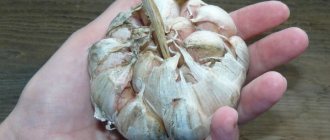
Planting spring garlic in open ground in the spring should be done according to all the rules, then you can get a good harvest. Despite the fact that winter garlic produces large yields and has large heads, many gardeners prefer to grow spring garlic. The reason is that it lasts longer and can provide the family with beneficial vitamins until the next harvest.
Gardeners who constantly grow this valuable vegetable on their plot know some secrets. They will help beginners grow garlic with minimal losses and achieve high yields.
Spring and winter garlic: differences
In order not to confuse winter and spring garlic, young gardeners need to become familiar with the main differences.
- The head of spring garlic consists of many small cloves. Moreover, the teeth located closer to the rod are much smaller. Winter garlic has a strong arrow to which large cloves are attached.
- Spring garlic is planted in the ground in early spring, and winter garlic in late autumn.
- The spring variety is propagated only by cloves, while winter garlic is grown by both cloves and bulbs.
- Winter garlic produces high yields.
- Spring garlic can be stored for 1-2 years at home. The shelf life of winter garlic is about 3-4 months. Most often it is used when preparing food (canning, pickling) for the winter.
- The winter variety has a strong stem. Spring garlic does not develop a arrow. The only exception is the Gulliver variety.
- Spring garlic has a more pleasant taste, so it is perfect for preparing various dishes.
Common Mistakes
The most common mistakes when sowing are:
- Incorrect sowing time. As soon as the snow has melted, you should plant garlic before the soil warms up. If you are late with sowing, the harvest will decrease by 2 times.
- Wrong choice of location. Spring garlic is poorly affected by temperature changes, so you should plant it in a well-lit place with sunshine and make sure there are no drafts. It is also wrong to plant garlic in lowlands, as water will stagnate there.
- Do not buy planting material in the store, since it is not known how long ago it was collected and how it was stored. In this case, you cannot be sure that you will get a good harvest of tasty garlic.
- Do not use small cloves for planting.
From the video we will learn the secrets and subtleties of planting spring garlic in the spring - what the planting material should be, when and how to plant it correctly:
Planting spring garlic is quite simple and caring for it does not present any difficulties. You just need to follow the planting rules and take into account all the tricks, and then you will get a good harvest of delicious spring garlic. This means that there will be vitamins on your table all year round.
0
0
Copy link
What varieties can be planted in spring
Interesting! This culture has a large number of varieties - about 60. They all have some differences: in taste, color, varieties of arrows, readiness time.
From the total quantity, everyone can choose a variety according to their tastes and needs.
Planting vegetables begins in spring. It is best to breed early and mid-ripening varieties at this time. In a short growing season, the plant should grow and form a head. Spring garlic can go through all these processes in 90-120 days.
The most popular varieties include:
- Gulliver. Garlic is a mid-late variety, does not bolt, yields are high, and stores well. The heads are grayish in color, the cloves are from 4 to 8. One clove weighs 2-5 g. The stem grows up to 50-70 cm. It is very rarely exposed to diseases. A ripe head of garlic can weigh about 40 g.
Varieties for the middle zone:
- Elenovsky . Refers to the average ripening period, without arrows. Garlic is white in color, the scales are dense, the head shape is round. The vegetable is resistant to various diseases.
- Victorio. Spring garlic does not bolt. Refers to mid-season varieties. Mature bulbs reach a weight of 30-40 g. The size of the cloves is small. Perfectly preserved for a long time. The taste is more pleasant and can be consumed even fresh.
- Sochi 56 . An excellent variety of garlic, and also high-yielding. The heads are covered with pinkish scales, some specimens acquire a brown tint. The weight of mature heads reaches 50-60 g. They contain from 20 to 30 cloves. In terms of taste, garlic is not very spicy.
- Abrek. The variety is not shootable. The heads of this variety of garlic are small - up to 30 g. The scales are quite dense, its upper layer has a creamy tint. Garlic is spicy to taste. Harvesting is always a joy.
- Kledor. The plant does not shoot, it is mid-season. Garlic is large, sometimes reaching up to 6-7 cm in diameter. The heads have white scales, the inner layer of which has pinkish septa. The teeth have a dense consistency and taste sharp.
In regions with cold climates, experienced vegetable growers also grow garlic. Some types of spring garlic are suitable for growing in such weather conditions.
- Novgorod. Belongs to mid-late varieties. The growing season is 120–130 days.
- Aleysky. A mid-season variety of garlic ripens 110–122 days after planting in the ground.
- Novosibirsk. The ripening period of a mid-season vegetable variety is from 75 to 85 days.
Above were examples of some types of spring garlic that are planted in early spring. It is advisable to grow several varieties of this vegetable in order to choose the right option for yourself.
Advice! You can try to grow new types of this crop, which are more adapted to the conditions and type of soil, and also produce high yields at minimal cost.
Harvest
Spring garlic is harvested 1 month after winter harvest. Usually this is the end of August - beginning of September. Signs of harvest readiness are yellowing of the lower leaves and lodging of the upper ones. 2-3 weeks before harvesting, stop watering the garlic. To harvest garlic, choose a dry day.
The heads of garlic are removed from the ground using a fork or a small spatula, being careful not to damage the garlic itself. The remaining soil is shaken off and the plants and tops are removed to dry in a ventilated room for 5-7 days.
The harvested crop is sorted into 2 parts:
- planting material,
- onions for food.
To do this, larger onions are left for planting, and medium-sized onions are left for eating. The main condition for selecting planting material is the absence of mechanical damage and signs of disease on the bulbs. The cloves themselves should be strong and dense.
Landing dates
Garlic is planted in the spring, and the sowing time depends on the climatic characteristics of the region. Garlic cloves can be planted in soil warmed to +3-5 degrees. This crop tolerates light frosts well, which may unexpectedly occur during this period.
- In the central zone of the country, for example, the Moscow region, sowing of this vegetable begins in mid-April - the first ten days of May.
- In the southern regions of Russia, garlic can be planted in open ground in the last ten days of March – the first ten days of April.
- In Siberia and the Urals, garlic is sown in May.
According to the lunar calendar
will help determine favorable days for planting . In it you will find out the most favorable days when you can start planting cloves in the ground. The main thing is that this crop cannot be planted during the full moon and new moon.
When can you plant summer garlic?
There are two groups of garlic - summer and winter, also called spring and winter. The division of groups is very simple - according to planting dates.
The differences between them are as follows:
- winter forms arrows with aerial bulbs, through which it reproduces; summer shooter does not form and reproduces by cloves;
- the summer bulb has a large number of cloves (up to 30 pieces), the winter one has about 10 cloves;
- the main advantage of summer is its long shelf life; it can be stored until the next harvest;
- Planting dates for summer garlic: late April - early May, winter garlic: mid-autumn.
To get a good harvest, it is necessary to plant summer garlic in open ground after the soil reaches a temperature above +5-6 °C.
This is explained by the fact that the formation and active growth of its roots and leaves occur only at low temperatures .
If the timing is delayed even by 1-2 weeks, the leaves and roots stop their active development, which will negatively affect the harvest.
Planting dates for spring - late April - early May, winter - mid-autumn
Site selection and soil preparation
The place for planting garlic is chosen in the fall. It should be well lit by sunlight. When preparing the site and soil for sowing garlic, it is necessary to take into account some nuances.
- To grow this vegetable, it is best to choose a cultivated area with fertile soil. This vegetable grows best on loamy and chernozem soil. Also, garlic takes root on light loamy or sandy loam soils with a neutral reaction.
- The site should be in an open and well-lit place, protected from cold winds.
Important! Areas where snow and moisture lie for a long time negatively affect the cultivation of garlic and their subsequent harvest.
- It is advisable that the site be located at a slight slope to drain excess moisture.
- To obtain a high yield, it is necessary to fertilize the soil well before planting. To do this, the following composition is prepared per 1 m2: humus, compost - 1 bucket each, superphosphate, nitrophoska - 1 tbsp. spoon, dolomite flour - 1 cup.
- The last stage of preparation will be disinfecting the beds with copper sulfate or potassium permanganate solution. After 2 days, the site will be completely ready for planting vegetables.
Advice! Experienced gardeners advise covering the beds with transparent film before starting work.
Popular varieties of spring garlic
There are more than 70 different varieties . From this variety it is not difficult to choose a variety to suit your taste, taking into account climatic conditions, site characteristics and soil.
Here are the most popular varieties:
- Abrek is mid-season, large, perfectly stored, not too sharp, light scales, white cloves.
- Aleisky - mid-season, the bulb is round, flat, stored until spring.
- Gulliver is medium late, productive, the bulb is round, slightly flat, the scales are light. Little susceptible to diseases and pests.
- Elenovsky - mid-season, productive, rounded heads. The color of the scales is whitish on the outside, and pinkish on the inside of the cloves themselves. The variety is resistant to diseases.
- Sochi-56 is mid-season and produces a stable and high-quality harvest. The shape of the head is slightly flat and round. The color of the scales can be white or purple, and on the teeth themselves – pink with a purple tint. The variety is resistant to diseases.
The best and worst predecessors
It is known that thanks to successful crop rotation, you can get a high-quality harvest.
Important! It is good to plant garlic in an area where the predecessors were crops such as oats, mustard, peas, cucumbers, zucchini, and strawberries.
Garlic does not do well in the area where root crops grew last season: potatoes, beets, carrots, etc.
You should not plant garlic after nightshade crops, for example, tomatoes, eggplants, bell peppers.
Recommended garlic precursors
When choosing a place for planting, you should pay attention to the root system of the predecessor . Garlic bulbs have short roots, so during growth they actively use minerals and fertilizers from the top layer of soil. Accordingly, the preferred predecessors will be crops with a long root system.
For reference. It is good to plant garlic after grains, pumpkins, legumes, and herbs.
Avoid areas where carrots, potatoes, beets, onions, peppers, and tomatoes used to grow.
How to prepare spring garlic for planting in spring
Preparation of spring garlic begins in the fall, immediately after harvesting. Planting material is not afraid of cold weather. It is packaged in clean bags and placed on the site in holes up to 50 cm deep. The top is covered with earth, dry leaves, and the top is covered with plastic film. In this form, garlic can withstand even severe frosts.
Interesting! Garlic is most often grown vegetatively. The winter variety can also be propagated using bulbs. Spring garlic reproduces well by cloves. These are a kind of buds that have a growth point and the beginnings of greenery.
Cloves for growing spring garlic can be purchased for planting in special stores, on the market or online. Before you buy garlic to plant in the spring, it's a good idea to familiarize yourself with some of the varieties that will work best in your area. They will ensure a minimum of losses and a good harvest.
It is necessary to plant healthy and strong cloves of spring garlic in open ground. They should be medium and large in size, weighing more than 3 - 6 grams.
Before planting, the cloves are separated from the head, while retaining the scales.
Garlic, which has only 2-3 cloves, is not suitable for propagation, since it has already outlived its usefulness. Therefore, it should not be used as planting material.
Watch the video! Spring garlic. Preparing for landing
Garlic grown independently as planting material must be sorted before planting. For propagation and further storage, choose strong and large cloves.
Smaller specimens can be planted in an area with potatoes, carrots and other vegetables to repel harmful insects. In the future, it can be used for preserving and preparing dishes in the summer.
In order for garlic cloves to germinate 100%, develop well and produce high yields, they must be treated according to all the rules before planting.
- Dry the heads well and separate them into cloves without damaging the scales.
- For planting, select the largest and most intact cloves.
- A few days before planting the seeds, they can be wrapped in a wet cloth and placed in the refrigerator. This way, the garlic cloves will grow roots faster.
Before planting the planting material on the site, it is processed.
3 ways to process planting material:
- Garlic cloves are placed in a bowl with warm water and kept there for 10-12 hours.
- Table salt (3 tablespoons) is diluted in warm water (5 liters). Garlic cloves are kept in this solution for 2-3 minutes.
- For disinfection, the quite effective drug Fitosporin, which has long become popular among gardeners, is also suitable.
- There are some other ways to treat seeds, for example, in an ash solution. This procedure should last about 30 minutes.
- Also, before planting garlic, it is important to disinfect the material. To do this, the slices can be kept for 1-2 minutes in a solution of copper sulfate in the ratio: 1 tbsp. spoon for 10 liters of water.
The next step in the preparation of garlic cloves will be to process them in a growth stimulant such as Epin, Zircon or others.
Garlic sowing time
The spring variety must be planted at the right time in order to obtain a high-quality and tasty product. The most suitable period for this is the beginning of spring.
It is necessary to start planting garlic when the air temperature reaches about 6 degrees. If you plant when it is already too warm outside, the harvest will be very small.
Also, the planting period depends on the location. The colder the region, the later they begin to plant the vegetable. However, it is important to pay attention to the temperature of not only the air, but also the soil. You can start planting when it is +3 degrees. This is already enough for the growth and development of the vegetable, since it is unpretentious in this regard. But if the earth temperature is from 8 degrees, then the garlic will grow even better and develop more actively.
At soil temperatures around 16, the harvest will be small and of poor quality. Also, if you plant garlic so late, its shelf life will decrease. Therefore, it is important not to be late, but also not to plant the vegetable ahead of time.
Rules for planting spring garlic in open ground
- Garlic cloves are planted in rows. A distance of 20 to 25 cm is maintained between them.
- Depending on the size of the lobules, the distance between them is determined (approximately 6-10 cm).
- In spring, the tines are buried 5-6 cm into the ground. Moreover, they should only be in a vertical position. When planting in autumn, planting material is placed in the ground to a depth of at least 10 cm. In this case, the garlic will be protected from winter cold.
- In the autumn, planting beds must be covered with mulch. It can be dry leaves or grass. After the snow melts, the covering is removed.
Watch the video! Planting spring garlic.
Landing
There are several types of planting material, which determine the method of planting to obtain the future harvest.
Teeth
To plant in spring in this way, follow these simple rules :
- the distance between the beds must be at least 25 cm;
- place the slices in the grooves;
- keep the distance between the cloves, it should be about 10 cm;
- planting depth - 6 cm;
- make sure that the teeth are positioned strictly vertically, without tilting;
- After planting, immediately mulch the beds with straw or sawdust from wood.
For a rich, healthy harvest, water regularly and apply the necessary fertilizers on time.
Bulbs (garlic seeds)
This method of spring planting guarantees a good and healthy harvest, but this method usually takes about 2 years. Although, the first small heads can be obtained already in the first year.
Algorithm of actions:
- the bulbs are wrapped in newspaper and stored in a dark place at a temperature of about +20 degrees;
- a month and a half before planting, transfer them to a cold place (refrigerator);
- before planting, the bulblets are dried, ventilated and kept for 2 hours in a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- plant garlic to a depth of about 4 cm, maintaining a free space between seeds of 15 cm;
- After planting, fill each hole with soil and level the soil.
- Immediately mulch the beds with straw or dry grass.
Care
When the first shoots appear, the plant needs to be given proper care: loosen the soil and weed it from weeds.
Particular attention should be paid to watering.
Important! During the development period, garlic requires abundant watering, but does not like stagnant moisture in the soil.
Watering
During the formation of heads, watering should be reduced so that excess water does not cause the vegetable to become infected with certain diseases. Also, you need to stop watering during rainy weather. 14 days before harvesting garlic, stop watering.
Top dressing
As soon as the first shoots appear and until the fruits ripen, the plant requires regular feeding with nutrients. Only in this case can you get a high-quality harvest in large quantities. This crop has a delicate root system, so it is difficult for it to freely absorb beneficial elements found in the soil.
After the first shoots, nitrogen fertilizers can be added to the soil. When the above-ground part of the plant grows to 6-10 cm, you can use the following fertilizer:
- 15 g of ammonium nitrate are diluted in 10 liters of water;
- Urea solution (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water);
- Bird droppings are diluted in water in a ratio of 1:12;
- Mullein with water (1:10).
Important! Fresh manure can only harm vegetable plantings. At the beginning of summer, it is recommended to fertilize garlic with infusions of fresh herbs.
Over the entire summer period, it is necessary to feed the vegetable with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers 2-4 times.
It is also good to use an infusion of wood ash for feeding. To do this, take 150 g of the substance and dilute it in 10 liters of water.
Important! When fertilizing garlic, special attention should be paid to the norms, since an excess of fertilizer affects the quality of the cloves.
20 days before harvesting, it is recommended to water the beds with the plant with a solution of potassium monophosphate.
Watch the video! How to feed garlic.
On our website there is a separate article on how to feed garlic.
How to grow summer garlic: secrets and nuances of care
Caring for summer garlic is quite simple, but it has a number of differences from growing the winter variety. Therefore, it is important to take into account all the characteristics of summer or spring garlic in order to ultimately obtain a rich harvest of a useful vegetable crop.
- Watering. Unlike winter garlic, which can do well without watering, summer garlic needs regular soil moisture, which promotes active plant growth. A lack of moisture is indicated by yellowed tips of the leaves. During the period of active leaf growth, which occurs from spring until July, summer garlic needs abundant watering. Then, when the bulb begins to form, this is usually indicated by 6 formed leaves, the amount and frequency of watering is reduced, and by mid-August it is completely stopped. This is due to the fact that moisture retards the development of garlic bulbs.
- Loosening and mulching. Periodically, beds with summer garlic need to be weeded and loosened. To reduce the number of weeds, it is recommended to mulch the soil in the beds with a layer of straw. This will also reduce moisture evaporation.
- Feeding summer garlic. All fertilizing of this vegetable crop is usually combined with watering. The first application of fertilizer is carried out after the appearance of several leaves. At this stage, fertilizers containing nitrogen are suitable, for example, mullein infusion or ordinary humus. It is not recommended to use fresh manure, as it promotes the development of diseases. After about 2 weeks, you can feed the garlic with liquid mineral fertilizer. During the planting of the bulb, you can use an infusion of ash or a complex of mineral fertilizers.
- Diseases and pests of summer garlic. Most varieties of garlic of this variety have good immunity to various diseases and pest invasions. However, occasionally plants can still be affected by thrips, nematodes, mites, and onion flies, to combat which it is necessary to use special preparations. Among the diseases you can find white rot, fusarium, black mold, bottom rot. To protect summer garlic, it is important to correctly follow all agrotechnical measures and regularly add ammonium sulfate to the plants for preventive purposes.
- Harvesting and storage. Garlic harvesting should begin in the second half of August, when two-thirds of the leaves turn yellow and fall off. A couple of weeks before, it is important to slightly free the garlic heads from the soil to allow them to ripen and dry out faster. Garlic should be pulled out in dry weather. To do this, carefully pull the bulbs by the leaves and place them on the bed to dry. Garlic is dried in the open air for 5 days, after which it is transferred under a canopy. After complete drying, the roots of the garlic are cut off a little and the leaves are shortened, leaving only 10 cm. It is recommended to store summer garlic in wooden boxes, bags or wicker baskets at a temperature of 4-6 degrees or 16-17 degrees.
Garlic is an important part of any garden, and its summer variety is a huge storehouse of useful vitamins and elements. Therefore, many gardeners advise not to be afraid of the difficulties in growing spring garlic, but to boldly experiment. After all, planting and caring for this vegetable crop is not very difficult, the main thing is to do everything correctly.
Pest and disease control
Despite the fact that garlic has a repulsive odor, it is susceptible to attack by many harmful insects. Also, the heads can be infected with bacterial and fungal diseases.
This culture is able to independently fight many diseases. However, at the first suspicion of a disease, you should immediately help the plant.
Garlic can be attacked by harmful insects such as moths, root mites, thrips, hoverflies, onion flies, etc.
The most dangerous diseases for garlic are white rot, black mold, downy mildew, and fusarium.
Advice! To protect vegetables from insects and diseases, you need to carry out the necessary preventive measures in a timely manner and strictly follow all the rules of agricultural technology.
- It is important to choose high-quality planting material for sowing. Immediately after harvesting, you need to re-sort it and get rid of low-quality damaged cloves.
- With good feeding and regular loosening of the soil, garlic becomes more resistant to diseases.
- A densely growing plant must be thinned out.
- You should start monitoring the condition of the vegetable after germination.
- To prevent insect attacks, the area is treated with ammonium sulfate (20 grams of substance per 1 square meter).
- In mid-June, this fertilizing needs to be applied again. Sick and weak plants need to be dug up to inspect the roots to determine the causes of this condition.
Rotten roots, yellow feathers or spots on them may be a sign of a fungal disease.
Bulbs affected by brown wounds, darkening of scales and a putrid odor indicate diseases of bacterial origin.
In case of fungal infection, the vegetable is treated with the following preparations:
- Gamair-TM. Dilute 2 tablets of the product per 1 liter of water.
- Alirin-B. You need 1 tablet diluted in 1 liter of water.
- Biological products will help fight harmful insects:
- Lepidocide. Add 50 milliliters of product per 10 liters of water.
- Bitoxibacillin. 35 milliliters of poison are diluted in 5 liters of water.
It is important to prevent the attack of the stem nematode. Small worms suck the juice out of the garlic. Soon its tender roots dry out and the head of garlic falls apart. This pest is difficult to control, as a result of which it can completely destroy the crop. Many gardeners plant plants like calendula and chicory between rows of garlic to repel worms.
Preparation of planting material
Healthy, strong bulbs are selected for planting. Immediately before sowing, the onions are disassembled into individual cloves. Moreover, cloves located in two outer rows are suitable for planting. The inner cloves are small, they will not grow into good garlic, they are left for eating. The yield of garlic directly depends on the size of the teeth.
The prepared teeth are wrapped in a towel soaked in cold water and stored for several days in a cool place, for example, in the refrigerator. A few hours before planting, the planting material is taken out and left at room temperature. Disinfection is carried out for several minutes in a pink solution of potassium permanganate or in a 1% solution of copper sulfate. For disinfection, you can use an ash solution (400 g of ash is diluted in 2 liters of water, boiled for 30 minutes), soaked for 2 hours.
Landing site requirements
The vegetable is demanding on the soil and area for planting. Garlic prefers:
- loams, sandstones and chernozems with a neutral or slightly acidic pH level;
- open and illuminated area;
- a protected, wind-free place;
- high beds without stagnant water, which will minimize the risk of fungal infection.
Garlic is not planted on the site after:
- onions and beets;
- carrots and tomatoes;
- eggplants and radishes;
- potatoes and peppers.
It is advisable to cultivate the vegetable after:
- cucumbers;
- zucchini;
- green manure;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- garden strawberries;
- pumpkins.
When planting spring garlic in the Urals in the spring, the soil is prepared in the fall. They dig the soil deeply, loosen it, and remove weeds.
To balance the soil composition, peat is added to clay and sandy loam soil. Peat soil is diluted with sand (10 kg). The soil must be fertilized by adding per 1 m2 of area:
- humus (6 kg);
- nitrophoska (1 tbsp.);
- superphosphate (1 tbsp);
- dolomite flour (250 ml glass).
It is recommended to disinfect the planting site with a solution of potassium permanganate or copper sulfate.
Experienced gardeners cover the area with agrotextiles or film before starting work.
Caring for spring garlic
Spring garlic needs to be watered sometime before July, at which time the garlic is growing. As soon as the sixth leaf appears, watering should be stopped, since moisture has a bad effect on the formation of the head. The period when heads begin to form is mid-August.
Fertilizing spring garlic
Garlic should be fertilized at the first appearance of seedlings. Fertilize the soil with infusion of ash, mullein or infusion of bird droppings. The next feeding is carried out a couple of weeks after the first, watering the garlic with mineral fertilizers. The last time the garlic is fed is during the formation of the heads, this period falls on the 5-6th leaf of greenery. To do this, use an infusion of wood ash.
To speed up the ripening time of a garlic bulb, you need to tie the greens of each bulb in a knot. Then the garlic will give up all its juices to the bulbs, and the growth of the plant will stop.
It is also necessary to weed and loosen the plants in a timely manner. Loosening is carried out after each watering, the next day.
What soil to plant in
The planting site must be prepared in the fall. The best choice for planting is neutral soil. Garlic does not like acidic soil at all. Soil acidity can be reduced. For this you can use saltpeter, chalk, dolomite flour. Winter varieties love sandy and loamy soil. It would be a mistake to use manure to fertilize the soil. This plant does not like this fertilizer. Moreover, manure can contain various harmful microorganisms and larvae of possible pests.
Garlic should be a mandatory crop in the garden. This vegetable is widely used in cooking and medicine. It is effective against a huge number of diseases. Its benefits cannot be overestimated.
Soil preparation
It is recommended to plant spring garlic after herbs, grains, legumes and pumpkin crops, cabbage, zucchini, and cucumbers. After garlic, onions, potatoes and carrots, the spicy vegetable can only be planted after three years.
It is not recommended to plant the plant next to beans, peas and cabbage. Garlic inhibits these crops. But since it repels many pests, its proximity will be useful for strawberries, onions, tulips, roses, gladioli and various fruit-bearing shrubs.
A site for spring garlic is chosen that is protected from the north wind and well lit. The soil should have a neutral reaction and be fertile loamy or sandy loam.
It is recommended to prepare the bed in the fall by adding the following to each square meter of soil:
- compost or humus - ½ bucket;
- complex mineral fertilizer – 15 grams;
- wood ash - 3 cups.
In the spring, the area is leveled and garlic cloves are planted in the garden bed.
Winter and summer garlic: planting features
It will not be difficult for an experienced gardener to grow garlic. The harvested autumn harvest of this vegetable crop is processed and suitable planting material is selected by sorting. The process before sowing in the ground involves the following steps:
1. Calibration. Healthy, undamaged teeth, large in size, dense and regular in shape (with one apex), are selected.
2. Disinfection. Disinfection is carried out in an alkaline solution, which is prepared from 400 g of ash and 2 liters of water. This mixture is brought to a boil and simmered for half an hour. It should cool, after which the garlic cloves are dipped into it for 60 minutes.
3. Germination. Summer garlic can be germinated for faster growth. For this procedure, you will need a piece of wet cloth in which the garlic is wrapped and placed in plastic for 3-4 days. It must be kept in a dark room.
This crop is planted depending on the time of year. Garlic comes in winter and summer varieties. Let's learn about the features of each of them.
Read also: How to prepare the soil for planting roses in open ground in spring
Planting winter garlic
In late autumn, garlic is planted in rows, the distance between which should be approximately 25 cm. Depending on the seedlings, the gap between the beds must also be observed. It should be 8-15 cm. The planting depth of winter garlic is deeper than summer garlic, but it should not exceed 20 cm. Such indicators are considered optimal for naturally cultivated soils. Sandy soils are the best for winter garlic. The land must be prepared 7-14 days before planting. Preparatory work consists of digging up the soil, freeing it from weeds, applying natural fertilizers (about 5-6 kg) and mineral fertilizers (superphosphate - 30 g and potassium - 20 g per 1 sq.m). A few days before planting, the soil is fertilized with ammonium nitrate (10-15 g per 1 sq.m.). If the soil is dry, be sure to water it.
Please note that growing garlic in one place is unacceptable for more than 2 years in a row. Otherwise, the soil will be infected with stem nematodes. In addition, garlic is very picky about soil. It needs treated, crumbly soils that contain a large amount of organic matter. Garlic is also incredibly sensitive to overly acidic soils. The best predecessors for planting this vegetable crop are:
It is advisable that the place for growing garlic is level and sheltered from the wind. Low-lying soils are not suitable for planting it because melt water is retained in them - this can lead to rotting and death of plants. It is not recommended to plant garlic in the ground where onions have been growing for at least 2-3 years. This way you can protect your crop from pests and diseases characteristic of this crop. The soil after garlic is perfect for growing any vegetables, provided that it is fertilized with compost (40-50 kg per 10 sq.m.).
The land where winter garlic grows needs to be mulched - this action is aimed at combating frost. It is best to mulch with a layer of up to 2 cm using dry peat or a mixture containing sawdust and garden soil. With the onset of frost, the beds should be covered with polyethylene and not removed until the first snow.
How to plant summer garlic?
Summer garlic is planted mainly in late April, when the soil is sufficiently warm. If planting is done at a later date, the process of bulb formation may be disrupted. During this period, the crop needs to be kept at a low temperature to avoid spoilage. If the soil is dry and too warm, the garlic will not be able to take root properly. Growing leaves will be forced to use the nutrient reserves of the cloves. In the future, the fragile root will not cope with the rapid growth of foliage, as a result of which the plant will starve and the yield level will significantly decrease.
For summer garlic, soils that are not too clayey are considered most suitable. And although this type of garlic is a little more difficult to cultivate than winter garlic, its shelf life can reach 1.5 years - this is the main advantage of spring garlic. The growing season and yield of a given variety largely depend on how the planting material is stored. There are 2 storage methods:
1. warm (20-25 °C);
2. cold (0+3 °C).
In the first case, the ripening of garlic takes 30-35 days longer, but the advantage of this method is the development of powerful plants with fairly large bulbs. The cold method promotes faster plant growth and clove formation. It should be taken into account here that due to the rapid ripening of the bulbs, their cloves are quite small, and the yield is not too high.
How to care for garlic?
Garlic is a perennial plant. It is very resistant to frost, loves sunlight, fertile soil and moisture. This plant calmly tolerates drought, but in the future this affects the yield (it decreases). Favorable conditions for cultivating garlic are to adhere to the irrigation regime, which is stopped a month before harvesting. Fertile soils and a deep arable layer are the most optimal parameters for growing this crop. Garlic propagation occurs vegetatively, that is, by cloves. We also note that high-quality garlic seeds can only be obtained in the southern highlands, where a sufficient amount of ultraviolet radiation is concentrated.
Most gardeners grow local varieties of garlic, but selective varieties are no less popular. They are cared for according to the traditional scheme, which involves:
Garlic needs to be watered during the period of active growth, when the head is formed. And when the bulbs are ripe, you can stop watering.
Fertilizing
Fertilizers must be added to the soil where garlic grows. For this, in spring (1 time) and summer (2 times) urea (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water) and liquid manure are used. Fertilizing and watering of garlic is done strictly at the root.
Varieties
Garlic is divided into two types:
- Winter (winter). It is planted in the fall and harvested in the summer of next year. It easily tolerates even severe frosts, has high yields, but does not have a long shelf life.
- Spring (summer). Planting is carried out in the spring. Its heads are not as large as those of winter, but it can be stored until the next harvest.
Winter varieties are quite unpretentious, and almost any of them can be grown in open ground. However, most often it is recommended to plant the following varieties:
- Losevsky is a mid-season variety, included in the State Register as a crop of agricultural importance, characterized by high frost resistance, large heads (up to 75 g), containing 5-6 cloves, stored for up to 6 months;
- Gribovsky is an early ripening variety, prone to bolting, medium-sized heads with 7–11 teeth, highly resistant to diseases and weather conditions;
- Komsomolets is a mid-season bolting variety, the heads are dense, contain 6–12 cloves, covered with pinkish scales, resistant to cold;
- Doctor is a mid-season, non-shooting variety, the heads are dense, contain up to 16 cloves, can be stored for a long time, and are easily transported;
- Jubilee is a variety of medium ripening period, predisposed to the formation of shoots, characterized by high yield and resistance to disease, the heads are large, consisting of 10–12 cloves.
Among the spring varieties, the most common are:
- Gulliver is a mid-season variety with massive heads (90–120 g), slightly flat in shape, containing 3–5 large teeth, covered with gray scales, the flesh is white, very sharp, can be stored for more than 8 months;
- Victorio is a moderately spicy mid-season variety, included in the State Register as a crop grown in vegetable gardens, medium-sized bulbs (up to 40 g), containing 10–13 cloves, stored for up to 8 months;
- Elenovsky is a recently bred, but already very popular variety, the bulbs are small (25–40 g), consist of 7–10 teeth, are highly resistant to frost and disease, can be stored for up to 2 years, both spring and winter planting are possible ;
- Sichinsky is an early ripening (80–92 days) variety, the weight of the heads is 40–45 g, the teeth are white, dense, slightly sharp, the plants are resistant to cold and disease, the shelf life of the heads is 1.5 years.
Features of landing
Garlic rows should be no more than 15 cm high and 90 cm wide. Before sowing, a number of works must be carried out to equip the soil with mineral components.
Planting is done so that there is no more than 2 or 3 cm from the top of the stem to the beginning of the tooth growth. If you plant deeper, it will take more time for the garlic heads to ripen. The distance between garlic heads should be 8 cm, and between rows - 20 cm.
Planting garlic cloves involves preliminary disinfection of the material with vitriol solution or ash liquor. Each clove is planted separately, that is, one clove is placed in one hole. The place for germination should be bright with sufficient air flow. You can pour a little sand at the bottom of the holes and bury the slices into it. Planting plants does not require moistening the soil.