Characteristics of decorative pepper
Decorative peppers have come into fashion recently, but they are quite an ancient culture. It was possible to see pots of pepper on the windowsill many decades ago, but in recent years many varieties have appeared, specially bred for home cultivation. This vegetable belongs to the nightshade family, is found wild in Asia and America, and is grown everywhere in apartments. It is a perennial ornamental plant; its bushes, as a rule, do not exceed 30–40 cm in height.
In reality, the lifespan of a plant in an apartment is about five years, but many people grow it as an annual, without leaving it for the winter. If pepper leaves, which have an oblong, lanceolate or ovoid shape, do not differ much depending on the variety, then the appearance (shape and color) of the fruits can be very diverse. The size, as a rule, does not exceed a few centimeters. A bush planted at home performs a decorative function both during flowering and during fruiting. One plant is enough, since the crop is self-pollinating.
As a rule, this pepper blooms in early summer, and the fruits ripen from August to October. Home-grown varieties are pungent and contain the alkaloid capsaicin. It is the fruits that are used in small quantities in cooking; vegetative parts of the plant are poisonous.
Varieties of decorative peppers
There are dozens of varieties of decorative peppers, and most of them are edible. Of course, these are the ones that are planted mainly by indoor gardening enthusiasts. The most popular varieties are the following.
- A small miracle is a plant up to 30 cm high, lush, with protruding red fruits weighing up to 5 g. Medium-spicy, used fresh and in cooking.
- Jellyfish is a bush no higher than 25 cm, heavily leafy. The fruits are thin, elongated, up to 6 cm long, red, spicy. It is highly unpretentious.
- Ogonyok is perhaps the most famous variety with fairly large (up to 40 g) bright red, burning fruits. Universal use.
- Aladdin is a variety grown in open ground, where it grows as a half-meter bush, on the windowsill - a little lower. The fruits have a transitional color: during the ripening process they are yellow, purple, and red. The taste is very spicy.
- Phoenix is a variety that grows as a low but spreading bush. It bears fruit on the windowsill for a very long time; cone-shaped peppers up to 4 cm long are directed upwards. The color ranges from yellow to red, the taste is moderately spicy.
- Salute is one of the easiest varieties to grow, bushes no higher than 25 cm. Peppers weighing up to 6 g, orange, with a fiery taste.
- Filius Blue is a pepper that bears purple fruits, but their color during ripening can be orange or red. It can bear fruit almost all year round. The bush is no more than 25 cm high, but spreading, requiring free space. The variety is high-yielding, the purpose of the fruit is universal.
- Indian Summer is a rather old variety, shade-tolerant, grows as a low, rounded bush. The fruits are round and weigh about 5 g, the color is dark red, the taste is sharp. The purpose of the fruit is universal.
- Sirius is a Dutch variety, a bush up to 20 cm high, bearing a large number of small fruits that change color from blue to dark red. Considered a novelty, it can bear fruit in an apartment for up to seven years.
Multi-colored decorative peppers
Although hot peppers are associated mainly with the bright red color in the photo, there are many ornamental varieties with fruits of other colors. If you want to plant a plant with edible peppers in original colors at home, you should pay attention to the varieties listed below.
Jamaica
This variety can be grown on a windowsill in a regular flower pot. It has fruits of an original diamond-shaped yellow color. One of the edible hot peppers, the spiciness comes mainly from the white core, and the walls can be simply sweetish.
Queen of Spades
An evergreen plant with a compact bush. Tolerates shade well. The height of the bush is about 25 cm, the shape is round. Bears purple fruits. Peppers are tasty, hot and aromatic, ideal as a seasoning and also used for canning.
Growing from seeds
Seeds of various varieties of ornamental peppers are now quite available both in regular and online stores, and their germination persists for 3–4 years.
Timing of seed sowing and pre-planting treatment, germination
At home, you can sow pepper seeds in pots at any time of the year, but most amateurs prefer to do this in February: this makes it easier to grow full-fledged bushes and get the first harvest in the warm season with sufficient natural light. Some seeds are sold ready to sow, while in other cases they prefer to be lightly prepared. Fresh seeds will sprout normally without this, but they are often treated with growth stimulants, for example, Epin, according to the instructions for the drug. In addition, many gardeners, just in case, disinfect seeds according to the usual schemes (for example, 20–30 minutes in a dark solution of potassium permanganate).
Ornamental pepper seeds look like sweet pepper seeds, only a little smaller.
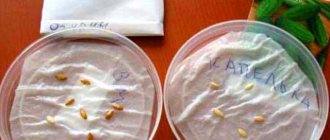
You can sow dry seeds immediately after pre-treatment, but often they germinate rather slowly, so first they are germinated according to the usual method: in a damp cloth at a temperature of 24–28 oC. As soon as tails appear from several seeds, they should be planted in the ground.
Preparation of containers and substrate, sowing of seeds and conditions for their germination
Ultimately, the pepper will grow in a half-bucket pot, but first the seeds can be sown in small cups of about 300 ml. For home growing, it is better to immediately buy ready-made soil in the store. It must be a loose composition, so humus is often specially added to ordinary universal soil or soil for peppers. In addition, add a little vermiculite or perlite to increase breathability and moisture capacity. The best way out is to sow the seeds in peat tablets.
The seeds are sown to a depth of about 1 cm, the cups are covered with glass and placed in a warm place. It is better if they are immediately placed in the light: as soon as the shoots appear, they will strive towards the light and in the semi-darkness they may stretch out excessively. Shoots may appear in 3–4 days or significantly later, especially if the seeds have not been prepared. Immediately remove the glass and reduce the temperature by 4-5 degrees for a week.
Further care before transplantation
At first, the seedlings are not watered, but only sprayed with a spray bottle so as not to over-moisten the soil. The water should be warm and settled. The light should be bright, but diffused: direct sunlight has a detrimental effect on young plants. If the soil was nutritious, you can do without fertilizing before the first transplant, but if the seedlings have stopped growing, they can be fed with any universal fertilizer. The first transplant (not picking, but transshipment!) is carried out when the third true leaf appears.
Pepper transplant
For the first transplant, take approximately liter pots with holes for water drainage in the bottom. Lay a drainage layer (2–3 cm of small pebbles or coarse sand), and then soil similar to the one in which the seeds were sown. Replant the pepper at the same depth as it grew before, being careful not to injure the roots. It is better to transfer the plant along with a lump of earth into a new container and carefully add soil, filling all the voids with it. Water the plant well with warm water and place it in partial shade for several days. It is advisable not to water it anymore for a week.
For each transplant, you need to select a pot according to size.
It is customary to replant ornamental peppers twice a year. The second, necessary, transplant into a large pot (about 5 liters in volume) is carried out in the phase of 6–7 true leaves; it is performed similarly to the first. During subsequent transplants, the pot and partially the soil are changed, being careful not to injure the root system.
Types of peppers and varieties with photos
In indoor conditions, mainly small-leaved varieties with poorly developed rhizomes, as well as those that are unpretentious to the microclimate, are cultivated. Pungent representatives of vegetable crops have better characteristics and a longer harvest period in a limited space. When choosing seed, preference is given to varieties whose plants do not exceed a height of 50 cm.
"Ogonyok"
Mid-season pepper, which enters the fruiting phase on the 115-120th day, is represented by medium-sized plants. The bushes are formed by branched shoots covered with wrinkled medium-sized foliage. The drooping fruits reach a weight of 20 g with a wall thickness of 1.5 mm. When biologically ripe, the color is bright red and the taste is pungent. The variety is recommended for use in canning.
"Aladdin"
Plants up to 60 cm in height are covered with medium-sized leaves with characteristic glossy outer sides. According to the ripening period, shrub pepper varieties "Aladdin" are classified as mid-season representatives. One specimen produces up to 16 red fruits. Maturation is extended over time. Fruit weight is 2-3 g. Before biological ripeness, the walls are colored slightly yellow.
Please note! Recommended for use as a seasoning in powder form.
"It's Summer for Baba"
This time-tested variety with a pleasant, moderately pungent taste is shade-tolerant. It is placed on western window sills without worrying about additional lighting. Low-growing plants produce rounded fruits, the weight of which does not exceed 5 g. Due to its universal use, Indian Summer pepper is used as a powdered spice, in slices for canning.
"Bonfire"
A vegetable crop that produces very spicy red fruits. The bushes are semi-spreading, of medium height. Thanks to this, the variety is suitable for cultivation on the windowsill. The cone-shaped fruits are directed upward and weigh no more than 10 g at biological ripeness. The rich scarlet fruits of the Koster bush pepper stand out in contrast against the background of medium-sized light green foliage.
"Filius Blue"
Indoor hot pepper plants produce purple pods. However, the fruits acquire this color only when they are biologically ripe, gradually changing green to orange and red. High-yielding peppers are valued for their ability to produce crops throughout almost the entire year. Spreading bushes do not grow more than 25 cm in height, but due to their branched shoots they require a lot of space.
Caring for indoor peppers at home
They care for indoor peppers almost like flowers, but they also have their own characteristics: after all, they are a vegetable crop.
Conditions of detention
The best place for pepper is an eastern or western window sill: there will be enough natural light there, additional lighting will be required only in spring or autumn, and for year-round fruit-bearing plants (and these are rare) - even in winter. The lack of light will be clearly visible by poor branch growth and weak flowering. The room must be ventilated periodically, without creating drafts.
The optimal daytime temperature is 23–25 °C, a little colder at night. Not only soil humidity is important, but also air humidity: it should be 60–70%. In case of lower indicators, it is necessary to spray the plants with water. During the warm season, it is useful to place the pots on the balcony and even take them out to the garden (if you have one), but when the temperature drops, they are returned to the windowsill.
Watering, fertilizers
Water the pepper with settled warm water as needed: the soil in the pots should always be moderately moist. The need for fertilizing is signaled by bushes by changes in leaf color and slower growth. Purple leaves indicate a lack of phosphorus, light ones indicate a lack of nitrogen. There is no need to wait for these signals. Feed peppers every two weeks. In this case, it is advisable to apply nitrogen fertilizing foliarly (spraying the leaves), but all nutrients can be applied at the root. It is better to alternate organic and mineral compositions.
Bush formation and pollination
Ornamental peppers will bear fruit without forming a bush, but by pinching the plants they are made more neat and their yield is slightly increased. Thus, the main shoot is often pinched immediately after the first flower appears on it, which causes the plant to branch. Then the shoots that interfere with the decorative appearance of the bush are pinched or removed. During long-term cultivation, fruit-bearing shoots are cut out.
When forming a bush, you can do almost anything to create a decorative effect.
Despite the self-pollinating nature of pepper, it should be slightly helped in this matter, simply by slightly shaking the branches with flowers; Pollination with a brush may not be necessary.
Caring for perennial peppers in winter
In winter, most varieties of ornamental peppers rest and prepare for new fruiting, but there are also those that bear fruit continuously. In any case, in winter it is possible for the air temperature to drop to 18–20 °C, but it is important to create conditions with sufficient illumination. Plants are watered moderately, the soil is loosened and sometimes fed.
Video: growing indoor peppers
What is indoor pepper?
Indoor pepper is a perennial unpretentious plant that is grown both in open and closed ground, as well as at home on a windowsill. Most varieties are used for food as spices and a source of vitamins.
Characteristics and description
The indoor plant has a compact size. The branched crop reaches a height of 20 to 50 cm. The bushes have a lot of leaves and fruits. In the summer, peppers are taken out to the balcony window sill and, if possible, transplanted into a greenhouse. Before the temperature drops, the peppers are transplanted back into the pot.
Mistakes in caring for ornamental peppers
If agricultural practices for decorative peppers are not followed, problems may arise. So, watering with cold water can lead to rotting of the roots and stunting of growth. Following advice about pinching the roots when replanting can weaken the plants so much that they will not bloom or bloom weakly. Too dry air can attract spider mites, a pest that sucks juices from leaves. Eliminating many errors usually puts the peppers in order: even simple humidification of the air can drive away the mites, but if there are a lot of them, you will have to use Fitoverm.
Purpose of round peppers and common varieties
Small round peppers are ideal for canning in jars; what is the variety called and where should it be grown? You can read further. Among spherical vegetables there are not so few large varieties.
Kolobok
This is one of the most popular varieties among gardeners. The weight of one pepper is more than 150 g. It is distinguished by thick walls and pericarp. It is so loved by gardeners due to its resistance to rot, mold and wilt.
“Koloboks” ripen quickly and bear fruit abundantly. The peppers are round in shape and have smooth skin. The pulp is juicy, the vegetables have a pleasant aroma. They are consumed fresh and also used for winter preparations.
Helios
One of the early varieties, distinguished by round-shaped fruits. It takes 110-120 days from seed germination to technical ripeness. Biological ripeness is achieved after 140-150 days. The plant is small in height - about 35 cm. The fruit weighs from 100 to 150 g, the walls are 6-8 mm, the skin is smooth. As it ripens, it acquires a yellow color.
It is recommended to sow the seeds for seedlings first. High-yielding variety that resists wilting. Peppers retain their marketable appearance and are suitable for both direct consumption and canning.
Scythian
Also applies to early peppers. 108-120 days pass before the onset of technical ripeness, biological ripeness occurs later - after 140-155 days. The plant is compact and low - about 35 cm. The fruits are round, weight varies from 150 to 220 g. At first they are light green in color, then they become bright red. They have smooth skin and tender flesh. The walls reach 8-9 mm in thickness.
The Golden Fleece
This variety produces round, slightly flattened peppers. It is classified as mid-season; it takes 115-125 days to reach technical ripeness. Biological ripeness occurs within 150 days. The height of the bush is about 50 cm, the foliage is dense. The weight of one vegetable reaches 180-220 g, fruits with thick walls are 8.5-10 mm.
When biological ripeness is reached, peppers of the Golden Fleece variety have a yellow-orange color. First, it is advised to sow seeds for seedlings. Has excellent taste. Resists verticillium wilt.
Sultan
This mid-season sweet pepper forms a tall bush of 45-60 cm with dense foliage. The fruits are round, with slight ribbing, large in size, weight in the range of 100-150 g. When they reach biological ripeness, which occurs in 158-165 days, they acquire a dark red color. Walls 8-10 mm.
The fruits have excellent taste. Seeds are planted through seedlings; sowing in cassettes is common. The variety resists wilting. Peppers can be used fresh in the kitchen or canned for the winter.
Maria F1
A mid-season hybrid (as the name indicates), producing abundant harvests. The bush is quite tall, the stem grows up to 85 cm. The peppers are round, slightly flattened in shape with a ribbed surface. When they reach biological ripeness, they acquire a rich red color. The weight of one fruit is 100 g, the walls are 6-7 mm.
Novogoshary
The variety forms a standard bush up to 60 cm high. The fruits grow with thick walls (from 8 to 11 mm), the pulp is juicy. The skin is red. If you follow the recommendations for growing this variety, you can get peppers weighing up to 140 g. Fruiting in these plants continues for one and a half months.
Diseases and pests
Pests rarely settle on the windowsill: only a spider mite can get into an open window. Unfortunately, its impact may not be immediately noticeable, but it can be eliminated. Fitoverm is a reliable assistant in this matter. Mealybugs may also develop in undisinfected soil and attack the root system. It is controlled with various fungicides.
It is not difficult to detect a tick, but this happens only in the later stages
If the soil is excessively waterlogged, peppers can develop fungal and other diseases. Most often it is affected by root rot and late blight. If spots appear on the leaves, the bushes are sprayed with copper-containing preparations. If the leaves wilt due to normal watering, you can try replanting the plant in clean soil.
Signs of late blight are familiar to all gardeners
Cordara
An early-ripening type of pepper, the “Cordara” variety is devoted to its bright yellow color; its golden fruits also grow upward. The plant itself is low and suitable for growing both in the garden and on the windowsill in pots. The fruit sizes are about 2-3 x 5-7 cm. Many peppercorns ripen on the bush at once, which gives the plant a refined appearance.
Hot peppers are very well used in cooking, both fresh and for preservation. The fruits of this variety are very well stored whole, dried, especially together with peppers of other colors.
When growing hot peppers in pots, you need to take into account that the bitterness is caused by light. The more light, the hotter the peppers become!
Fruit characteristics and yield
The color, shape and size of the fruit depend on the subspecies , but the most common are Capsicums with red, yellow or purple peppers. When the ripening period begins, the entire bush is strewn with small bright fruits, sometimes they can hide under the leaves, and sometimes protrude upward like small horns. In some varieties, they are very elongated and twist.
The color of the fruit changes depending on the degree of ripeness , which is why peppers of different shades can coexist on the same bush.
Pros and cons of growing
- Pros:
- When preparing first and second courses, pepper will add a pleasant aroma and taste.
- Based on Capsicum, you can make a tincture that can be used for medicinal purposes.
- When added to dishes, it can stimulate appetite.
- This plant can decorate any interior.
- Unpretentious when growing.
- You can even grow it on a windowsill.
- High germination rate.
- Minuses:
- Small fruits.
- Do not consume in large quantities, as you can burn the mucous membrane.
- It is necessary to carefully monitor the temperature, otherwise the plant may die.
Transplantation and propagation
Transfer
Transplantation is carried out for both adult plants and seedlings. One-year-old bushes undergo this annually, for which the substrate in the pot is changed. Seedlings are transplanted as they grow using the transshipment method, selecting a slightly larger planting container.
Reproduction is carried out by seed and cuttings.
Propagation by seeds
Sowing of seeds is done in the last days of winter. The container with the planted seeds is placed in conditions with a temperature of twenty-five degrees Celsius and high air humidity. After the first shoots appear, the temperature is reduced by five degrees.
Flowering period and subtleties of pollination in a pot
The beginning of flowering depends on the time of sowing and occurs either in summer or winter. The flowers of ornamental pepper are bisexual , so they easily self-pollinate when air moves.
- To facilitate pollination, the bush can be shaken periodically.
- During abundant flowering, it is necessary to apply mineral fertilizers according to a schedule, as this period is difficult for the plant itself.
A sign of mineral deficiency can be a change in leaf color from purple to too light. Fertilizing is carried out with mineral fertilizers in the spring every 10-14 days.
Varieties of varieties
For growing at home, it is advisable to choose only small-leaved varieties with a weak root system and unpretentious hybrid varieties. Often on sale there are decorative perennial species with a sharp taste of fruit. They have the best varietal characteristics and bear fruit well in limited space. The height of a bush for home cultivation should not exceed 40-50 cm. The most popular varieties:
- Ogonyok. Potted pepper with mid-early ripening period. Fruiting occurs in 115-120 days. The bush is medium-sized and branched. Large pods reach a weight of up to 45 g, have a rich red color and a pungent taste;
- Aladdin. It is represented by a medium-sized bush, which at home reaches 50 cm. This is an ultra-early ripening variety, fruiting is abundant and long. The pods are small, cone-shaped, aromatic and spicy. The color of the fruit changes as it ripens; ripe peppers have red skin;
- Poinsettia. One of the most decorative varieties. The bush reaches a length of up to 35 cm, on which numerous oblong leaves are formed. The pods grow up to 7.5 in length and have a pungent taste. As the fruits ripen, they acquire red flowers and are located at the ends of the shoots in the shape of a bouquet;
- Explosion Amber. Pepper is a compact bush, which is convenient for growing on a windowsill. The height of the plant does not exceed 30 cm. The fruits have an early ripening period and are up to 2.5 cm long. The pods are very sharp, the color of the skin depends on ripening. Ripe peppers should have a bright scarlet color.
When purchasing ornamental pepper seeds, you should carefully read the description on the package, and also try to purchase seed material only in specialized stores. Sometimes, under the guise of a houseplant, they sell seeds of ordinary hot pepper, which are not suitable for home cultivation.
Alkaloid preparations isolated from larkspur
Alkaloids
Melliktin
It is used in the following cases:1.2.3.4.5.6.
Tetanus physiotherapy
Mellictin is contraindicated in the following pathologies:
- myasthenia gravis and other pathologies, one of the symptoms of which is a decrease in muscle tone;
- renal and liver failure;
- decompensation of the heart.
1.2.3.
atropine
Elatine
Elactin is indicated for the following conditions:
- pathologies characterized by hypertonicity of skeletal muscles due to disruption of the pyramidal tract;
- brain dysfunction with signs of muscle hypertension;
- traumatic, infectious and postoperative brain damage;
- dyskinesia of various origins.
myasthenia gravis renal failure
Delsemin
In case of overdose, an injection of a mixture of proserine and atropine is given to prevent the following symptoms:1.2.
fatigue
3.
Recommendations for growing Capsicum
When growing Capsicum, certain problems may occur, and in order to preserve the plant, you need to solve them in a timely manner.
The following difficulties may arise:
- Wrinkling of fruits. This may be a consequence of insufficient moisture; it is recommended to spray the bush more often.
- Loss of plant color. The reason is lack of moisture.
- Falling leaves. In this case, it is necessary to increase the luminous flux, and you can also install additional lighting.
- Withering and loose leaves. This may happen because the plant is freezing. The recommended temperature should be set.
- Slow growth of the bush and too small leaves. This is a consequence of insufficient light and nutrition. Capsicum needs to be provided with brighter lighting or fed with appropriate mineral fertilizers.
So, Capsicum pepper is a beautiful ornamental plant that will not require constant attention and care, but some features are still worth considering. When consumed in moderation, this pepper is quite beneficial, but you need to be extremely careful as excessive consumption can cause burns.
Common Mistakes
When growing decorative indoor peppers, you should carefully consider the advice of professionals. If you make mistakes during planting or caring for the plant, it may die. Diseases may begin to develop that will negatively affect the condition of the pepper.
The following mistakes are usually made:
- Violation of the watering regime. The water should be warm; if you use cold water, the root system will begin to rot.
- Pinching the root at the time of thinning. This will not lead to death, but the planted indoor pepper will take a long time to recover.
- The appearance of pests. If any are found, there is no need to throw away the bush; simply treat it with a chemical or folk remedy.
- Insufficient air humidity. The problem is easily solved by purchasing an air humidifier immediately after sowing.
The plant may shed its leaves if there is a sudden change in air temperature when moving the ornamental bush from room to room. The problem can be solved by using additional lighting.
How to grow
It doesn't take much time or effort to grow Capsicum . The plant is unpretentious and has a high rate of growth and development. For this reason, pepper is very popular among gardeners.
Lighting and location
Most of all, the plant loves light , so it will be difficult to grow it in a dark room. It is most convenient to grow it on a windowsill, but too much direct light can burn the plant, so a darkened window facing south is preferable.
Attention! Capsicum does not like cold or hot places: look for a place where the temperature ranges from +10 to +20°C.
Features of watering and humidity
During the year, Capsicum will need moderate watering . But in summer, during flowering, plants need to be watered quite often: once every 3-4 days with settled water. The basic rule of watering is not to leave the soil dry.
Watering is reduced if:
- the fruit began to set and begin to ripen;
- the temperature dropped below +15°C (reduce to once a week).
It is necessary to spray the plant every day to maintain the required air humidity.
How to feed correctly
To feed Capsicum you will need several kilograms of mineral fertilizer . The plant is fed from March to September 2 times a month. However, if additional lighting is installed in winter, then you will have to feed much more often - once every 20 days.
Features of reproduction
Capsicum propagates by standard seed method and cuttings .
Before planting, seeds are soaked for 1 hour in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. They can be planted immediately after soaking or first placed in a damp cloth where they will hatch. As soon as the root appears, the seeds can be planted. After this, they are placed in the ground to a depth equal to the diameter of the seed. In order for the seeds to germinate as quickly as possible , the container is placed in a warm place with a temperature of about 25°C, and as soon as the first shoots appear, it is moved to a cooler place.
Cuttings are carried out only in spring or autumn ; for this, the cuttings are planted in the ground.
Reference. Capsicum cuttings quickly take root in the ground. As soon as this happens, you need to perform pinching.