- Updated: June 9, 2019
Not many gardeners, especially beginners, follow the rules of crop rotation. And it often happens that fertilizers are applied on time, the greenhouse is built according to all the rules, and the beds are warm. And we manage to collect a very small harvest from tomatoes. To avoid such difficulties and disappointments during the harvest season, it is necessary to follow certain recommendations for choosing predecessors for tomatoes.
Each type of crop has a need for a certain nutrient more than others. For example, carrots strongly draw nitrogen from the soil, and if you plant it in the same place next year, it will be small and not juicy, since the soil will no longer be saturated with this element to the required extent. By observing crop rotation, tomatoes will need to be fed much less, and the risk of getting sick is reduced to almost zero, provided that the basic care rules are followed.
Tomatoes: botanical description
Tomato is a herbaceous plant of the Solanaceae family. In our climate, it is cultivated as an annual crop. The homeland of tomatoes is South America.
In botany, the fruits of the plant are considered berries, but in everyday life they occupy a leading position among vegetables.
After what crops can tomatoes be planted?
Annual tomato bushes reach 60-90 cm. The tips of the shoots are strewn with buds. Fruit ripening is consistent. After fruiting, the above-ground and underground parts of the plant die off.
Perennial tomatoes have climbing shoots. In the process of vegetative development, the culture needs support. Fruiting continues for a long time, until frost. The species is characterized by high productivity. The height of the bush can reach 3 m if it is provided with good support.
Perennial tomatoes
Tomatoes are a heat-loving vegetable crop. It needs to be grown in well-lit areas or in greenhouses. Grows and develops well at temperatures of +25 °C and above.
When planting, bushes must be given plenty of space so that as they grow, the plants do not interfere with each other.
What and with what can be planted in one bed
I offer you a short table of vegetable compatibility. More detailed information is provided later in the article.
| Vegetables | Good neighborhood | Bad neighborhood |
| Asparagus | Tomatoes | No |
| Beans | Corn, celery, garden savory, cucumbers, radishes, strawberries | Onion and garlic |
| Beet | Cabbage, broccoli, lettuce, onion, garlic | Beans |
| White cabbage, broccoli, Brussels sprouts | Beets, chard, potatoes, celery, dill, lettuce, onions, spinach | beans |
| Carrot | Legumes, tomatoes | No |
| Celery | Beans, tomatoes, cabbage | No |
| Corn | Cucumbers, watermelons, pumpkin, peas, beans, pumpkin | Tomatoes |
| cucumbers | Beans, corn, peas, cabbage | No |
| Eggplant | Beans, pepper | No |
| Melon | Corn, pumpkin, radish, zucchini | No |
| Onion | Beets, carrots, chard, lettuce, peppers | Legumes |
| Peas | Beans, cucumbers, turnips, carrots, corn, radishes. | Onion garlic |
| Potato | Beans, corn, peas | Tomatoes |
| Zucchini | Corn, melons, pumpkins | No |
| Tomatoes | Carrots, celery, cucumbers, onions, peppers | Corn, kohlrabi, potatoes |
In addition to the neighborhood of one vegetable crop with another, it is good to consider other possible neighborhoods - vegetables and flowers, vegetables and herbs. Such combinations in garden beds are not only beautiful, but also useful.
Flowers next to vegetables.
Some flowers act as pest traps, luring insects to them. Nasturtiums, for example, are very popular with aphids.
These pests will prefer to feast on nasturtium and will not pay attention to nearby vegetables.
Vegetables and herbs.
Planting herbs nearby will give your vegetables a more refined taste. They also repel harmful insects. Rosemary repels beetles that attack beans. Thyme repels cabbage pests. Onions and garlic repel aphids. Oregano, like marigolds, is a good all-purpose barrier against most insect pests.
When deciding which vegetables to plant nearby in the garden, you need to be guided not only by scientific data, but also by common sense. Lettuce, radishes and other fast-growing plants can be planted between melons or pumpkins. Lettuce and radishes will ripen before the pumpkin grows. Shade-loving green leafy vegetables such as spinach and chard are grown in the shade of corn.
Everyone has heard about compacted planting, about growing 3 crops per season in one bed. Let's figure out what you can plant and with what. Some crops do not like unpleasant neighbors, but if you remove them before planting tomatoes, you can use this method. For example, if you want to dig up dill before the tomato fruit begins to set, you can sow the herb crop between the planned rows of tomatoes. To begin with, try compacting familiar plants: tomatoes, onions, cucumbers.
Please note right away that they do not like tomatoes if the following crops grow nearby:
- broccoli or cauliflower;
- peppers, eggplants (they have the same pests);
- fennel;
- dill (if you do not plan to remove it for early greens);
- corn and other tall crops on the south side, where they will shade the bed.
What to plant near tomatoes? If you are good at controlling pests such as bollworm, you can plant corn on the north side of your tomato bed. You can set up a tomato plantation next to potatoes if you are sure that you can protect the plantings from late blight and the Colorado potato beetle.
You can sow basil in a tomato bed. It helps the main crop protect itself from pests. Try a tomato that grew next to this herb. Both the size and taste of the fruit will be significantly better than those of greenhouse vegetables.
Tomatoes also get along well with the following plants:
- beans;
- celery;
- strawberries;
- cabbage;
- radishes;
- sorrel;
- parsley;
- carrots.
Plant tomato bushes near bird cherry trees and the tomatoes will be protected from cutworms. If the site is dominated by thickets of nettles, vegetables will grow well in such a neighborhood. You can plant seedlings among spicy or flower crops: calendula, mint, sage. Peppers can also be grown among these herbs; they will benefit from such an environment.
Tomatoes after legumes
Is it possible to plant cucumbers after tomatoes?
Plants such as beans, beans and peas are sometimes given very little space on the site. On the one hand, this is justified: why occupy useful space with crops if their fruits can be bought for pennies in a store? On the other hand, after growing legumes, the soil is enriched with important microelements necessary for the full development of tomatoes, for example, nitrogen. After planting them, the soil should rest for some time.
On a note! After harvesting beans, peas and beans, you should not throw away the green mass of plants. It needs to be finely chopped and buried in the ground. In this way you can enrich the earth with useful substances. Tops are a good fertilizer.
After all the preparatory work, you can grow tomatoes.
Tomatoes after legumes
Legume tops are a good organic fertilizer. As a result of growing beans, beans, and peas on the plot, it will be possible not only to obtain tasty fruits that can be eaten fresh, preserved for the winter and dried, but also to enrich the soil in which tomatoes will grow well.
Attention! Solanaceous and legume crops are susceptible to fusarium. If this disease is noticed during the cultivation of legumes, tomatoes cannot be planted; they will also be susceptible to fusarium. It is better to plant crops with high resistance to the disease.
Choose the right predecessors
After which the tomato grows best:
| Cabbage Is a good precursor for tomatoes. Moreover, all varieties are suitable - from ordinary white cabbage to colored or Beijing. It is important to clean the bed well after cabbage . Pathogens and larvae of various pests can overwinter in the plant remains of this crop. | |
| Beans and legumes Excellent as pre-cultures for tomatoes. They saturate the soil with nitrogen, so there is no need to add this microelement to the soil after planting. After harvesting, the stems and leaves are crushed and scattered on the ground . Then the bed is dug up so that the plant residues saturate it with nitrogen during foundation. | |
| Pumpkin This includes pumpkins, zucchini, squash, etc.. Another good predecessor for tomatoes. After harvesting, the stems and roots are removed . There is no need to leave them, they decompose poorly | |
| cucumbers After this crop, you can safely plant tomatoes. It does not deplete the soil and feeds from a shallower layer than tomatoes. It is important to remove all remnants of cucumber vines . They are not a fertilizer, and diseases can overwinter in the plant mass | |
| Roots This includes beets, carrots, turnips, rutabaga and much more.. The crops do not deplete the soil and are fed from great depths, which is important. After harvesting the root crops, the stems can be left and the soil can be dug up . They are a good fertilizer | |
| Onion and garlic These crops are good predecessors for all vegetables. They disinfect the soil and make it healthier. After harvesting, the above-ground part is not left on the garden bed . It is better to dispose of it, as it is not suitable for fertilizer | |
| Green manure This includes a number of plants: mustard, broad beans, vegetable peas, alfalfa, annual lupine, meadow clover. They are all mowed down, after which the soil is dug up . You can plant even after harvesting another crop - a month and a half is enough to fertilize the soil well |
Tomatoes and potatoes
What can you plant after tomatoes?
The natural similarity of the two crops suggests that they prefer fertile soils rich in nitrogen. After growing potatoes, the soil experiences a nitrogen deficiency, therefore, if there is a need to grow tomatoes in a potato field, you need to intensively apply nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
Attention! It is simply unrealistic to provide the soil with enough nitrogen in one season. And an overdose will affect the quality of tomatoes.
Potatoes and tomatoes are affected by the same parasites and bacteria. It is not possible to harvest the entire potato crop - a couple of potatoes will still remain in the ground, no matter how hard you try, because harvesting in small areas occurs “with a shovel”, and in large areas using machinery.
Tomatoes and potatoes
The fruits remaining in the soil are affected by bacteria, which will happily add tomatoes to their diet next season. Therefore, you should not count on a good harvest of tomatoes when planting on a plot after growing potatoes.
To minimize labor costs in controlling parasites, you need to be vigilant.
Pests of tomatoes and potatoes:
- Colorado beetle. The overseas guest expands its distribution area every year. With enviable activity, it infects potatoes and tomato tops en masse. Treatment against the pest gives a positive result, but requires a constant change of preparations, since the Colorado potato beetle adapts perfectly to any chemicals. When treated repeatedly with the same product, pests develop immunity: they live and thrive as if nothing had happened.
- Wireworm. Another pest that causes a lot of trouble. As a result of its vital activity, gnawed stems and damaged fruits can be observed.
- Medvedka. The pest loves moist soil. He will not miss the opportunity to enjoy either potatoes or tomatoes. Loves green plant stems.
- Late blight is a fungal disease that affects both crops. The disease develops on leaves and stems. If you do not fight, the disease will spread to the fruits: potatoes and tomatoes will turn black and will be unfit for consumption.
Conclusion: planting tomatoes in a bed where potatoes were grown is not recommended!
When should you not sow tomatoes?
You should not plant tomatoes in place of other members of the nightshade family. These include: peppers, potatoes, eggplant and physalis. You should be careful with plants that are susceptible to the same diseases as tomatoes.
The soil in which potatoes grew contains virtually no nitrogen. This will have a detrimental effect on the growth of tomatoes. You will have to frequently fertilize the soil, which is not only expensive, but can also lead to a poor harvest, since it is very difficult to distribute the feed evenly. Excess fertilizer, as well as deficiency, is harmful to plants.
See also
Description of the best varieties of Lyubov Myazina's signature tomatoes, cultivation
Read
In addition, bacteria and parasites from potatoes can spread to tomatoes. Small potato fruits and plant particles often remain in the ground after harvest. Parasites also overwinter in the soil along with the vegetable. Next season, it is better to choose crops that are resistant to pests and diseases of nightshade vegetables.
After planting potatoes, the most likely occurrence of parasites such as:
- Colorado beetle;
- mole cricket;
- wireworm
Among the diseases, late blight is possible.
Having sowed tomatoes after potatoes, the farmer will spend a lot of time, effort and money on fertilizing the soil and fighting parasites, but there will still not be a good harvest of tomatoes.
Is it possible to plant tomatoes after strawberries? Strawberries are a perennial plant; they are replanted when the beds become old or the harvest deteriorates, which indicates depletion of the soil. Is it possible to grow good tomatoes in this place?
No, tomatoes should not be planted after strawberries. The reason is the same as in the previous case: strawberries consume a lot of nitrogen. The soil should rest for a season or more before planting any vegetables.
If it is not possible to take a break, you need to thoroughly prepare the soil:
- dig up;
- clear of weeds;
- dry the soil;
- saturate with organic fertilizers;
- add nitrogen and mineral complexes with potassium.
After planting, tomatoes need regular feeding. The same preparation must be carried out if strawberries were previously grown on the site.
Tomatoes after onions
Due to its specific taste, the succulent plant is rarely affected by pests. Without proper care, green onions become wild and thrive among weeds. The exotic taste of the plant and the phytoncides it secretes into the soil repel pests, so gardeners tend to plant tomatoes after onions. How does the earth feel? Is it possible to plant tomatoes in the garden if their predecessor was an aromatic vegetable - onions?
Green onions are perennial plants, but in our climatic conditions they are grown as an annual crop. After harvesting the bulbs, the soil is prepared for planting the following crops.
Soil after growing onions
Soil characteristics after growing onions:
- a slightly alkaline soil reaction is observed, which has a beneficial effect on nightshade crops;
- onions are indifferent to potassium and nitrogen fertilizers, so the soil after onions is rich in potassium and nitrogen;
- onions release phytoncides - special substances that, when released into the soil, help repel pests and destroy bacteria;
- bacteria do not linger in the soil, since they are indifferent to onion roots.
Conclusion: the considered factors allow us to conclude that it is possible to grow tomatoes after onions and then carry out the correct rotation of fruit crops.
After what crops can tomatoes not be planted?
Tomatoes are not planted after plants of the same family. They are susceptible to the same diseases and pests, and have similar root secretions that are toxic to followers. Over the course of a season, a certain supply of pathogens accumulates on the site and the permissible threshold of pests increases.
These are all nightshade crops:
- potato;
- eggplant;
- vegetable pepper;
- tobacco;
- physalis.
You cannot plant tomatoes in close proximity to potatoes. This leads to the rapid spread of late blight and damage to tomatoes by characteristic potato pests - wireworms and nematodes.
You should not place tomatoes after strawberries, even though they are not biologically related. The place for garden strawberries is changed every 3-4 years. By that time, the soil is greatly depleted, it contains many small roots and root secretions.
In addition, the crop has a common disease with tomatoes - late blight. For the same reason, it is advisable not to place them in adjacent beds. The area after the strawberries is sown with legumes or green manure crops; tomatoes are planted only the next year.
Tomatoes after strawberries
Strawberry and strawberry plantations grow over time and require a new planting site. The problem arises of choosing the right plants to plant in this place. Is it possible to plant tomatoes after strawberries? Will the predecessors of tomatoes affect their development and fruiting?
Strawberries are not the best predecessor to tomatoes when planting. If you do decide to plant nightshades, you need to be prepared for the fact that the harvest will be meager.
Strawberry bushes absorb all useful elements from the soil, so the soil after growing it is depleted of minerals and nitrogen. And the last element is extremely important for the normal development of nightshade crops.
Soil after growing strawberries
There is a way out of this situation, but you need to prepare for labor-intensive work:
- The soil after strawberry plantation must be thoroughly processed. First of all, you need to dig it up well.
- During digging, it is recommended to remove all weeds, especially wheatgrass. The root system of the weed is often intertwined with the roots of the strawberry, which makes caring for the plantation difficult.
- After all the manipulations, the soil is dug up again and organic fertilizers, such as manure, are added. You can add peat fertilizer, but in a minimal amount. Wood ash will promote the development of tops and fruits.
- After strawberries, the soil should rest a little. After which a complex fertilizer containing nitrogen and potassium should be added to it.
When growing tomatoes, they need to be fed with organic and mineral fertilizers so that other vegetable crops can be grown in the future.
Then plant the bell pepper. What can you plant after bell pepper?
Owners of small plots, for whom literally every meter of land is valuable, often wonder how to maintain crop rotation with minimal losses for harvest volumes, and to do this in such a way that none of the necessary crops is left uncovered. Compliance with the rules of crop rotation is really very important - if you ignore these rules, the soil will gradually become depleted, as well as become clogged with pathogens of all kinds of diseases and voracious pests. What can you plant after bell pepper?
What definitely shouldn’t be planted?
bell pepper is absolutely incompatible with all its relatives from the nightshade family, that is, after it, under no circumstances should you plant eggplants or tomatoes, as well as potatoes or any types of hot peppers! this does not mean that they will not grow at all, but over time they will greatly deplete the soil. Moreover, it is not recommended to plant nightshade crops not only before or after each other, but also just next to each other! The proximity of hot peppers to sweet ones is considered especially unacceptable - cross-pollination can easily lead to the fact that all the fruits, without exception, will eventually acquire a bitter aftertaste. so the different members of the nightshade family should ideally be placed at a fairly decent distance from each other! You should not plant after bell peppers and representatives of the Pumpkin family: zucchini with squash, as well as pumpkin or cucumbers - just as in the case of the above-mentioned nightshade crops, they will create completely unbearable conditions in the beds, not only gradually depleting the soil, but also accumulating toxic compounds released by themselves. At the same time, despite the fact that all kinds of pumpkin crops grow extremely poorly after bell peppers, they are excellent predecessors for it!
neutral crops
they have absolutely no effect (neither good nor bad) on the quality of growth and development of crops planted after them. and, fortunately, in this case, summer residents have a very rich choice; fortunately, there are many neutral crops! So, after sweet peppers, you can safely plant various varieties of beets (both fodder and sugar or traditional table), any types of cabbage (and despite the timing of its growing season), carrots, radishes, all kinds of herbs, greens, spinach, everything without exception types of lettuce, celery and radishes with turnips, garlic and onions, as well as beans, peas or beans. All these crops grow wonderfully after peppers! It is especially good to plant various root crops after the predecessor in the form of bell pepper - the root system of peppers lies at a relatively shallow depth, and the main root of root crops is able to reach the deep layers of the soil, thereby allowing the surface soil layers to “rest”!
The best choice
A wide variety of grains, as well as all kinds of green manure or clover for cutting, respond best to the predecessor in the form of sweet pepper. But vegetables are really missing from the “ideal” list of followers, but in this case it is quite possible to plant any neutral crops after pepper. The almost complete absence of 100% ideal followers that can easily be planted after pepper is largely due to the fact that during its growth and development, sweet pepper not only absorbs almost all nutrients from the soil, but also leaves behind a fairly decent amount of all kinds of toxins, contaminating the soil to one degree or another. That is why, in the case of bell pepper, we can only talk about the relative admissibility of growing certain garden crops after it.
Zucchini and tomatoes
There is such a thing: a squash boom, when plants build up good green mass and spread throughout the garden. Thanks to modern breeding, more compact varieties have been developed. What kind of tomato harvest can you get if you plant them after zucchini grew in the garden?
After zucchini, all types of tomatoes grow and develop well, even cherry tomatoes, since their predecessors enrich the soil with all useful substances. In addition, the root system of nightshades is located much deeper than zucchini, so the tomatoes will receive all their nutrients from deep in the soil, which the zucchini roots could not reach.
The soil after zucchini is fertile
However, there are certain limitations that are important to note. You cannot plant tomatoes after zucchini if the latter had viral diseases - they can easily spread to tomatoes.
The best predecessors for tomatoes. The need for crop rotation. Why alternate crops on the site
Vegetable crops have different abilities to absorb nutrients from the soil.
Continuous cultivation of any crop in one place leads to its depletion. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the nature of the location of the root system of various crops: for example, carrots and beets, thanks to their powerful root system, are able to absorb phosphorus and potassium from the lower layers of the soil, and onions, cucumbers and green - from the top. Growing the same crop in one place for several years leads to the spread of diseases and pests, so representatives of the same family must return to their original planting site after 3–4 years. It is for this purpose that crop rotation must be organized in the garden.
Rotation of crops should also contribute to effective weed control. Plants with a well-developed, fast-growing leaf surface (cabbage, potatoes, zucchini), placed with large row spacing, have the ability to suppress weeds, and conversely, crops that develop slowly and form a small vegetative mass are not able to resist weeds (carrots, dill, parsley). Consequently, the alternation of these crops makes it possible to create favorable conditions for their growth and development.
To create a rational rotation of crops, you need to know after which predecessor they should be placed. Predecessors are the crops that occupied the site in the previous year.
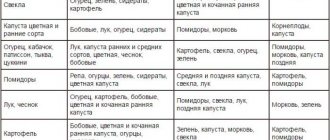
Many generations of gardeners and scientists in different countries have determined which predecessors are the best for a particular crop, and after which they should not be grown (Table 1).
What if you do nothing?
What will happen if you do not observe crop rotation and next season leave the plantings as they were this year? This approach is justified only in greenhouses, because not a single summer resident has the opportunity to change the location of the greenhouse every year. If you grow tomatoes in a greenhouse in the same place, you need to take care of the condition of the soil in advance in order to get a good harvest.
Advantage of rotation:
- as a result, microelements are exchanged;
- harmful microflora dies;
- the soil is enriched with useful substances necessary for the growth of tomatoes;
- Over the winter, pests, without receiving food, are doomed to death.
Why practice crop rotation?
As the season changes, you can alternate between different types and families of plants. When growing tomatoes in greenhouses every year, you should adhere to the following methods:
- Organic and mineral fertilizers must be added to the soil in increased quantities;
- as necessary, treat the soil against pests and to prevent late blight;
- carry out partial soil replacement;
- The following composition will help reduce the acidity of the fertile layer: it is recommended to add 50-80 g of lime per 1 m2 of usable area, because tomatoes need a neutral environment;
- it is necessary to automate watering.
Conclusion: when growing tomatoes in greenhouses, you should not rack your brains about which crops to plant, you need to apply the measures described and follow the conditions. This is the only way to get a good harvest every year.
Basic Rules
The annual change of place of sowing of agricultural crops is called crop rotation. The method is based on the different nutrient needs of plants. In addition, different crops are susceptible to different diseases and pests. Using crop rotation techniques allows you to reduce the amount of fertilizing and protect the crop from parasites.
What are the rules for planting vegetables:
- Root vegetables and fruit plants should be swapped. So, if beets grew in the beds last year, you can plant tomatoes this season.
- Plants that consume large amounts of nutrients (strawberries) are planted after crops that require a minimum amount of minerals. For example, corn or onions not only give the soil a rest, but can also improve it.
- Plants from the same family cannot be planted for 2 years in a row. Tomatoes and eggplants require the same substances to grow. Cucumbers and pumpkins are susceptible to the same diseases; it is possible that a new crop can be infected through the soil.
- There are vegetables that can enrich the soil (onions, garlic). Planting tomatoes in these places will increase productivity.
Changing the planting location is not necessary for all plants. Thus, potatoes and corn can grow and produce a good harvest in the same place for several seasons in a row. It is worth keeping a diary of planting vegetables in open ground. This will make it easier to navigate the territory, and if there is a decrease in yield, find the reason.
Crop rotation does not eliminate the need to fertilize plants, but will help reduce its frequency to a minimum.
It is not always possible to change the landing site. When planting tomatoes in the same place as a year ago, you should resort to such manipulations as:
- replacement of the top layer of soil;
- use of nitrogen fertilizers;
- correct proximity of plants;
- planting mustard crops (garlic) in the fall, after harvesting tomatoes.
But even using all the options for improving the soil, the planting site must be changed every 3 years.
Crop rotation planning rules for tomatoes
If rotation is not observed, the soil is depleted, so plants cannot be planted in the same place; seasonal or intraseasonal rotation must be observed. Complex fertilizers must be regularly applied to the soil. Changing the seed fund gives a good result. This method is especially recommended for potatoes.
However, in order to resolve all issues and get high yields, it is necessary to observe a seasonal rotation of crops:
- When planting vegetable crops in beds, you need to divide them by type and family.
- First you need to draw a detailed planting plan, you can make a table.
- Seasonal crop rotation must be carried out in accordance with the rules of agricultural technology.
After fulfilling the above conditions, you need to find out what is the best way to plant tomatoes.
Crop rotation table
Ideal predecessors of tomatoes when planting in open ground:
- Carrots and beets;
- White cabbage and cauliflower;
- Pumpkin;
- Beans, peas, beans;
- Roots;
- Onions, garlic.
If there is not enough garden space, flower beds are reduced and vegetables are grown in place of ornamental crops.