Composition and mechanism of action of the drug Horus
The main active ingredient in the antifungal drug is cyprodinil. It belongs to the organic compounds of the aminopyrimidine class. For 1 kg of fungicide there are 750 g of active ingredient.
Cyprodinil penetrates the cells of pathogenic fungi and inhibits the synthesis of amino acids occurring in them. As a result, the vital activity of the parasites is disrupted, which leads to the cessation of the growth of mycelium on vegetation.
Important! The active substance of Horus, as indicated in the instructions for use, is effective only on young plants and trees. Therefore, cyprodinil will not be able to help an adult tree or shrub older than 3 years, since it will not be able to penetrate deep into their structure.
Among the pathogenic fungi on which the fungicide has a detrimental effect are:
- basidiomycetes;
- ascomycetes;
- deuteromycetes.
A feature of the systemic drug is its effectiveness, despite the humidity and air temperature. At the same time, it is safe for insects, fish, animals and humans.
Where is it used?
Gardeners praise Horus, noting its effectiveness against most fungal infections. It is not a universal fungicide, but is successfully used to combat various types of fungi, such as
- basidiomycetes (cause moniliosis);
- actinomycetes (provoke scab);
- deuteromycetes (lead to fruit rot).
It should be taken into account that cyprodinil penetrates only into the tissue structure of young trees and shrubs. It is not suitable for processing aged crops.
The manufacturer indicates in the instructions for use which diseases the drug is indicated for (see photo):
- on stone fruits (cherries, apricots, plums, cherries, peaches) - against fruit rot, monilial blight, coccomycosis, clusterosporiasis;
- on pear and apple trees - from Alternaria, scab, moniliosis and partly from powdery mildew;
- on grapes - with a complex of rots of different types of berries (black, rhizopus watery, olive moldy), from gray and white rot.
In practice, the effectiveness of using the product on roses, strawberries and wild strawberries has been proven - against ash and fungal infections. The drug is also recommended for treating coniferous ornamental trees (as a preventive measure and for treating browning).
Scope of application
Horus is a plant treatment drug that is most often used to treat fruit bushes, trees and grapes. The active component of the product is used in personal and agricultural applications for the treatment of various fungal diseases, including:
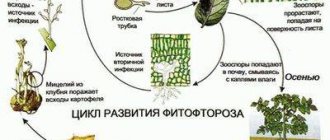
- Alternaria blight. A disease that affects vegetables, shrubs, fruits, fruit trees and berry plants.
- Moniliosis. It is a widespread disease that primarily affects fruit trees. At the same time, shrubs suffer from the disease less often. The first symptoms of the disease are drying of branches and leaves, dying off of inflorescences. Pathology can lead to significant damage - a reduction in yield by 70 - 80%.
- Powdery mildew. As indicated in the instructions for use, Horus fungicide copes with white bloom on grapes and roses.
- Scab. A contagious disease that spreads quickly on trees. Expressed in the form of spots on foliage and fruits.
- Rot of grape berries. An insidious fungus that can spread to the bunches during their flowering, as well as to the berries and wood themselves.
- Monilial burn. Most often, stone fruit crops, especially cherries, are affected by this disease.
The drug Horus has a wide spectrum of action, which is indicated in the instructions for use, so the fungicide should always be in the gardener’s “first aid kit”.
Instructions for use of systemic fungicide
When the first symptoms of fungal infection of garden crops appear, spray with Horus twice, repeating the treatment after a week or 10 days. However, in case of monilial burn, fruit trees are sprayed three times, since twice-time treatment is not enough.
Horus is a highly effective Swiss broad-spectrum fungicide
To protect the garden and prevent the appearance of diseases, the initial spraying is carried out during the “green cone” phase, the second – after 7-10 days. This treatment will protect the garden from scab and ensure successful vegetation of fruit trees.
Particular attention should be paid to grapes, which must be processed three times:
- during the period of bud formation (at the beginning of flowering);
- during the closure of berries in a bunch;
- at the beginning of berry ripening.
The garden can be cultivated both in early spring and late autumn, preferably in the morning or evening, in calm weather. The main thing is that the ambient temperature does not fall below +3º C. However, if the weather conditions are too hot, it is useless to use the fungicide, since its effect is reduced at temperatures of +18-25º C and above.
If you follow the instructions for use, you can prevent the spread of the disease to healthy parts of trees and block the infectious process.
Advantages and disadvantages
The instructions for use contain not only information about the composition and use of the Horus fungicide. The description of the benefits of the product notes the following:
- Possibility of using the fungicide even at air temperatures less than +10 °C.
- Fast absorption of the active substance. After treatment, the product penetrates into the plant structure in just 2 - 3 hours.
- Safety. The fungicide is non-toxic to most insects, birds, animals and people. It also has low toxicity to the inhabitants of the reservoir.
- Possibility of combination with other agricultural pesticides.
- Convenient packaging.
- Clear instructions for use.
- Economical.
- Groundwater safety.
The disadvantages of the fungicide include:
- Locality of impact. The product does not spread throughout the entire plant at once, but works only in certain areas of it.
- Difficult penetration. Cyprodinil is not able to pass through the thick skin of leaves that mature shrubs and trees have. Therefore, the drug is recommended for use on young crops, which is also reflected in the instructions for use.
- Carrying out treatment during the growing season of the plant. It is worth considering that Chorus is effective only at temperatures ranging from +3 °C to +25 °C.
Compatibility with other drugs
The manufacturer notes high efficiency with the simultaneous use of “Chorus” and other means of protection. The effectiveness of treatments in tank mixtures with the preparations “Topaz” and “Skor” has been proven.
When preparing mixtures, it is recommended to first check the products for compatibility. Prepare a small (0.5 l) amount of a solution of each drug, combine them in one container and observe the reaction for 2-3 hours.
If there is sediment, the appearance of flakes, foam, or seething, there is only one conclusion - the drugs are incompatible. If there are no changes or very little flocculation is observed, then the products are compatible and can be used in tank mixtures.
Before preparation, first dilute “Chorus”, and then another drug, and then mix it. Be sure to follow the dosage and consumption rates - act strictly according to the instructions.
Preparation of solution and dosage
Chorus is actively used in gardening. The effectiveness of the drug depends entirely on how correctly the working solution is prepared. Therefore, before applying the composition, you should carefully read the instructions for using the fungicide.
Important! The working solution must be prepared immediately before use; during storage it loses its properties.
Instructions for diluting the composition:
- The container in which the fungicide is prepared should be filled ¼ full with clean, settled water.
- Then it is necessary to introduce the drug into it, according to the dosage for the specific crop being treated, specified in the instructions for use.
- Mix.
- Add the remaining water.
- Mix thoroughly until smooth.
- Start spraying.
The instructions for use indicate the exact dosage of the product, which depends on the type of crop being treated.
| Fruit crop | Possible pathologies | Dosage of the drug |
| Plum, cherry, peach, apricot, sweet cherry, etc. | Leaf curl and monilial burn. | 2 g of Horus per 10 liters of water. |
| Clusterosporiasis, coccomycosis, fruit rot. | 2 g per 5 - 6 liters of liquid. | |
| Pear, apple, quince, other shrubs and trees with achenes in the fruits | Scab, fruit rot (moniliosis), Alternaria blight. | 2 g per 10 liters of water. |
According to the instructions for use, the consumption of the working composition depends entirely on the size of the crop being treated. As a rule, one shrub or tree accounts for 2 to 4 liters.
Important! Horus treatment of stone fruit crops should be carried out only in the evening.
Mistakes during spring processing of gooseberries and currants
Among the most common mistakes common to both beginners and experienced gardeners are the following:
- Treatment of plants with insecticides during flowering. Carrying out the procedure at this stage of the growing season can lead to the accumulation of toxins in the bud, which makes the fruit unsuitable for consumption.
- Carrying out processing in rainy, sunny and windy weather. Rain can wash away medications, wind can blow them away, and sunlight can cause burns.
- Failure to comply with the proportions of the solution during its preparation. A solution of weak concentration may be ineffective; a product with a high content of the active substance can not only harm the plant, but also lead to its death.
Learn how to care for blackcurrant bushes in early spring.
Spring treatment of gooseberries and currants from pests and diseases is an extremely important and necessary procedure. If you want to see your plants healthy and regularly receive a bountiful harvest, you need to carry out the appropriate measures on time and in full accordance with the instructions.
When and how to use Chorus
Horus is an indispensable garden tool. The treatment procedure is carried out by spraying. It is important to follow the deadlines specified in the instructions for use. Usually the fungicide is used several times. The first treatment is before the flowers bloom, the second is 10 - 14 days after the flowering period, the third is 15 days before harvest.
Since the instructions for use indicate that the fungicide does not work at temperatures above +25 °C, it is recommended to spray in cool times - at +3 °C to 10 °C.
Important! The protective effect of Horus lasts for 10 days.
Fruit trees
Chorus is actively used against diseases of fruit trees such as powdery mildew, Alternaria, scab, and monilial blight. Treatment must be carried out twice - during bud break and 2 weeks after flowering.
To preserve the fruits and increase their shelf life, it is worth spraying the tree 15 days before harvesting. This point is also reflected in the instructions for use and should not be ignored, since the safety of the fruit for human health depends on it.
It is better to spray fruit trees with Horus at the first signs of the disease or as a preventive measure.
Coniferous trees
Coniferous plantations often suffer from browning. The fungicide Horus will also help to cope with this problem, treatment with which should be carried out in the spring, when shoot growth begins to increase.
Roses
Fungal diseases and ashtray can be cured by using Horus at the stage of setting buds on the bushes. It is important to take into account that the effectiveness of treatment depends on the ambient temperature. The instructions for use indicate that roses should be sprayed during a period when the average daily temperature does not exceed +10 °C.
Strawberries and wild strawberries
Strawberries and strawberries can suffer significantly from gray rot, spotting and powdery mildew. In this case, infection can even occur from last year’s foliage that remained on the site. Spraying with Horus fungicide will help cope with the problem.
The treatment is carried out three times. According to the instructions, the dosage depends on the time of the procedure:
- The first use of the drug should be before tying buds. The working solution contains 6 g of substance per 10 liters of water.
- The second treatment is appropriate during the period of berry formation. The mixture consists of 10 liters of water and 3 g of Horus.
- The third spraying is carried out after harvesting. The dosage corresponds to the first treatment (6 g/10 l).
Grape
According to the instructions for use, Horus can be used to protect grapes from gray rot, downy and powdery mildew. In this case, the working solution for spraying must be more concentrated than for other crops.
Instructions for grape dosages:
- Primary treatment during the period of bud formation – 6 g/5 l of water.
- Secondary spraying is carried out when the clusters are formed - 5 g/5 l.
- The third treatment is carried out when the berries ripen - 6 g/5 l of water.
Attention! The drug Horus for grapes should be used only in calm and dry weather. Each leaf must be processed on all sides.
Restrictions and security
Hazard class for humans – class 3. When working, use PPE and comply with generally known personal safety standards. At the first signs of acute poisoning, you should stop working and seek medical help. Treatment is symptomatic; there are no specific antidotes.
The manufacturer establishes a ban on the use of pesticides in the sanitary zone of fishery reservoirs. The use of the drug by aviation is prohibited. Hazard class for bees – class 3.
The turnaround time for manual work is 7 days, for mechanized work - 3 days.
The waiting period for harvesting is 28 days for pome fruits, 14 days for stone fruits and 7 days for grapes.
Precautionary measures
Like any other chemical, Horus fungicide requires compliance with safety instructions when using it:
- Spraying must be carried out in protective clothing, using goggles, a mask and gloves.
- If the product gets into your mouth, you should immediately take activated charcoal.
- When in contact with the drug, eating and smoking are not allowed.
- After treatment, you must wash your hands and face with soap, wash your clothes and dispose of the containers used for the solution.
- Fungicide waste is removed to places inaccessible to people and animals.
Safety rules when working with Horus Fungicide
Cyprodinil has low mobility, so it is considered relatively safe for humans. However, before preparing the Horus fungicide solution, you need to put on personal protective equipment: overalls, boots, rubber gloves, goggles and a respirator. For mixing you need to allocate a separate container.
When spraying, a simplified PPE kit can be used, with a petal respirator. Other precautions are the most common: do not eat, drink or smoke during treatment. Pregnant women, children, nursing women, allergy sufferers, and so on should not approach the treated area closer than 15 meters. If during the manipulations your health worsens, you should stop them.
In case of poisoning, it is recommended to take a glass of water with activated carbon (calculate the norm by weight). After 5 minutes, induce vomiting and call an ambulance.
Bee flight limit for the drug: 12 hours. The protection zone of the apiary is one and a half meters. In addition, you should not carry out treatment near bodies of water.
Analogues of the drug Horus
Horus fungicide has clear and simple instructions for use, in which you can find out the dosage for a number of crops - peach, apple, strawberry, etc. It is noted that the one-component preparation can be combined with other pesticides to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Like any remedy, Horus has several analogues, which differ in the active substance and spectrum of action. Among them are:
- Champion. This Fungicide, the main active substance of which is copper, is used for the treatment and prevention of fungal pathologies. But, unlike Horus, it can also be used for nightshade crops and hops.
- Angio. The fungicide contains two active substances at once, so it can be used to treat not only fungal infections, but also viral and bacterial diseases. At the same time, it is actively used to combat various types of agricultural pests.
Why are berry bushes treated in spring?
It is not enough to simply plant any berry bush in order to regularly receive abundant harvests. After planting, it’s time to take no less, and sometimes even more important, measures to care for the plant. One of these procedures is the treatment of fruit bushes from diseases and pests.
Did you know? The largest currant harvests in the world are obtained in Russia, followed by Poland and Germany in terms of volume of berries grown. In Russia itself, most of the harvest of this crop is grown in Siberia.
From pests
Despite the fact that many modern varieties of fruit and berry crops are resistant to pests, insects and arachnids pose a threat to the normal growth and development of most plants. The danger of pests, in addition to eating and destroying the plant and its parts, lies in the transmission of viruses by insects.
Many pests, before fruiting or shortly after it, move from the bush to the soil next to it. In the root area they hibernate, thus spending the winter. They awaken in the spring, after the soil has warmed up.
In order to minimize the risk of pests appearing on garden plantings and destroy the larvae already present in the garden, treatment is carried out in the fall. And to consolidate the results of autumn procedures and destroy the remaining larvae, spraying with insecticides and acaricides is repeated in early spring.
From diseases
Diseases of garden shrubs are fungal, viral and bacterial. Bacterial diseases, such as root and stem cancer, do not pose a great danger; there is no point in using chemicals to treat them. It is enough to apply fertilizing on time, the bacteria will die on their own.
Pathogens react especially to superphosphate.
Diseases caused by viruses are also not treated, but for a different reason - there are no effective methods for treating such diseases. The only effective way to combat viruses is to quickly remove the affected plant and destroy all its parts outside the garden.
The most common diseases of gooseberries and currants are fungal diseases - they can be treated quite well, especially if they are diagnosed early. Fungal diseases include anthracnose, powdery mildew, white spot, rust, septoria, etc.
Did you know? In unripe currants, the content of ascorbic acid is 4 times higher than in ripe ones. In overripe fruits, the concentration of vitamin C is even lower.
Spring treatment against possible diseases is carried out in order to prevent the development of the disease and destroy fungal spores remaining from the previous season. Treatment is most often carried out in early spring, before active sap flow begins, that is, before the buds open.
Release form, composition
The fungicidal agent "Horus" is produced by the Swiss company Syngenta, which occupies a leading position in the development of protective agents for cultivated plants against common diseases.
The drug is available in the form of granules resembling grains, intended for preparing an aqueous solution. The fungicide is sold packaged in bags of 1; 2; 3 or 15 grams; kilogram packages are available for large farms.
The drug contains the fungicide cyprodinil at a concentration of 750 g per kilogram. The active substance is an organic compound 4-cyclopropyl-6-methyl-N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine, belonging to the class of aminopyrimidines. Its antimycotic effect lies in the ability to penetrate into the cell of a phytopathogen and stop the process of amino acid synthesis. The component is aimed at destroying several classes of fungus (Ascomycetes, Deuteromycetes, certain species of Basidiomycetes); the drug is absolutely safe for plants and animals.
The drug is suitable for treating ripening fruits shortly before harvesting, since after 7-10 days the remaining cyprodinil decomposes into harmless elements.
You can buy the agricultural product Horus in specialized stores and garden centers. The price for a two-gram package in Moscow is 35 rubles.
There is an analogue of Horus called “Guardian”, produced by the Ukrainian company Ukravit. It is also based on cyprodinil at a concentration of 500 g per kilogram. It is practically never found on sale in Russia.
Dilution of the drug and recommended consumption rates
Horus fungicide is classified as a water-dispersible preparation for systemic action. 2-3 hours after treating the plant, it dries and forms an invisible protective film on the surface of the area, while simultaneously penetrating into the tissue structure. After this time, the precipitation is no longer dangerous. There is no need to re-treat the plant with medicine after rain.
All procedures with this product are carried out in early spring or summer at a temperature not lower than -3 and not higher than +25 degrees.
The working solution is prepared immediately before use. The diluted drug should not stagnate, as it will lose some of its beneficial properties. The sprayer is filled 1/4 full with clean water, and then Horus granules are added, depending on the instructions and the type of plant that needs to be treated, and water is added to the maximum volume in the tank.
The required amount of the drug for the prevention and treatment of infections in various crops is shown in the table. The average consumption rate of the substance when treating woody and shrub plants is 1 liter per 1 square meter. m area. Upon completion of the process, the unused or remaining solution is disposed of as it is no longer suitable for storage.
Unopened packages with fungicide are stored in a dark, dry place out of reach of children at a temperature of -10 to +15 degrees. Open containers retain their properties at the specified temperatures for no more than 1-2 weeks.
Grape processing
The protective agent “Horus” (fungicide) is used against oidium, gray rot and mildew. The instructions for grapes include the consumption rate of the drug, which is 6 g per 5 liters of water, the rate of use of the working solution, the value of which corresponds to 2 liters per hundred square meters.
During the growing season, the young vine and leaves are processed in three stages at different times of the season. The first spraying with the preparation “Horus” (fungicide) for grapes is carried out at the moment of bud formation and before flowering begins, the second treatment occurs during the formation of clusters of berries, and the third is carried out when the fruits ripen and color.
Toxic properties
The drug "Horus" belongs to the third class of toxicity. This means that the product has low toxicity for humans, subject to strict rules of use. The advantage of the drug is that it is low toxic to bees and does not accumulate in the soil. It has a negative effect on aquatic organisms, so it is prohibited to use it near lakes and reservoirs. The product has low toxicity for warm-blooded animals, but it is better not to treat crops if there are domestic animals nearby.
For strawberries and wild strawberries, treatment is carried out after harvesting.
Processing of fruit trees
When peach, plum, apricot, sour cherry seedlings are affected by clusterosporiasis or coccomycosis, the first treatment with Horus is carried out during the growing season, and subsequent spraying is carried out after 10 days. When treating 1 hectare of plantings, 3.5 g of the drug per 10 liters of water is required.
Treat peach, cherry, apricot and other stone fruit trees with monilial burn with Horus-fungicide. With the appearance of the first signs of infection during the growing season, the first treatment with the drug is carried out, and subsequent spraying is carried out after 14 days. When treating 1 hectare of plantings, 2 to 3.5 g of the drug per 10 liters of water is required.
If fruit rot appears on stone fruit plants, the first fungicide treatment is carried out during the growing season, and the second spraying is carried out two weeks before harvesting the fruits. When treating 1 hectare of plantings, 3.5 g of the drug per 10 liters of water is required.
When scab, Alternaria blight, moniliosis or powdery mildew appear on pome fruit trees (pear and apple trees) during the growing season, the first spraying of the tree crowns is carried out in the green cone phase or the end of flowering. Subsequent processing is carried out after 10 days. When treating 1 hectare of plantings, 2 g of the drug per 10 liters of water is required.
The amount of working solution consumed per 100 m2 is 10 liters. Workers entering areas treated with fungicides to carry out manual work related to crop care is allowed only after 7 days. To perform mechanized activities, it is enough to wait 3 days.
Treatment of stone fruit and pome-bearing crops in large areas is carried out using tractor sprayers. You must first calibrate the spraying equipment before use, taking into account the speed of movement of the spraying device, the supply of solution, and the uniform distribution of the working solution. The air stream is directed to the crops using throttle valves.
Trees are treated from both sides, covering the entire crown. The volume of working solution is used depending on the size of the tree and ranges from 400 to 9000 liters per hectare. Tips with a hollow spray cone and appropriate filters can be used. Air pressure ranges from 2 to 5 bar.
How does the drug work?
Since the active substance is more effective at lower temperatures, the use of the drug is more effective in the spring. In summer, when the air temperature rises above 25° C, the Horus fungicide begins to act more actively, but within half an hour its effect quickly disappears. The time for protecting a culture from a pathogen is 7-10 days.
Distinctive characteristics of the fungicide:
- cyprodinil quickly penetrates plant tissue through the leaf surface;
- the substance moves systematically throughout the plant and is not washed off by rain 1-2 hours after spraying;
- is most active at air temperatures from +5 to + 22° C;
- exhibits maximum medicinal properties in the first couple of days after infection of the culture.
Due to the action of the substance, the synthesis of amino acids in pathogenic microorganisms slows down, which disrupts their development and the growth of the mycelium itself. However, it should be noted that cyprodinil affects the disease only on young leaves of the plant. It is this fact that the gardener should pay attention to if he wants to achieve maximum effect of the pesticide and a quick recovery of the crop.
The drug is used for fruit trees