Choose the desired variety
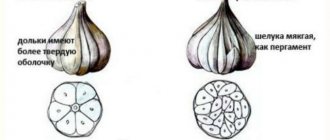
Types of winter garlic differ among themselves in the size of the head, the number of cloves, keeping quality, taste and even aroma. You can choose a variety with good keeping quality, the desired bulb size or number of cloves.
| Name | Characteristic | Photo |
| Alcor mid-season | With a sharp taste and high yield. Qualities: frost resistance, dense head, up to 5 cloves, no more than 35 g. Stores well. | |
| Belarusian early ripening | Large (50−80 g), sharp, with good winter hardiness and keeping quality. Resistant to diseases. Up to 8 teeth. | |
| Gribovsky anniversary mid-season | Frost-resistant variety with a flat-round bulb up to 40 g. Qualities: drought and disease resistance. There are up to 10 cloves in an onion. | |
| Lyubasha mid-season | A high-yielding variety with excellent winter hardiness and resistance to drought and fusarium. Large onion (up to 120 g). Well kept. | |
| Mid-season sail | The variety is considered medium-sized (30−50 g), high-yielding. Pests and diseases: stem nematode, downy mildew, bacterial rot. | |
| Moscow region mid-season | Excellent frost and disease resistance, medium head (60 g), stores well. | |
| Spas mid-season | A large variety (100 g), combining such qualities as winter hardiness, excellent shelf life, and disease resistance. |
Diseases and pests of garlic
The most common types of pests:
- stem nematode - a white worm 1.5 mm, feeds on plant sap, found on clayey, heavy soils, affected plants develop poorly, leaves fall off, the bulb begins to disintegrate;
- onion and garlic mites - heat-loving pests attack the roots and turn the bulbs into dust;
- onion fly - reproduces during periods of high humidity, lays eggs at the base of plants, and the emerging larvae feed on the juicy pulp of garlic, then go into the soil.
Garlic diseases: rust, black mold, etc.
How to plant garlic for the winter: recommendations
To plant garlic correctly in winter, you need to understand what kind of crop it is and what its requirements are. After planting the clove, the plant begins to grow its root system. For successful wintering, the roots must grow 10 cm, and green feathers must not appear from the soil.
The winter planting plan is as follows:
- We take into account the landing dates.
- Choosing a location.
- Soil preparation.
- Preparation of planting material.
- Planting cloves or bulbs.
- Care and feeding.
Now let's look at all the points in more detail.
How to do it correctly: 7 subtleties (important: read to the end)
Planting winter garlic itself is not difficult at all; even the most inexperienced beginner can cope with this work. However, there are a number of subtleties, the observance of which will allow you to obtain the maximum yield of this spicy vegetable.
Landing place
Although garlic is not whimsical, it will not develop normally anywhere. For it you need to choose an open and well-lit place. In shade, plants slow down in development and form small heads. Therefore, there should be no large trees, bushes or buildings nearby that cast a thick shadow.
Areas that are damp, swampy, flooded or flooded, or where underground groundwater comes too close to the soil surface should be avoided. Being constantly in a state of high humidity, garlic rots, becoming affected by fungal infections.
Note: If necessary, if it was not possible to find a suitable place, you should build a high bed, raising it by 20-25 cm.
Preparing the bed
For garlic, light and loose, humus-rich and fertile sandy loam or loam with neutral acidity and good air and water permeability are best suited. If the soil in the selected area does not meet these characteristics, then you will have to slightly modify its composition with your own hands.
Heavy, dense and damp clay soils require special preparation - they must be lightened by adding sand and low-lying peat (a bucket per m2) for digging. Poor, friable sandstones that do not retain moisture need to be structured with clay components and humus (a bucket per m2).
For acidified soils, alkalization should be carried out by adding dolomite flour, fluff lime, chalk, etc. at 200-500 g/m2, depending on the pH readings. You can measure the acidity of the soil using a household pH meter or simple litmus paper.
The bed allocated for winter garlic should be dug up in advance, two or three weeks before the day of planting, to a depth of about 25-30 cm. The soil should settle a little and become compacted, otherwise the cloves, finding themselves in too loose soil, will go deep and sprout later.
At the same time, during digging you need to apply fertilizer (per 1 m2):
- garden compost or humus - 7-8 kg;
- simple/double superphosphate - 35-40 g/15-20 g;
- potassium nitrate/potassium salt - 20-25 g or wood ash - 150-200 g.
Note: Nitrogen-containing fertilizers (fresh manure, chicken manure, urea, etc.) cannot be applied in the fall for winter planting, since nitrogen will inevitably provoke a sharp growth of green mass.
The best predecessors
When choosing a place for a bed for winter garlic, you need to take into account exactly what plant was planted on it in the previous season. It is necessary to understand after what onion crops cannot be planted, and which predecessors are considered the most suitable.
The root system of garlic is quite superficial and is located shallow. Therefore, it is better to plant it after those plants whose roots go into deeper soil layers and choose food from there. At the same time, the spicy vegetable will receive the unspent beneficial substances lying above.
It is preferable to place winter garlic in the garden after:
- tomato;
- eggplant;
- all types of cabbage;
- berries (strawberries, wild strawberries, strawberries);
- greens (lettuce, parsley, basil, etc.);
- legumes (peas, beans, etc.);
- cereals;
- pumpkin (cucumbers, zucchini, etc.).
The question of whether it is possible to plant garlic where other onion crops grew before should not even be considered. Since these closest relatives have the same pests and diseases, they cannot be planted after each other. Otherwise, the harvest will be unimportant.
You should not set up a garlic bed where root vegetables grow (radishes, turnips, beets, carrots, etc.), or after potatoes. It is permissible to return garlic to its original area only after 3-4 seasons.
Preparation of planting material
First of all, you should purchase and then properly prepare planting material purchased or collected with your own hands, because the future well-being of the plants depends on it. You can choose the right variety in the article about the best varieties of winter garlic.
Next you should proceed as follows:
- Disassemble the heads into individual slices.
- Select the healthiest, most viable and strong cloves that are not damaged. All sick and deformed ones should be mercilessly thrown away.
- Disinfect selected specimens in a solution of any fungicide (Maxim, Topaz, Fitosporin, etc.), following the instructions. You can soak the cloves for half an hour in a solution of ordinary table salt (50-60 g/1 l), potassium permanganate (weak light pink) or copper sulfate (1%).
- Dry the garlic in the shade and in a draft (literally for 1-2 hours).
Direct landing
Step-by-step instructions for planting winter garlic.
- Using a hoe or small spatula, dig parallel grooves along the long side of the bed, 15-20 cm apart. Or use a stick to make small individual holes according to the pattern: 10*12 cm - between large cloves and 6*8 cm - between small ones.
- Place a thin sand cushion (3-5 mm) at the bottom of the grooves or holes, which will reduce the risk of rotting and the development of fungal infections.
- Having turned the bottom down, place the cloves, without pressing, on the bottom of the planting grooves or holes, leaving 8-15 cm between them (depending on the size). At what depth (from 4 to 15 cm) to place winter garlic when planting depends on the structure of the soil. There is no need to bury the cloves deeply in heavy clay soils; it will be difficult for seedlings to break through the dense layer of soil. In light sandstones, on the contrary, bury it more deeply, because moisture in such soil is retained worse, quickly going into deeper layers.
- Fill with soil and level the surface of the bed with the back of a rake or your hands.
- Lay a layer of mulch from rotted sawdust, compost, peat, etc.
Note: There is usually no need to water newly planted winter garlic, since it has enough natural precipitation to take root properly.
Planting bulbs
Experienced vegetable growers recommend updating winter garlic planting material every 3-4 years, because it gradually becomes smaller and degenerates. This spicy vegetable can be grown not only from clove cloves, but also from seed bulbs that ripen at the ends of the arrows.
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Prepare seed material by collecting garlic while digging. You can purchase it in stores, nurseries, garden centers, etc.
- Select the largest and smoothest bulbs.
- Plant at the same time as the main garlic planting.
- Place the seeds in grooves made in increments of 8-10 cm. The distance between individual bulbs is about 2-2.5 cm. Planting depth is no more than 2-3 cm.
- In mid-summer next year, dig up all the grown one-toothed onions.
- Late in the fall, again plant the single-toothed heads obtained from the bulbs using standard technology. In another year, normal multi-toothed garlic will grow from them.
Care
There is no need to take any special care of garlic planted before winter, because usually after a month it goes safely under the snow and does not require any care. The only thing is that it is advisable to mulch the beds, insulating the plantings with straw, sawdust, mown grass (hay), leaf litter, etc. This can be done not immediately, but later, with the onset of severe cold weather.
To better retain the snow cover, you can lay branches or spruce branches on top. Such a shelter is relevant in cold and northern regions (for example, in Krasnoyarsk, Omsk, Novosibirsk, etc.), but in the central zone (Kirov, Nizhny Novgorod, Saratov regions, etc.) it is not necessary.
Note: In the spring, with the arrival of warmth, the cover from the garden bed must be immediately removed, otherwise the garlic may dry out.
Also read and bookmark when and how to remove garlic from the garden, as well as how to properly store it at home.
When exactly to plant garlic in the fall: planting on time is the key to a good harvest
Experienced people believe that winter garlic should be planted some time before the onset of frost. If your planting material consists of bulbs, then they are planted 2 weeks, and if with cloves, then 3-4 weeks before frost. On average, you need to meet it until the last days of October. In Siberia, garlic is planted in September.
Sometimes inexperienced gardeners ask whether it is possible to plant garlic in November. We answer: it is possible, provided there is a long, warm, dry autumn. The deadline is considered to be the first days of November.
You should not focus on exact calendar dates; it is better to take into account weather forecasts and temperature drops below +10 degrees.
For those who like to work according to the lunar calendar: in 2022, the days from 11 to 15 and from 24 to 26 October will be favorable.
Garlic arrows are eaten
When not to plant garlic
Winter garlic planted early will definitely sprout. This sharply reduces winter hardiness and jeopardizes the entire future harvest. If, on the contrary, you are late with planting, then the plant will not have time to develop the root system. In this case, in the spring you will find completely empty beds.
Harvesting and storage
Winter garlic is harvested in the second half of July and early August. It is important not to be late in harvesting, as the bulbs may break into slices and the crop can be re-cultivated. It is advisable to remove spring species from the second half of August until the end of September. It is important to harvest on time to avoid shortening the crop's shelf life.
There are signs by which you can understand that the crop is ripening:
- new leaves are no longer formed, and the old ones have turned yellow;
- opening of the seed pod;
- The heads of garlic are fully formed and externally correspond to the specific species.
After the crop is dug up, it must be left to air dry at a temperature of no more than 25 degrees for one and a half weeks. At the same time, ripe bulbs still receive some nutrients from the stems.
If the weather does not allow leaving the plant outside, then you can use the room as a dryer; the temperature should not exceed 30-35 degrees. After drying, it is necessary to cut off the roots and feathers. Many gardeners do not prune spring varieties, but braid them and hang them.
The storage in which the garlic will be stored should not be too wet or too dry. The room should be treated with a bleach solution approximately 2 months before planting the crop. The winter variety is stored at a temperature of 2 to 4 degrees, and the spring variety at 16-20 degrees. The heads with three layers of scales are stored the longest.
Experienced vegetable growers advise storing garlic in the following ways:
- interweaving of plants in the form of braids and wreaths. To make the structure durable, twine is woven into it. A hook is made at the end and hung;
- tying the heads into bundles by the leaves;
- placing garlic in nets or stockings;
- in glass vessels or baskets.
Stored vegetables must be periodically checked for rot, which will extend their shelf life.
In conclusion, we can say that growing garlic in open ground is very interesting and useful. It doesn’t matter whether you are an experienced gardener or a beginner, if you follow the above recommendations, you will get a good and, most importantly, healthy harvest that will be stored for a long time and delight you with its taste.
0
0
Copy link
Choosing a place and predecessors
According to the rules of crop rotation, it is better not to plant such a crop after onions and garlic, since they have already taken the necessary substances and compounds from the soil. You should not choose a place where carrots, beets, turnips, or late pumpkins grew. After these crops, the soil will not have time to recover in time for autumn planting.
The best predecessors are zucchini, eggplant, cucumbers, and peppers. They have a short growing season, and they take up slightly different compounds and different concentrations of minerals from the soil.
Preparing the soil for planting
A month before planting garlic crops, cover a sunny open area or bed with humus or compost at the rate of 5-6 kg per square meter, add 20-30 g of superphosphate and potassium salt. You can sprinkle the ground with sifted ash at a rate of 100 g per 1 m². After these procedures, all the soil is dug up onto the bayonet of a shovel and leveled with a rake.
Non-acidic soil must contain sand.
RECOMMENDATION!
We did not indicate that the bed needs to be cleared of the remains of its predecessors, because by burying the green mass in the ground, you will enrich the soil with useful microelements.
Area where suitable predecessors grew
Garlic loves to change where it grows. It can be returned to its original bed only after 5 years. This crop does not produce a good harvest after onions, tomatoes, peppers and eggplants. The reason is that plants can have the same diseases.
If squash, zucchini or pumpkins have been in the garden before, the garlic promises to grow especially large. You can plant it after cabbage or legumes. Teeth feel good next to strawberry palestine.
Processing garlic before planting before winter
Planting garlic in the fall before winter is often done using cloves. But if you are rejuvenating a variety or want to get rid of diseases of this crop, then it is better to use bulbs (seeds collected in the summer from the opened arrows).
Processing of cloves and bulbs comes down to discarding the material: the planting material must be clean, medium or large in size, and must have a solid shell. It is preferable to disinfect in a solution (1 tablespoon of salt per 1 liter of water) for 3 minutes, and then rinse the teeth for a minute in a weak solution of copper sulfate (0.5 level tsp diluted with 5 liters of water).
Slight elevation
For planting, it is best to choose an open and sunny place. There is no point in focusing on the lowlands: this crop does not like stagnant moisture.
For the same reason, you need to avoid shadows from fences, buildings and tall trees. Winter garlic reacts negatively to dampness and prefers well-ventilated places.
It is better to make the bed higher; this will protect the cloves from excessive soil moisture. Melt water will drain and go deep, and the plants will receive exactly as much moisture as they need.
- Author: Inna Kiseleva
Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
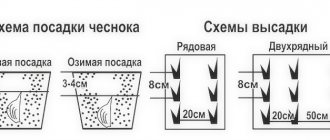
Planting depth of garlic before winter
The teeth are planted in pre-prepared furrows. They are made no deeper than 20 cm. It is better to sprinkle the bottom of the grooves with an even, small layer of sand. In steppe and arid zones, many gardeners water the furrows with a small amount of water before planting. In the middle zone it is not necessary to do this, especially in rainy autumn.
Garlic is planted to a depth of no more than 20 cm.
At what distance should I plant garlic?
Let’s combine the data on planting depth and distance into a convenient table:
| Material | Distance between furrows, cm | Distance between bulbs in a row, cm | Planting depth, cm |
| Bulbs | 10−15 | 5−8 | 2 |
| Teeth | 20−25 | 15−20 | 3−4 |
IMPORTANT!
If you are late with planting, increase the planting depth by 2-3 cm to prevent freezing.
Planting material is inserted into the grooves by hand, bottom down and gently pressed into the ground with your fingers. Sprinkle soil or mulch on top in an even layer. If the winter has little snow, then the beds are covered with plant debris, roofing felt or polyethylene. In conditions of abundant snowfall, no covering material is required.
NOTE!
The bulbs will produce a single-toothed large onion next year. Having dug up the clove at the end of summer and dried it, it is planted again in the fall. Next year, an updated variety with a large head will grow.
A useful video will tell you how to plant winter garlic in the fall.
Landing Features
Planting garlic depends on several determining factors. Let's consider the features of planting this vegetable crop:
- Garlic varieties have two large groups - spring and winter. They differ in properties and planting methods. Spring garlic is moderately hot, contains up to 25 cloves in the head, and the stem is soft. It is famous for its keeping quality and is planted in spring. The winter variety has large teeth and a dense stem. Gives large harvests, which come at the time of home harvesting. Planted in autumn. It is not stored for a long time (read our article for more information on whether it is possible to plant winter garlic in the spring).
- Planting garlic depends on the climatic conditions of the area. Early snowfalls will help to insulate the crops, the need for shelter will disappear; in the northern regions, covering is mandatory.
- Planting agricultural technology includes: compliance with crop rotation, planting dates, the presence of a sunny area, loamy soil, not using fresh manure, pre-sowing work, mandatory mulching when planting before winter.
- To obtain a large amount of high-quality planting material, bulbous seeds of bolting varieties are used.
Simple rules for caring for winter garlic
It’s not enough to know how to plant winter garlic correctly, you also need to know how to care for it!
Care begins in April. As soon as the snow melts from the garden bed, you need to remove 2 cm of mulch. This will make it easier for the feathers to germinate. Why can't you remove all the mulch? Mulching material protects young shoots and helps retain heat. The first watering is done in May, when all that remains of the snow is memories, and the soil will obviously need moisture. Water the seedlings regularly. Garlic is fed three times: after the first greenery appears, urea or a weak solution of bird droppings is added in liquid form. The second time, the culture needs a nitrophoska solution (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water). The last feeding in June consists of ash (a glass per bucket of water) or superphosphate (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water).
IMPORTANT!
Before applying fertilizer, the bed must be moistened to avoid chemical burns!
In summer, watering is gradually reduced. If the arrows have reached 10 cm, they are broken out, leaving a few pieces to determine the timing of ripening or seed propagation.
NOTE!
Fried arrows with sour cream are considered a delicacy.
Garlic crops are regularly loosened throughout the growing season.
The planting distance between the bulbs is 15-20 cm.
Rules for harvesting winter garlic: harvest on time
This crop is harvested in mid-summer. A good advisor here, oddly enough, is raspberries. The time when raspberries are actively collected in baskets for jam is considered the best time for harvesting garlic. But in order not to make a mistake, it is recommended to follow the left arrows. As soon as the arrow opens and the opened bulbs appear, and the lower leaves of the plant turn yellow, it’s time to harvest.
Garlic is harvested strictly in dry weather!
The plant is carefully dug up with a pitchfork and easily removed from the soil, being careful not to damage the roots. It is better to shake off the entire crop from the soil and place it in a spacious, covered place to dry.