess amounts of organic matter well; it should be fertilized with mature compost or humus in moderation. When digging, use a bucket per 1 m2. Fertilizers are applied 5 days before planting.
Harvesting begins as soon as the tops turn yellow. For cleaning, choose a dry, sunny day. To avoid possible damage to the crop, use a pitchfork.
Garlic harvest
The collected garlic is shaken off the ground and placed in the sun for 2 hours for disinfection. Afterwards, the harvest is transferred under a shed or to a barn for two weeks, where it is laid out in a thin layer (about 5 cm) so that the tops dry.
Next, the roots are cut off from the bottom, leaving 2-3 cm. The tops are cut to 15-17 cm. The harvest is placed in baskets or boxes that allow air to pass freely. For storage, leave in a dark room at room temperature.
Which garlic is planted with heads
Some vegetable growers have never seen garlic planted as whole heads. However, experienced gardeners prefer cultivating bush garlic in their garden plots. Bush garlic is also called family or multi-bud garlic. It is this that is used for planting with heads in order to obtain a full-fledged root crop.
For owners of small garden plots, it will be more advisable to plant garlic in heads. Thanks to this, you can significantly save space. You can also plant the crop scattered on the site to protect cultivated plants from attack by insect pests. This achieves a double benefit - obtaining a garlic harvest and protecting garden crops from damage by pests and diseases.
Harvest and post-harvest work
When harvesting single clove garlic, an important point is the timing of the work.
When to remove garlic heads
Ripe bulbs are dug up in mid-summer, as soon as the green leaves begin to turn yellow and dry out. The longer the rhizomes of plants are in the ground, the deeper the ripened bulbs will deepen. The ripe crop is harvested on a cloudy day or in the evening. Direct sunlight can ruin an entire vegetable crop in a few minutes.
Necessary tools and technology for digging single teeth
In industrial quantities, seedlings are collected using special equipment and tools. Gardeners and gardeners carry out work harvesting garlic using a shovel. The bulbs are dug up, cleared of soil and dried. After drying, the tops and roots of the bulbs are cut off. Garlic is ready for storage in a ventilated, dry place.
Why doesn't garlic form cloves? 3 main mistakes: why winter garlic grows small
Everyone who plants winter garlic tries to follow all the rules so that it grows large and strong. However, often you try and try, but the garlic turns out small. Why is this happening? How to avoid this?
1. Very often garlic grows small, simply because it has already become “emaciated”. This happens primarily when we use garlic cloves as seed. That is, they planted it that year, this year they selected the crop for sowing and planted it, next year they collected it again, took it away, and so on. To preserve the varietal properties of garlic, it must be periodically renewed. That is, growing it from bulbs.
This planting method is very useful for renewing seed; it is quite simple, but the bulbs must be prepared in advance.
2. A common reason for a failed harvest, characteristic in principle for the entire garden, is lack of nutrition. Garlic may also begin to shrink for this reason. Therefore, before planting, we fertilize the soil in advance. It is best to do this a couple of weeks before planting.
Add to the soil per 1 sq. m.:
- 5 kg of rotted humus or compost
- 20 g superphosphate
- glass of wood ash
Along with these fertilizers, we dig up the soil. After a couple of weeks, the bed is ready for planting.
3. Also, the garlic may be small because it did not have enough moisture. Be sure to water the bed during the germination of cloves, the growth of greenery and at the beginning of the formation of cloves. During the ripening period of the bulbs, 3 weeks before harvesting, watering must be stopped.
RESULTS
If you want garlic to grow large, renew the planting material, additionally fertilize the soil and regularly water the plantings.
Barren land
Sometimes you can hear from summer residents: “In the garden I grow cucumbers, tomatoes, and potatoes. Vegetables produce a good harvest, and only garlic does not please with large heads.”
The culture loves loose, crumbly soil, rich in microelements. It will grow well in an area with fertile soil and neutral acidity.
Dense soil must be diluted with sand or peat, it depends on its composition. In early spring, urea is added, since during this period garlic needs nitrogen. When the heads begin to form and grow, the need for other substances appears. At this time, feed with superphosphate, which contains the following compounds:
- gland;
- fluorine,
- aluminum
At the end of July, the plants are fertilized with potassium salt or the tops are pollinated with ash. In the fall, when digging up the site, you need to add organic matter. Winter garlic will grow well on loam, while spring varieties are best planted in sandy loam soil.
One head variety of garlic. Garlic varieties
Garlic varieties
Garlic is considered one of the oldest agricultural crops. There is reliable evidence that the cultivation of garlic was carried out by farmers of Ancient Egypt. The ancestor is a bulbous plant native to the foothills of Central Asia.
Principles of Garlic Classification
Garlic (Allium sativum) is a herbaceous perennial plant. According to the modern classification, it belongs to the Amaryllidaceae family of the Onion subfamily. An individual plant consists of an underground bulb, root system, stem and leaves. The height of the peduncle stem varies from 20 to 50 cm.
In countries that traditionally grow and consume garlic, various varieties are used. Today, about 600 sub-cultivars can be distinguished, descended from several basic varieties of the plant. Their characteristics vary due to differences in climatic conditions in the areas of original cultivation. For example, varieties obtained through selection from original varieties growing in colder regions are characterized by good winter hardiness.
There are currently no international standards for the classification of garlic. Most varieties are usually divided into groups depending on the time of planting, the characteristics of the growing season and the characteristics of the final product.
Ability to form arrows
- Bolts are found only among winter varieties. During the growing season, the plant forms an arrow-peduncle. The height of the false stem can reach 1.2 meters and twist in a spiral at the top. An inflorescence is formed on it, from which airy bulbs ripen. From them, one-toothed garlic seeds are already grown - healthy garlic seeds that preserve the breeding potential of the variety. At the same time, bolting varieties do not lose the ability to propagate with cloves removed from the head. When growing, it is necessary to carefully monitor the crops and remove shoots from plants not intended for subsequent propagation. If you miss the period of formation of peduncles, you can lose up to a third of the expected harvest.
- Non-shooting species are sprouted only from cloves. They do not require additional costs for field work to remove flower stalks.
Planting season
Based on their ability to tolerate low temperatures and preferred planting time, two groups are distinguished.
- Winter varieties of garlic are planted in the fall, a few weeks before the first frost. High-quality seed planted in compliance with technology, if it manages to take root before frost, successfully survives the winter period. Some varieties are able to survive soil freezing down to minus 22 degrees without loss. Winter garlic ripens in mid-summer, several weeks earlier than spring garlic. The finished product looks more attractive, its large round bulbs consist of several large cloves, uniform in size and shape. If the temperature is maintained within 1-3 degrees, garlic can be stored until December or January without loss of commercial quality. The group of winter crops includes the most disease-resistant and high-yielding varieties, which is why they are mainly cultivated on an industrial scale. The growing season is 75-90 days for non-shooting garlic and 110-120 for shooting garlic.
- Spring varieties of garlic are only non-shooting. Cloves, peeled from last year's mature bulb, are planted in the spring, when the soil warms up a little after the winter period. Spring garlic ripens around the end of July or the first half of August. A distinctive feature is the large number of cloves in the onion. The lobules do not fit tightly together and can vary noticeably in shape and size. The varieties belonging to the spring group are suitable for long-term storage. If you keep commercial garlic in a refrigerator, at a constant temperature of 1 to 3 degrees, it is perfectly preserved almost until the beginning of summer. The growing season is from 90 to 110 days.
Planting cloves for seeds in the fall
Garlic
is planted 2 weeks before the temperature drops steadily.
For central Russia, this approximately corresponds to the end of September. Selected garlic should be used to obtain healthy seed material - bulbs. To get healthy garlic for planting, the heads are separated into cloves, which are planted one at a time. The best companion for garlic is garden strawberries. At the end of September, the cloves are embedded to a depth of about 3 cm.
The teeth should be planted away from each other, preferably in a sunny, slightly elevated place. After planting, you can sprinkle the clove with earth, you can add rotted manure, humus, and peat. The thickness of the covering layer is 2 cm. Before frost, you can add a layer of straw or stems of cut autumn flowers on top. Such mulch will delay soil freezing, which will allow the cloves to take root, but will not allow them to germinate.
One bulb of garlic. Such a different garlic
You can grow garlic all year round and always have a healthy product on your table.
After all, there are two separate types of this crop: winter and spring. They have external differences and require an individual approach.
How to distinguish them?
- The spring variety prefers summer (it is planted in the spring), while the winter variety loves winter and feels great when planted in autumn.
- Winter crops cannot be stored - they need to be eaten right away, but spring crops are perfectly preserved and will decorate your table even in winter.
- The winter one grows identical cloves, but the spring one loves variety - its segments are different and there are a lot of them.
- Winter varieties have a central stem, while spring varieties do not.
- The benefits of winter garlic are much more pronounced, because it has a larger amount of glycosides in its reserve (and its taste is much sharper and richer than spring garlic).
Nowadays, gardeners prefer to grow winter garlic, since it grows larger, its yield is higher, and it ripens earlier.
In addition, it is necessary to plant winter garlic in the fall, when the main work in the garden has already been completed and you can calmly start planting it without fuss.
But spring garlic can be stored well indoors for a long time, and its taste is much milder than winter garlic - not so hot.
Therefore, it is best to plant both types of garlic in your plots.
Now let's look in more detail at the issues of growing winter and spring garlic.
Winter garlic is an irreplaceable friend
The strong, persistent properties of this type of garlic allow it to easily withstand cold weather. It begins to grow actively in early spring.
Its root system is strong and strong; even in the fall it has time to form and prepare for the winter period.
For winter planting, it is best to take bolting species - they will give more yield.
Choosing a variety
For breeding, opt for climate-tested species from domestic breeders. Then planting garlic before winter will guarantee a healthy, rich harvest.
Some of the best varieties:
♦ Lyubasha. Growing this type of garlic is easy. After all, Lyubasha is a universal garlic type.
This variety grows well in all climate zones and on any soil. He will delight us with an abundance of large bulbs weighing up to 120 g.
♦ Polessky. A large dense bulb is capable of forming up to 7 large fleshy cloves.
Polessky is distinguished by an abundance of dark green leaves (an average of 8-10 leaves per plant).
♦ Garkua. This variety is ideal for sandy and clay soils with good drainage.
Excellent productivity (with a seed consumption of 1100-1200 kg/hectare, the yield can be up to 15 tons/hectare).
The taste of this variety is medium spicy; one onion can contain up to 18 cloves.
♦ Herman. The species has a particularly pungent taste and excellent shelf life (up to 8 months). Growing this type of garlic is recommended for beginning gardeners, as it is very unpretentious and strong.
♦ Scythian. Garlic of this variety has small airy bulbs of light purple color.
The bulb itself is larger, dense, flat-round in shape, consists of 6-9 large pinkish cloves.
Skif's taste is medium spicy.
Growing winter garlic
♦ When to plant garlic. The time for planting winter varieties is individual and depends on the climate conditions of your region.
Remember the main principle: winter garlic should appear in the beds a month and a half before the arrival of persistent cold weather.
And the soil temperature should be about +10°-15°C.
- Approximate dates for planting garlic crops in the middle zone: mid-September, in the south: early October. Winter crops feel great after cabbage, zucchini, tomatoes, cucumbers and legumes.
♦ Where to plant. Choose a place that is sunny, ventilated, level, and not flooded by spring floods.
Garlic does not like acidic soils; the ideal soil for it is neutral or slightly alkaline.
The type of land doesn’t really matter – garlic does well anywhere.
♦ Selecting planting material. To grow garlic you need the strongest and healthiest heads without mold or rot.
Even if one clove from the head turns out to be unsuitable, then all the others are rejected. The selected segments for planting must have a “clothing” (a solid, undamaged film shell).
- It is best to use garlic cloves collected this year for planting. Plant only dry, ungrown garlic! The exception is soaking the segments before sowing in Fitosporin for 6-7 minutes for disinfection.
You only need to separate the cloves from the head immediately before planting. The base of the garlic clove should be smooth, with strong scales.
Other reasons
Probably all owners of land plots know that vegetables planted in the shade will not produce a good harvest, and although garlic ripens in the ground, it needs a lot of light. In spacious fields illuminated by the sun, large bulbs will grow.
It happens that even on black soil, with normal moisture and regular fertilizing, small heads are dug up in the fall. After tomatoes, potatoes, and onions, the crop feels uncomfortable.
Planting in place of such predecessors is also one of the reasons why garlic grows small in the garden.
Some gardeners tie the leaves into a knot a few days before digging up the heads. Scientists do not confirm that this procedure helps to enlarge the bulbs, however, the effect on the crop’s greens still has positive aspects:
- Scales form from the dried above-ground part of garlic, which prevents infection from entering the root crop.
- Nutrients are directed not to the leaves, but to the head.
- The bulb stops growing and does not spoil for a long time.
Experienced gardeners plant garlic after alfalfa, cucumbers, clover, beans, and cabbage. Carrots, eggplants, and radishes free the soil from nutrients because they draw out everything contained in the soil.
Garlic will not grow well after onions, since both crops are affected by the same pathogenic microorganisms and pests.
Why do garlic heads not set? Why didn't the garlic start?
In the spring we came to the garden and discovered that our garlic had sprouted very poorly. We planted three different “varieties”: one of our own and two others bought at the market. Great hopes were placed on large garlic, which is usually traded by southerners. It had white bulbs and very large teeth. All three varieties were planted in the same bed, one after the other. Southern garlic died completely. Our own has sprouted, but rarely. The garlic bought from a pensioner performed best. It wasn't that big, but it was lilac. They say that lilac garlic stores well.
At the beginning of May, we planted several more rows of our winter garlic, which stayed with us until spring. But when they began to harvest, they discovered that the new garlic did not set bulbs. One thick stalk grew, like a leek. Why did this happen? After all, we planted our own garlic, that is, the same as in the fall. The autumn one grew normal bulbs (pictured). Now it is clear that for planting garlic will have to be purchased again. Tell me what kind of garlic to choose so that it winters well? N.P. Maslova, Nizhny Novgorod region.
In our newspaper we have already discussed the topic of poor wintering of garlic (Magic Bed No. 8(185), 2010). The reason is that in the Nizhny Novgorod region there were frosts without snow in December. If the garlic was planted shallowly and not covered with tops or other mulching material, then in most cases it froze.
Now about the fact that different varieties of garlic overwintered differently. Large garlic purchased at the market was most likely overfed with organic fertilizers. Under these conditions, it grows a very large bulb (gardeners say “inflated”). This is good for sale: garlic quickly gains weight and gets an excellent presentation. But it is not suitable for storage. Typically, such bulbs are poorly stored and do not overwinter well.
At the same time, there are examples where garlic brought from the south (but grown with normal doses of fertilizers) overwinters normally. Naturally, subject to planting conditions: depth of 5 cm and mulching of the bed.
And finally, the main question: why did the garlic planted in spring fail to set bulbs? Garlic varieties are divided into winter and spring varieties. There is almost no difference in taste. You can distinguish by appearance: the spring variety has many small teeth and very thin, “papery” scales (the winter variety has dense ones).
The main difference is in the timing of planting. Winter garlic is planted two weeks before heavy frosts (in the middle zone this is approximately mid-October). Spring garlic is planted in the spring, as soon as the soil allows (usually in April). The fact is that for normal growth, winter garlic must go through a cooling period. Only in this case does the bulb begin to form. When planting in the spring, and even later (in May), the bulb does not form. The plant simply thickens the base of the stem. Such plants will not overwinter, they will simply rot. But you can eat them as food and put them in pickles in the same way as ordinary teeth.
If you have grown a lot of “stem” garlic, try pickling it. To do this, chop finely and sprinkle with salt. You can simply leave the garlic in the garden and consume it as needed. Unlike “normal” garlic, the leaves of “spring” garlic have not yet dried out. As long as they are green, the plant continues to grow.
Care
Planted aerial bulbs grow and develop quickly, therefore, the plant needs additional care.
Watering and fertilizing
Basic fertilizers and top dressing are applied to the soil before planting begins. But sometimes a vegetable crop requires increased care. Feed the onetooth several times during the growing season. Winter vegetables are fed for the first time in early April with organic fertilizers or urea. The next stages of work are carried out in early May and then in June.
When using nitrogen fertilizers, keep in mind that an excess of nitrogen promotes the development of the above-ground part of the plant and stops the formation of rhizomes. Watering is done as needed, with warm, settled water. During dry periods, irrigation work is carried out once every 7-8 days.
Loosening and mulching the soil
Loosening the soil is carried out in conjunction with watering and helps eliminate weeds from the garden bed. Also, loosening the soil provides access to oxygen and moisture to the rhizomes of the plant, where the processes of formation and development of the vegetable crop occur.
Mulching the beds protects the plant from drought, pests, and the spread of fungal and viral diseases.
Diseases and pests: control and prevention
If the rules of crop rotation, soil preparation and planting material were followed when planting seeds, then the risk of diseases and pests is minimal. Good predecessors for garlic are cucumbers, herbs, carrots or beets. It is not advisable to plant vegetables after garlic and onions.
In case of plant infection, special preparations for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes are used.
Planting garlic heads. Preparatory work before planting
One of the conditions for garlic to produce large heads is to correctly combine the soil in the garden bed. This vegetable prefers loamy-sandy soils of neutral composition.
To get a good garlic harvest, you need to properly prepare the soil.
In order for garlic to produce large heads and grow healthy, its predecessors must be the following crops:
- legumes,
- pumpkin,
- cabbage
For the same purposes, it is not recommended to plant garlic in soil where tomatoes, potatoes, onions and garlic grew. This promotes infection by nematodes and fusarium, and will also cause the new harvest garlic heads to not be large enough.
The beds are prepared a month and a half before planting winter garlic, namely in August. You should choose a sunny place to ensure that this vegetable develops large heads in winter thanks to a sufficient amount of sunlight.
It is recommended to add the following fertilizers to the soil (per square meter):
- 1 bucket of compost or manure,
- 1 tbsp. l. superphosphate,
- 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate,
- 1 cup fluff lime, chalk or dolomite flour.
Loamy soil should be mixed with coarse river sand or peat so that the garlic heads have the opportunity to be saturated with oxygen, which will allow them to grow large enough. Proportion: 1 bucket per 1 m2.
Peat soils, on the contrary, are mixed with a bucket of loamy soil and sand for each square meter, and sandy soils - 2 buckets of peat and loamy soil for each square meter. All types of soil should be fertilized with all the substances listed above.
After applying fertilizers, the beds are dug up and compacted. And at the very end, copper sulfate is also added in the proportion of 1 tbsp/10 l of water. For every square meter of soil, 1 liter of solution should be used to grow a crop with large heads. After tilling the soil, the beds are covered with polyethylene and left until our vegetables are planted.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of growing
Many gardeners wonder why complicate life, and grow garlic from aerial seeds; it is easier to plant ordinary cloves of any variety of vegetable crop. But it is from the one-toothed plant that a high-quality and large harvest of vegetables is obtained. Garlic propagated from aerial bulbs is distinguished by its natural immunity to diseases, pests and unpretentiousness to climatic conditions and soil composition.
See also
Description of garlic variety Azure, cultivation and yield
Read
The main advantages of the single-tooth blade:
- The seed material quickly takes root in the soil and allows you to grow a good harvest of garlic already in the first planting season.
- The garlic bulb is not divided before planting in open ground.
- Vegetables grown from aerial bulbs rejuvenate your favorite varieties of garlic.
- The seed material is resistant to frost, diseases and pests.
The disadvantage of single-clove garlic is the high price of planting material and the time it takes to obtain a full-fledged bulb with a large number of cloves.
Important nuances
To get the maximum crop yield, take into account the interesting features of the planting material. If you dig up a one-toothed tree, it falls into a natural state of rest. This can be adjusted using the temperature setting. If the crop begins to deteriorate, a person looks for the reasons for this, without even thinking about the temperature. To ensure normal storage, the room must be between 5 and 10 °C.
Failure to maintain the temperature will bring the crop out of dormancy.
Growing single clove garlic is not the only important condition for obtaining a harvest. Enough attention is paid to the storage location. The room should be well ventilated, dry and cool. For storage, nets or boxes are used, which are placed on racks.
If the garlic was grown according to all the rules, premature digging contributes to rapid drying. Among the total storage volume, 2% of single teeth with mechanical damage are allowed.
How to grow garlic from air plants?
Planting garlic using aerial bulbs is carried out 2 times a year:
- spring varieties are planted in early spring after the last frost;
- winter - a month before the onset of frost.
Winter garlic is planted at the end of September or until mid-October. Air bulbs are placed in the ground in the standard way - lowercase. There should be at least 20 cm between the rows. To avoid mistakes, it is recommended to adhere to the following scheme - 45–50 cloves per linear meter.
How to care for crops?
Care of crops must be regular. If a gardener has planted winter bulbs, the soil should be covered with a large amount of snow. There may not be enough precipitation during the winter. In this case, all the snow is raked into the beds. This approach will ensure early seedlings.
Dry weather negatively affects the growth of seedlings. If a person lives in a region with an arid climate, he must take care of thoroughly watering the crop. The beds must be watered at least once a month. Particular attention should be paid to watering in May.
Crops also need feeding. The fertilizer application procedure occurs in two stages. At the end of March and until the beginning of April, the soil is saturated with nitrophoska. In the first week of June, the beds are sprinkled with wood ash and ammophos.
Harvesting air bulbs
The best bulbs come from purple-colored garlic of mid- and early-ripening varieties. It should be collected from tall, strong plants, on which the inflorescences begin to dry out, but do not yet fall apart. Cutting and storage is carried out together with the stem. Dry in the shade and store in a dry place. Two weeks before planting, excess husks are removed from the bulbs, sorted by size and placed in a refrigerator at a temperature of 0 to +4 °C.
Planting garlic using just the cloves is an easy and cheap growing method. But if you do this constantly, then over the years the harvest loses quality and decreases. As a result, the plant may degenerate. To maintain the best varietal properties, it is necessary to constantly replace planting material by at least a quarter. The best replacement method is to grow and plant your own single clove garlic.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Single clove garlic is a crop that is obtained by planting the best airy bulbs. For several years in a row, gardeners have been using a similar method of propagating garlic. Why him? This helps not only to get a rich harvest, but also to renew it. This procedure is necessary to keep the vegetable yield at a high level.
Growing garlic bulbs (seeds)
In the spring, the cloves will produce a feather; you cannot pick it for greenery, since the purpose of planting is seeds (bulbs), which form at the end of the peduncle during the summer. At first the garlic produces florid arrows and then blooms.
Large, smooth, bright purple seeds ripen if the plant receives enough:
- water;
- sunlight;
- oxygen with careful loosening of the soil.
By autumn, the bulbs should ripen well, but it is not advisable to miss the moment when they break through the thin shell. The arrows need to be picked at the stage of yellowing of the leaves and ripening of the seeds. To prevent the bulblets from spilling out of the shell onto the ground, experienced summer residents tie them with gauze.
More about classes
Taking into account the size of the garlic, it is determined which class the vegetable belongs to - I or II. If the parameters of the clove correspond to the first class, in further development the head will turn out to be normal. A smaller set forms an unusual onion, and one large one without cloves. It is used as planting material.
This approach makes it possible to obtain material for propagating valuable varieties. It can be stored for 2–3 years, without deteriorating the quality of the crop, but only increasing it. When planting winter and spring garlic, adhere to the main recommendations. This allows you to obtain a large onion for further propagation and consumption.
One clove is garlic, which is a material for planting, which has technological advantages compared to a regular clove:
- Features a round appearance. In this case, the size may change, but the shape does not. Regular teeth are elongated.
- The center of mass of single-clove garlic coincides with the center of the pea itself. The center of mass of the clove is shifted to the bottom.
- The single-tooth shape is similar to a pea, so it allows for calibration before planting.
- Planted seeds have a healthy immune system, so they are not susceptible to parasites and vegetable diseases.
- It takes root without problems and survives the winter.
- Garlic, which grew from a single clove, produces a harvest the very next year.
- A large onion does not need to be peeled.
- The yield of single cloves is much higher than cloves of the same weight when planted.
Despite the many advantages, culture also has disadvantages. Fortunately, there is only one - a higher price, which is explained by the labor costs in growing, caring for and cleaning.
How to grow
Usually the one-toothed one is planted in the fall and dug up the following year. Care for it like regular winter garlic. For various reasons, you can miss the planting date and the seeds will remain idle. It's OK. One-tooth can also be planted in the spring, taking into account the weather forecast.
It is important to germinate it before planting. Otherwise, the set may not have time to form a head of cloves and will grow into a large single-clawed one.
Pre-planting preparation, planting, care and harvesting are carried out in the following order:
- In the fall, before plowing or digging the soil, it is necessary to apply fertilizers. Up to half a ton of aged manure or compost, 500 g of superphosphate and 300 g of potassium salt per hundred square meters.
- A month before planting, the one-tooth must be soaked in a growth-stimulating solution from Rostock, Biomaster or other stimulants. The next day, wrap it in cotton cloth and put it in plastic bags to prevent drying out. Place in a refrigerator with a temperature of approximately plus 5 °C. After four weeks, the seeds should grow roots up to 1 centimeter.
- Plant at the beginning of field work, at a soil temperature of at least plus 2 °C. Carefully, so as not to damage the roots, insert the bulbs into the furrows to a depth of 5 - 6 cm. Row spacing is 40 - 45 cm, rows with an interval of about 8 cm.
- After emergence, fertilizing with ammonium nitrate is necessary. Scatter dry saltpeter under watering and mulch with peat or humus.
- At the beginning of summer, you can feed with an ammonia solution at the rate of 2 ml of ammonia per liter of water, and complex fertilizers.
- Basic care consists of timely watering, loosening and weeding.
- The crop is harvested in September, when the plant stems lay down. Dry under a canopy or in a dry room for a month, then sort through.
- It is better to store spring garlic at a temperature of 16 to 20 °C in a dark, dry room.