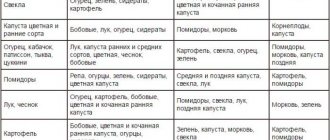
The need for crop rotation
Crop rotation is the competent alternation of vegetable crops in garden beds; its goals are:
To achieve these goals in full, cultures are alternated, taking into account not only the compatibility of cultures. With proper crop rotation, you need to take into account the time for restoration of fertility and natural cleansing of the land. It must get rid of the larvae of pests and pathogens typical for this vegetable.
For example, after potatoes, it is better to sow pumpkin in the garden a year later. If you replenish soil fertility with mineral fertilizers, cucumbers and onions will grow well. It is better to plant a potato plantation next year after cabbage.
Best neighbors, what to plant next to peppers?
Mixed beds are popular. The correct choice of vegetable crops is, first of all, disease prevention and protection from pests. It is recommended to plant sharp-smelling plants that produce phytoncides next to pepper:
The planting pattern for peppers in such beds differs from the standard one. When transplanting seedlings, planting holes are placed at intervals of 40-45 cm. The plants listed above are planted between the bushes. You can sow carrots next to the pepper bushes. It will repel insects with the smell of tops.
Good and bad predecessors
The easiest thing to understand is not to plant bell peppers. It belongs to the nightshade family, just like potatoes, tomatoes, physalis, and eggplants. Therefore, they are the worst predecessors. Their nepotism implies the presence of the same pests on the beds, the crops are susceptible to common diseases, and they take the same nutrients from the soil.
Therefore, we can say for sure that it should not be planted after tomatoes and other vegetables from the nightshade family. A close relative of sweet pepper is bitter pepper; these varieties not only do not need to be alternated, they should not even be planted in closely spaced areas.
It’s easier to grow healthy peppers on beds laid out in place of last year’s plantings of zucchini, carrots, and cucumbers; they grow well after onions. When planting, add a large amount of organic matter to zucchini and cucumbers; it rots well over the course of the season. The crop reacts poorly to fresh organic matter: it gets sick more often and forms ovaries later. During the season, manure (humus) rots well, making the soil loose and useful for this crop.
Pepper care
Adult plants, like seedlings, cannot be left without moisture and fertilizing. Water them with warm, settled water regularly (on average once every 4-6 days), preventing the soil from drying out and crusting. After watering, be sure to loosen the soil to a depth of 1.5-2 cm.
It is recommended to maintain the required level of humidity using mulching. Remember to only renew the mulch once every 3-4 weeks as it subsides.
Feed sweet peppers 2-4 times per season, alternating mineral and organic fertilizers. For the first feeding, which should be done two weeks after planting, prepare a solution of 25 g of potassium sulfate, 30 g of superphosphate and 15 g of urea per bucket of water. Water the peppers at the root.
Instead of such fertilizing, you can use complex fertilizer or an infusion of bird droppings dissolved in water (1:20), as well as folk remedies: infusions of ash (1 glass per 5 liters of water) or nettle with the addition of manure and EM preparations.
When ovaries form on the pepper, apply a second feeding, slightly reducing the dosage. Dissolve 10 g of urea and 25 g of superphosphate and potassium sulfate in a bucket of water. Two feedings of pepper are usually enough. Only if the plant has slowed down in growth, you can “feed” it more, but not more often than once every two weeks.
- How to feed sweet peppers for growth and harvest
In order for the bell pepper to please you with its juiciness and excellent taste, you should also please it with proper and timely feeding.
What can be grown after pepper and what cannot be grown
The roots of the plant are shallow, therefore, it consumes nutrients from the upper layers of the soil. In root crops, the roots penetrate much deeper. In this regard, you can plant after pepper:
In addition to root vegetables, there are a number of vegetables that are classified as neutral plants. They are safely planted after sweet peppers. In addition to the root crops mentioned above, neutral plants include:
It would be a mistake to plant pumpkins to replace sweet peppers. It is good to sow it before nightshade crops, but it grows very poorly after them. And all because of the toxins accumulated after the peppers. Any melons and melons planted after it (squash, zucchini) will be oppressed by harmful toxins.
Best companions
For a good harvest of sweet peppers, crop rotation alone is not enough. The fertility of plants grown next to beans increases noticeably. The smell of beans repels all pests from the bushes, the roots enrich the soil with nitrogen. Plants growing next to bean bushes receive nitrogen in an easily digestible form.
The correct choice of garden neighbors has a positive effect on the growth and development of garden crops. It is known that you can also plant them on the same bed with peppers. The following vegetables will be good neighbors for them:
It is clear what crops can be used to plant peppers, and what vegetables can be used to compact its beds. There is no need to listen to vegetable growers who say: I have been growing peppers in one place for decades and getting a good harvest. It is better to alternate any plantings, be it tomatoes, onions or any other vegetable crop. It is necessary to sow green manure after harvesting if the garden is so small that it is very difficult to follow the rules of crop rotation.
Bell pepper is one of the most common vegetables grown in our country. It is valued by gardeners for its taste, as well as its large composition of vitamins and microelements. In terms of vitamin C, bell peppers surpass all other vegetables.
Not recommended crops
The following crops should not be grown in the place where the tomatoes were planted:
- other or similar varieties of tomatoes;
- potato;
- tobacco;
- physalis;
- strawberries;
- strawberries;
- eggplants.
This recommendation is due to the fact that tomatoes with the listed crops are affected by similar diseases and pests. Therefore, even after disinfection of the soil, signs of pathologies that previously affected planted tomatoes may appear on newly grown plants.
There is another argument against planting these crops on the former site of tomatoes. The fact is that tomatoes make the soil more acidic, and in such an environment the listed plants cannot fully grow, develop, and most importantly, bear fruit. Because of this, crops planted in the wrong place either die or produce a poor harvest.
DIY drip irrigation for tomatoes from plastic bottlesRead
What can be planted after tomatoes from melons? The answer to this question is clear: nothing. This is due to the fact that watermelons, melons or pumpkins planted in a former tomato area will bear fruit poorly, and the summer resident will receive a very modest harvest.
Many summer residents plant bell peppers next to tomatoes. It is not recommended to carry out such planting in a bed where tomatoes were previously grown for only one reason: the yield of bell peppers may be reduced significantly. If such a prospect does not frighten the gardener, he can plant this plant crop in place of tomatoes without fear of the bush being damaged by diseases or pests.
The role of alternating vegetables in a summer cottage
The yield of any crop, including bell pepper, directly depends on the choice of planting site in the garden and compliance with crop rotation. Therefore, it is very important to plan the location of the plantings and their neighbors in advance before planting. Crop rotation is certain rules in planting crops; you need to know exactly which vegetables can be planted and after whom. The amount of harvest and the health of the plants depend on the correctness of fruit rotation.
Bell pepper on a bush
Each vegetable treats weeds differently. So, most often the beds are left without weeds after cabbage, peas or potatoes, making it easier to grow other crops in their place. Each crop has its own biological characteristics, therefore, to prevent the appearance of insects and weeds, it is worth alternating them so that they are in their place no earlier than 4 years. This rule helps prevent soil depletion and increase its fertility.
The best varieties and hybrids of sweet peppers for open ground
Successful cultivation of sweet peppers and their harvest largely depends on the correct choice of varieties and hybrids. Which peppers are best to plant in open ground?
- Peak NK . A mid-early variety 70-80 cm high with red fruits weighing 130-160 g (juicy wall thickness 5-6 mm). The plant bears up to 14-15 fruits. Maturation is simultaneous. Plants are resistant to verticillium, mosaic, and alternaria. The growing season is 120 days. Placement intervals are 40x50 cm or 45x45 cm. The variety is unpretentious, recommended for cultivation in many regions, including the middle zone. For fresh consumption and processing.
- California miracle . Mid-early (110 days) pepper with cube-shaped fruits, green in technical ripeness, later - red. Weight 90-130 g, thick-walled (7-8 mm), aroma is pronounced. Resistant to mosaic, characterized by long-term fruiting. Bush height 55-65 cm. Planting pattern 30×60 cm. For salad purposes and for processing. The fruits are stored for a long time.
- Freckle F1 . Large-fruited, early-ripening hybrid with orange-colored fruits with stable yields in all weather conditions. The height of the bush is 1 m, the fruits are prism-shaped, tetrahedral with a concave apex. Wall thickness – 7 mm, weight 160 g, yield 12-13 kg per 1 sq.m. Planting density 3.5 pcs. per 1 sq.m. Planting 30x50 cm when maintaining a crop of 2-3 stems.
- Bogatyr . The bush is spreading and powerful, 75 cm high, yield 8 kg/sq.m. Average ripening period (130 days). The fruits are red in color, up to 17 cm long, weighing 200-300 g with thick walls, universal purpose, without signs of bitterness with a long shelf life. Layout 50×35 cm.
- Cockatoo F1 . Early ripening (90 days) productive hybrid, 65 cm high, large fruits in the form of an elongated yellow prism, weighing 200-220 g, up to 17 cm long. Plants are resistant to unfavorable climatic conditions and stress. The planting density is 4 pcs. per 1 sq. m. Productivity 8 kg/sq. m. No shaping is required for this pepper.
- Ultraviolet . Mid-season hybrid (period before harvest 125 days). At biological maturity, cube-shaped fleshy fruits of dark purple color (10x10 cm), weight 200 g. Resistant to mosaic, planting density 3 pcs. per 1 sq.m. Productivity is 8-9 kg/sq.m.
Purple pepper in biological ripeness
Variety "Vesnushka"
All of the above varieties and hybrids are suitable for planting in open ground and under film cover. It should be taken into account that varietal peppers are zoned to a particular region and seeds can be taken from them for future plantings.
Hybrids are the result of crossing several varieties or genetic modification and are not adapted to the weather conditions of any particular region due to their versatility. Therefore, they require more careful agricultural technology for sweet peppers in open ground. Hybrid seeds do not have maternal qualities.
Seed preparation technology
The technology for growing bell pepper begins with preparing the seeds:
1. Sorting . First, very flat and damaged seeds are removed by visual inspection. Then prepare a salt solution (1 tsp per 200 ml of water) and dip the material into it, mix and after 3-4 minutes drain it along with the floating seeds. Heavier fragments remaining at the bottom are washed and dried on a cloth.
2. Disinfection . To do this, use ready-made preparations (Vitaros, Fitosporin-M, Maxim, etc.) or a crimson solution of potassium permanganate. Seeds, wrapped in gauze or bandage, are dipped into the solution and kept for half an hour. Then they are washed and stored for germination.
Bell pepper seeds
3. Germination . To do this, use cellulose sponges or gauze folded in several rows. Seeds are laid on the selected material, covered with it on top, the “sandwich” is placed on a saucer and a little water is poured. Subsequently, they are moistened as they dry from the spray until roots appear (8-10 days). At the same time, it is important not to overdry the seeds, but also not to overwater them, since they need both oxygen for breathing and moisture for swelling. To speed up the process, you can pre-treat the seeds with the growth stimulator Epin.
4. Hardening . During the germination stage, the swollen seed material should be alternately placed in the refrigerator several times (12 hours each) and removed from it.
If all the germination secrets are followed, the seeds will quickly sprout and be ready for planting as seedlings.
Agricultural technology for sowing seeds for seedlings
The optimal time for sowing seeds for most varieties is 50 days before planting in open ground. If you use a store-bought substrate, you should take either a universal one or one for tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants (nightshades).
You can also prepare the soil yourself. To do this take:
- 3 parts humus;
- 5 parts peat;
- 2 parts of garden or turf soil.
Another recipe consists of the following ingredients:
- 2 parts peat;
- 1 part sand;
- 1 part garden or turf soil.
In both cases, it is advisable to calcine or steam the soil and add 1 tbsp. ash onto a bucket of substrate.
Preparing the soil for sowing seeds
For sowing, use special containers or plastic half-liter glasses, boxes of yogurt, kefir, juice, etc. Store-bought products already have holes to allow excess moisture to escape and air to reach the roots. You will have to make them in improvised pots. It is better to place them on the side surface at a height of 1.5-2 cm - this way the water will not immediately flow into the pan, and the roots will fill the entire space, tending to the depth.
When the seeds are ready for sowing, you should:
- rinse all containers with a solution of potassium permanganate;
- fill ¾ with soil;
- moisten with a light solution of potassium permanganate;
- spread the seeds;
- sprinkle with soil 6-8 mm;
- tamp lightly;
- water;
- cover with film;
- put in a warm place until shoots appear.
If subsequent picking is expected, then sowing can be done in large shallow containers, spreading the seeds according to a 1×2-3 cm pattern.
After what can you plant bell peppers?
Before planting, you need to remember that it does not tolerate various types of organic fertilizers . Because of this, it is best to work them into the soil where it will grow a year before planting. Only after a while can Bulgarian seedlings be planted in this place.
The technology for planting this crop is not much different from planting tomatoes. A vegetable, like no other, needs fertile soil filled with nutrients. Therefore, when planting sweet peppers in holes, special fertilizers should be added to the seedlings. It grows quite slowly. Due to the location of the root system, it needs a lot of moisture. The roots are located in the upper layers of the soil, so they require frequent watering.
Bell pepper bed
After which it is better to plant pepper:
These crops fertilize the soil well; after them there is no need to loosen it, so the soil is ideal for Bulgarian vegetables. Onions and garlic can also be excellent precursors. A good vegetable harvest can be obtained in the beds where there were root crops before.