When wondering what can be planted with raspberries, you should take into account the composition of the soil and the area of the plot. On depleted lands, all plants need more nutrition, and for dense plantings, the amount of nutrients required increases. This is extremely inconvenient for the gardener, so it is worth choosing the most suitable neighbors. Raspberries produce a large number of shoots, which is why some plants may not survive near them. At the same time, other species negatively affect the development of this berry crop.
How to grow strawberries from seeds.
The main thing in the process of growing strawberries is to be patient and start doing this before spring. The fact is that strawberry seeds take a long time to germinate , sometimes even a month.
After this, the strawberry seedlings need to get stronger, grow larger, and only then move to a permanent place in the garden plot. So it turns out that somewhere at the end of February you should start sowing strawberry seeds.
But if your variety is rare, and you want to propagate it quickly, then the trouble will pay off. However, it may also happen that not all bushes retain the properties of the mother berry variety.
Strawberries from seeds.
Strawberry seeds should be sown in a box 15 cm deep. To do this, fill it with fertile soil and water it. Bring the box into a room with a temperature of 20 degrees and place two to three strawberry seeds every 2-3 cm and with a distance between rows of four to five cm.
Sprinkle a one to two mm layer of wet sand on top. To create a greenhouse effect, place a plastic bag over the box. And of course, make sure the soil is moist.
With the appearance of the first strawberry shoots, the film should be removed immediately, and when two true leaves appear, the seedlings should be picked. Water strawberries carefully so as not to wash out the roots.
Such strawberries will need to be planted in the garden when the return spring frosts have passed. She is still far from beautiful strawberry bushes, these are still tender sprouts of future powerful strawberry bushes, but with good care they will take root well and quickly grow and there is a possibility that they may bloom in the same season. In the first days after transplanting strawberries into the ground, they need to be shaded and watered in the morning and evening.
Is it possible to plant strawberries and raspberries next to each other?
By themselves, these berry plants do not have a negative effect on each other. But they have a common pest, the raspberry-strawberry weevil. This is a black beetle 2-3 mm in size. With the appearance of buds on raspberries and strawberries, the female pest begins to lay eggs inside. At the same time, she gnaws the stalk, as a result of which the bud droops and falls off.
But the damage caused by the weevil does not end there. In the near future, young beetles emerge from the larvae and cause harm during their flowering period. Now it becomes clear that if raspberry and strawberry plantings are located nearby, then when pests appear in one area of berries, they can easily move to nearby strawberry and raspberry areas.
The peculiarities of wintering and the spread of the pest also do not allow any one plant to be the predecessor of each other. Beetles hibernate and hide under dry leaves, dead plant debris, and clods of soil. And even if you uproot the raspberries or strawberries, removing all the leaves and other plant debris, flower weevils may remain in the ground. Early in the spring they will emerge from wintering and will again harm plants. Strawberry varieties
Regardless of the region, climate and size of their summer cottage, few people refuse to grow raspberries - a tasty, sweet, aromatic berry. Beloved by many, it has been known since childhood as a pleasant remedy for colds. Juicy, healthy raspberries are a real natural storehouse of vitamins, microelements and organic acids necessary for human health.
Raspberries get along well alone.
In order for the fragrant harvest to be generous every year, the berry bush needs to create the right conditions. The fastidious raspberry is demanding of sun, moisture, soil fertility, protection from winds, frost, and waterlogging. Few people think that the health and productivity of this berry garden also largely depend on the companion plants that have settled next to it.
Why can't some plants be planted nearby? A little fun theory
In the plant world, as in any biological community, there are certain relationships between different species.
Plants that find themselves in close proximity have different effects on each other:
The raspberry bush does not get along with all plants.
There are cooperative relationships - when green partners help each other in growth and development. There are frequent cases of depressing effects on the immediate environment when growing together: inhibition of development, deterioration in yield and taste of fruits, up to the complete death of the rival plant.
What affects plant compatibility
The compatibility of plants is influenced by a wide variety of factors that you need to know when choosing a place for the future planting of a particular crop.
Factors that influence the compatibility of growing vegetable and fruit crops include:
- a uniform list of nutrients that plants need for growth and fruiting. When it coincides, cultures begin to compete with each other;
- depth of the root system. In a situation where the root system of different plants lies at the same depth, the stronger representative pulls water and nutrients onto itself (for example, raspberries). As a result, the weaker plant begins to wither and will soon die;
- plants release certain substances into the soil (amino acids, biologically active substances, hormones, antibiotics, enzymes) that negatively affect the growth of some neighbors. Although for other plantings their effect will be positive. This effect is used when preparing the soil for planting a certain crop. The third factor is the least known. Plants often release such substances from their roots, although leaves are also capable of producing volatile compounds.
These three parameters are used to determine the optimal neighbors for gooseberries or those with which co-growing is contraindicated.
In addition, there are other factors that can have an indirect effect on the growth and development of various plants growing nearby:
- light. Cultivated plants need light and warmth to bear fruit well. When planting gooseberry seedlings near tall trees, a shadow will form that will completely or partially cover the bush. As a result, fruiting will occur actively only on the side that does not experience a deficiency of heat and light;
- soil composition. In poor soils and without periodic feeding, some plants will absorb all the available nutrients, leading to the death of their less “lucky” neighbors.
Depressants
This phenomenon is explained by the natural competition of plants for light, moisture and nutrients in the soil, as well as the formation of colins by them.
Colins are complex chemicals released by higher plants into the soil, air or water when washed off their leaves. Some plants also synthesize phytoncides - volatile biologically active compounds that kill bacteria.
Raspberries may die if a competing plant is planted nearby.
Incompatible plant species cannot be planted together, especially if one representative of the flora is superior to the other in terms of the level of inhibitory substances. But if a gardener pursues the goal of limiting and “moderating the ardor” of some crop, then he can take this effect into his arsenal.
How to choose the right place to plant raspberries?
Rows of raspberries
It is best to place from north to south. To do this, trenches are dug 40–50 cm deep, the distance between plants in a row should be 20–50 cm depending on the variety, the distance between rows should be 1–1.5 m minimum. When planting, 5–8 liters of water are poured under each plant.
Interesting materials:
How should the drain hose of a washing machine be positioned? How to properly wash car glass? How to properly put a tablet in the dishwasher? How to properly unlock the drum of a washing machine? How to properly wash trousers in a washing machine? How to properly wash jeans in an automatic washing machine? How to properly wash things in an automatic washing machine? How to properly install a belt on a washing machine? How to properly install a washing machine on a wooden floor? How to install a Samsung washing machine correctly?
Who is stronger than raspberries?
Raspberries are the most delicious, sweetest, and favorite of all known garden berries. Each ripe berry is a real natural multivitamin capsule. Plus easily digestible carbohydrates, fiber, pectin, minerals, organic acids. Probably, nature wanted as many people and animals as possible to be able to enjoy and receive treatment from the juicy and healthy fruits. How else can we explain the fact that she endowed this plant not only with amazing properties, but also with the character of an aggressor. Raspberry always behaves in an active, economical manner, self-confidently seizing new territories and displacing its neighbors. In conditions of a shortage of free space, the owner of a garden plot is forced to take decisive measures against the growth of the raspberry “jungle”.
Sorrel will stop the spreading of raspberry bushes.
For raspberries, the retaliatory aggressor, superior to it in this quality, is sorrel.
Sorrel with its high acidity, planted around the perimeter of the raspberry tree, will stop the bushes from spreading across the area. It has been noticed that the “sorrel” border strip acquires a restraining force if its width is at least 50 centimeters.
Metlitsa cannot be removed!
It is interesting that the removal of broom, which is considered a weed, from the row spacing of raspberry trees is considered a mistake by experts.
With its strong root system, this tenant restrains the development of adventitious roots of the bush, as if giving a “busy” signal. In addition, the broom prevents the soil from drying out in the moisture-loving raspberry field.
The broom will not allow the soil to dry out.
Corn, grapes and sea buckthorn
The young growth of the bush is held back by the corn sown nearby. Raspberries will not feel comfortable next to grapes and sea buckthorn.
You should not plant raspberries next to sea buckthorn.
Friendship: with whom and against whom?
Garlic repels insect pests.
Many plants have the ability to repel insect pests and even protect against diseases.
- For example, calendula successfully fights raspberry fly . Spicy herbs (garlic, parsley, marjoram, basil) and flowering plants with a specific aroma (marigold, yarrow, tansy, chamomile) release volatile substances into the air that interrupt the smell of the “breadwinner” plant for pests. Not feeling it in this place, the insect flies to another territory.
- Undeservedly expelled from the site , nettle, getting along well with raspberries , also reduces the number of insects attacking tender juicy berries.
- of red elderberry growing nearby will also play the role of a guard .
What is best to plant next to raspberries?
Apple trees get along well next to raspberries.
- The apple tree is rightfully considered the best friend for raspberries . These cultures not only coexist peacefully, but also help each other. Raspberries save the apple tree from scab, and the apple tree saves raspberries from gray rot.
- Beds with dill located nearby increase the yield of raspberries by attracting pollinating insects to their flowers. Plus dill is very good for health.
- Raspberries will not mind being adjacent to plums, pears, rowan berries, red and black currants, and honeysuckle . It’s good to plant tomatoes next to it.
- Decorative crops will decorate raspberry plantings and help them grow: rose bushes, barberries, various types of junipers .
Green manure will help increase the fertility of the land.
Raspberries are very demanding on soil fertility. Some gardeners advise planting a herbal mixture of vetch and oats along the raspberry rows. The combination of a legume plant with a cereal will play the role of green fertilizer: it enriches the soil with nitrogen and nutrients, promotes its loosening, and suppresses weeds.
What not to plant strawberries with
Some gardeners still believe that it doesn’t matter what you plant strawberries with, they are unpretentious and will still grow. This statement is only partly true. Indeed, strawberries will grow, but will they bear fruit? Will there be a rich harvest? What will the berries taste like?
Experienced gardeners do not recommend planting strawberries next to the following crops:
- Jerusalem artichoke.
- Solanaceae.
- Horseradish.
- Sunflower.
- Plants from the clove family.
Tomatoes and potatoes can destroy strawberries in a few months, since these crops spread late blight.
Sunflower, cabbage and Jerusalem artichoke greatly deplete the soil. Sunflower seeds are poisonous to strawberries.
Raspberry bushes completely dry out the soil, shade the beds, and strawberries will completely stop bearing fruit.
They do not love each other
Raspberries and strawberries are bad neighbors, mutually oppressing each other . They share common pests and diseases, the root system is located at the same level and competes for access to nutrients.
The proximity of cherries also causes suppression of raspberries and a decrease in the yield of berry bushes.
Cherries negatively affect the growth of raspberries.
Description of the Albion variety
The Albion hybrid is defined as a variety of remontant strawberry varieties capable of repeated fruiting.
Strawberry Albion (lat. Albion) has the following features:
- Strong and branched bushes with a wide leaf blade, pointed along the edges of the leaves.
- With powerful branching, the bush itself develops no higher than 30 cm.
- Stolons have pubescence that is anthocyanin colored.
- Elastic peduncles rise above the dark green foliage, which, when developing berries, allows them not to sag under their weight.
- The formation of fruit buds occurs under neutral daylight conditions (NDS). This allows strawberries to bloom and form berries during the season without stopping, without reference to the duration of daylight hours.
- Albion strawberries begin to bear fruit a year after planting. Peak yield occurs in mid-August.
- The variety is well cultivated in many regions of Russia. In the Middle Zone, four stages of harvesting are possible; in the north of the country, Albion strawberries will only have time to ripen three times. Late harvests in cold climates will not have time to fully ripen in open ground, since this time falls on the first frost.
- The high productivity of the variety bushes lasts 3–4 years, after which new strawberry beds are laid.
- Able to survive frosts well, but unstable in the face of heat.
- Excess moisture makes the berries tasteless.
Albion strawberries
Characteristics of berries
The pride of any varietal strawberry are berries that have the following characteristics:
- The fruits are large in size, depending on the frequency of fertilizing. One ripe berry weighs from 30 to 50 grams. The berries themselves grow up to 4–5 centimeters in length and are bright red in color.
- The external color of the fruit is rich garnet, the flesh of the berry is lighter. The berry ripens from the top to the bottom, and when ripening is not complete, a white color is noted at the base of the sepals. The nut seeds have a sandy-grass color.
- In most cases, Albion berries are cone-shaped in shape, however, they can be oval or heart-shaped.
- The juicy pulp has a rich strawberry aroma, a high level of sugar content and a dense structure. Thanks to this, the berries do not spoil or become deformed.
- The brightness of the taste manifests itself in full force during the second wave of fruiting. Sometimes strawberries are picked before they are fully ripened, and then the berry does not have time to gain flavor and remains sour. It is necessary for the berry to ripen and take on a burgundy color.
Albion strawberries are used in cooking.
Of these you can:
- make jam;
- cook syrups;
- make tinctures;
- close compotes.
Strawberries of this variety are well suited for deep freezing; after defrosting, they retain their shape and have a pleasant appearance. It is also permissible to eat fresh berries directly from the garden.
Advantages of the variety
The value of this hybrid lies in the following qualities:
- has industrial value;
- has a magnificent appearance;
- has excellent tasting qualities;
- easy to transport;
- has a long shelf life;
- resistance to pests and diseases.
Disadvantages of the variety
The main drawback of Albion is its low tolerance to frost, which is understandable, given the sunny and warm homeland of its selection.
You can also note:
- it is likely that some of the bushes will die after a rich harvest;
- decrease in yield at temperatures above 30°C;
- wilting and small ovary due to insufficient watering;
- instability to brown and white spotting;
- As fruiting progresses, the berries become smaller by the end of the season.
Region of natural growth of the Albion variety
The variety was bred for regions with a mild and humid climate. The most suitable area for growing Albion strawberries in open ground is the southern part of Russia.
In cool climates, strawberries need shelter. This will allow Albion berries to be cultivated for commercial purposes on a large scale. By providing artificial lighting for the NSD crop for a long period, it is possible to obtain a crop in the greenhouse regardless of the time of year.
A review made by the author of the channel “Tatyana T” will allow you to evaluate the Albion variety of strawberries.
Raspberries: properties, growth characteristics
Common raspberries are found in almost any part of the Russian Federation. This deciduous shrub has a perennial rhizome, from which biennial aboveground stems emerge, reaching one and a half meters in height. The root system is sinuous, woody, with a large number of adventitious roots, which form a branched system.
All stems are erect, with oval, alternately arranged leaf blades of a dark green color and slight pubescence on the surface. During flowering, the shrub is decorated with small white flowers, collected in racemose inflorescences, located mainly at the top of the stems or in the axils of the leaves.
STRUCTURE OF THE RASPBERRY BUSH AND INDIVIDUAL ORGANS OF THE PLANT: 1 – offspring; 2 – adventitious roots; 3 – buds on the rhizome and root; 4 – replacement shoot; 5 – fruiting stem; 6 – rhizome; 7 – overgrowing roots; 8- side branch; 9 – bud; 10 – flower; 11- node; 12 – internode; 13 – sheet; 14 – main kidney; 15 – additional kidney; 16 – core; 17 – wood; 18 – bark; 19 – spikes; 20 – covering scales; 21 – embryonic leaves; 22 – embryonic inflorescence; 23 – axillary bud
When it comes to using raspberries, you can use almost any part of them.
- Both the fruits, the leaves, and the shoots themselves have a lot of useful properties, the main ones among which are the following:
- antitoxic effect;
- antipyretic effect;
- antibacterial and antifungal effects, which is especially important when there are staphylococci and other similar fungi in the body;
- diaphoretic effect;
- normalization of the condition in hypertension, gastrointestinal diseases, anemia.
Often, decoctions and infusions from the plant are used as an expectorant for laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis and common viral ailments. Sometimes the culture is used as a sedative for nervous disorders and depression. In this case, its effectiveness is explained by the presence of a large amount of copper in the composition.
Why you can’t plant some plants nearby
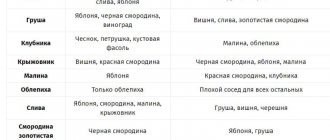
Compliance with crop rotation requirements on the site ensures high yields of each of them, not to mention reducing the likelihood of plants being damaged by diseases and pests. Based on this, when growing raspberries, it is worth considering the proximity of desirable, undesirable and neutral neighboring plants.
Positive Neighborhood
The apple tree is deservedly considered the most suitable neighbor for the described culture . It not only does not harm the bush, but also promotes its development, protecting against infection and further spread of gray rot. In turn, raspberries protect the fruit tree from scab.
Dill beds located next to raspberry plantings will be no less . Such greenery attracts pollinating insects to raspberries, thereby increasing the yield of the crop. For the same purpose, you can plant garden flowers (asters, peonies) around the raspberry tree, as well as crops used as aromatic spices: garlic, basil, coriander.
Neutral neighborhood
The proximity of raspberries is also possible with plum, pear, rowan, honeysuckle, although one should not exclude the possibility of placing shrubs near tomatoes and ornamental flower bushes: roses, barberry and juniper. Mint, pumpkin, bush beans, cabbage, gooseberries, and sage are also considered “neutral”. Flowers such as lilies, snapdragons, lilacs, and calendula will not interfere with raspberries, although they will not be able to help the crop.
Oppressive neighborhood
Bad neighbors will be strawberries and raspberries planted next to each other, which mutually oppress each other. They have common pests and can be affected by the same diseases, not to mention the root system of crops located at the same level, which will compete for nutrients and moisture in the soil.
With fruit and berry crops
Let's consider several of the most possible options for the neighborhood of raspberries with other inhabitants of the garden:
- Blackberry. Good partnership. It makes similar demands on environmental conditions, which greatly facilitates the care of plantings. Contrary to popular belief, crops do not cross-pollinate with each other, so you will not get hybrids from such a neighborhood. To prevent the shoots and roots of growing bushes from intertwining, raspberries and blackberries are planted at a distance of 2 m from each other or limiters in the form of tin or slate sheets are dug between them.
- Apple tree. A reliable friend and companion of the berry bush. Protects raspberries from gray rot, and it saves the neighbor from scab infection. But! Growing raspberries and apple trees in the neighborhood is allowed only if the fruit tree is young. As the apple tree grows older, it gradually begins to displace its weaker companion from its territory.
- Grape. In the inter-rows of this berry crop, many gardeners grow young raspberry cuttings, which is quite justified: in the fertile microclimate of the vineyard, young plants quickly take root and develop well. However, adult bushes of both crops will shade and “eat” each other, and raspberries will most likely lose in the competition for water and nutrition.
- Strawberry. An unsuitable neighbor for raspberries. The suction roots of both crops lie at the same level, so competition is inevitable. In addition, both strawberries and raspberries suffer greatly from a common pest - the raspberry-strawberry weevil.
- Cherry. Refers to the unfortunate neighbors of raspberries. Its powerful roots will oppress the berry bush and over time “strangle” it.
- Walnut. Known to gardeners as the worst antagonist of all cultivated plants. The substances released by its roots accumulate in the soil and inhibit the development of neighboring crops. Needless to say, raspberries planted near this giant have no chance of full growth and high-quality fruiting.
- Currant. Some gardeners consider it too weak a companion for raspberries. The latter, indeed, grows too quickly and actively absorbs nutrients from the soil. However, with timely removal of root shoots and proper application of fertilizers, raspberries and currants coexist peacefully in the neighborhood.
Video recipe for the occasion:
:
Now about growing different varieties of crops in one area. Have you ever heard about cross-pollination of raspberries and the subsequent deterioration of varietal qualities? Don't believe it, this is a horror story for beginners. Bisexual flowers bloom on raspberry branches, which means the bush does not need a pollinator plant. Even if suddenly pollen from one specimen gets onto another, a slight change in characteristics can only be noticed during generative propagation, and growing raspberries from seeds in amateur gardening is not accepted (long and troublesome).
Measures against the growth of raspberry “jungles”
Given the tendency of raspberry rhizomes to quickly grow throughout the area, over time, gardeners have to deal with the problem of excessive growth of raspberry bushes, limiting it in all ways. Typically, the spread of the crop throughout the garden is observed in a southern direction, which means that it is recommended to dig in slate sheets from this side of the bed, deepening them to the depth of rhizome growth .
A simpler and safer way to fencing raspberry plantings would be to plant plants around the perimeter that contain the bushes. The leader in this regard is considered to be sorrel, which contains a large supply of a wide variety of acids, in particular at the rhizome level. It is they that get into the soil that prevent the growth of many other plants.
Why you can’t remove the broomstick
Metlitsa is another excellent tool for limiting the growth of raspberry bushes . This weed grows deeply into the soil and over time forms a dense path between the rows of raspberry plantations. It not only limits the growth of bushes, but also promotes good moisture retention in the soil, which is especially important for moisture-loving raspberries on hot summer days. Therefore, if the broom does not choke out other crops growing nearby, then you should not get rid of it.
Planting and care
It is better to plant clubs in early spring or early autumn, so that the plant has time to grow a sufficient number of roots in the new soil and bloom at the end of the first summer in a new place. Because This “crossed” crop tends to grow strongly, so the places for planting bushes should be separated from each other by at least 1 m. It is better to choose a sunny place for propagation, but partial shade is also possible.
The soil for cultivation should be sufficiently loose and fertile. For better reproduction, it is worth additionally fertilizing it with manure solution and diluting it with peat. In order for the crop to feel comfortable and bear fruit abundantly in subsequent years, it is worth covering last year’s soil with a certain amount of peat every year.
The only thing this “crossed” variety really needs is abundant watering, especially in the hot season. However, waterlogging of the soil is unacceptable, because the shadow of the leaves creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of pests, which will be difficult to find in the resulting thickets and get rid of them.
The plant also needs periodic weeding, but unnecessary vegetation should be pulled out carefully, because the roots of the crop are located close to the soil surface
Careless and sudden pulling out of a harmful plant can harm the roots of the clubberry, which can cause it to die.
Corn, grapes and sea buckthorn: characteristics of each “neighbor”
Like the previous plant, corn can keep raspberry plantings from spreading excessively throughout the area without causing serious harm to existing bushes. The only thing that can harm the cereal crop in this case is to protect the raspberries from the sun's rays, which will negatively affect the size and taste of the future berry harvest.
Neighborhood with grapes and sea buckthorn is more undesirable for raspberries , since the rhizomes of all three plants are at approximately the same level and will compete for nutrients and moisture in the soil. Since sea buckthorn is stronger in development, it is likely that all the bushes of the latter will begin to lag in growth and will soon completely wither away.
Plants that repel pests
Raspberries are one of those plants that often suffer from insect pests, so the gardener will have to make every effort to protect the future harvest. A radical solution to the problem is the use of insecticidal chemicals, but if you need environmentally friendly berries, then it is worth studying the issue of beneficial crop compatibility in this regard.
It is best to plant raspberry bushes next to aromatic plants that can repel pests . For example, they will grow well next to red elderberry, the smell of whose berries is clearly noticeable within a radius of several meters from the plantings. Marigolds, garlic, ferns, coriander and celery have also proven themselves well , often found not only next to raspberries, but also near blackberries or strawberries.
Plants that are compatible with each other mutually support each other throughout the entire period of growth and development, therefore, if you have not yet planted raspberries on your site, the issue of proper proximity should be given increased attention. Combined with responsible further care, this action will help achieve maximum yield and protect you from unnecessary problems.
There are no similar entries.
What is useful to plant
Planting raspberries on a personal plot will be 100% effective if you take the choice of “neighbors” for the plant very seriously. Of course, it is not always necessary to plant other crops next to homemade raspberries. Ideally, it is not recommended to plant any green specimens near raspberries.
You can simply combine several remontant plant varieties in this zone. However, as a rule, the problem of any personal plot is the lack of free space: everything is planted very compactly, because you want to worry about the compatibility of flowers, fruit trees, and berry bushes on a piece of land. In this case, it is simply necessary to consider what grows best near the raspberry tree.
The optimal solution is to plant other berry bushes nearby: blackberries, as well as various varieties of currants. Raspberries next to currants or blackberries will feel great. But not only plants that bear berries can make good company for your raspberry thickets. Very often, gardeners prefer to root barberry, rose or juniper in the soil near the raspberry tree. In this way, you significantly stimulate the growth of the bush, and it will begin to bear fruit at the right time, and quite actively at that.
Interestingly, if you want your home raspberry bushes to be more actively pollinated, you can plant dill next to them. Since this green specimen has a pronounced aroma, it will attract insects to the area, which will have a beneficial effect on the development of shrubs (more berries will form on them in the future).
What should you plant next to the raspberries you are growing so that the nutritious berries ripen much more intensively on the bush? Many gardeners give preference to fruit trees: if you correctly determine which “neighbor” is more suitable for the plant, you can improve the yield of raspberries. These trees most often include plum, cherry and pear.
However, that's not all. Few people know that the apple tree is considered one of the best “neighbors” for raspberry shoots. Plant this tree next to a raspberry tree and you will get a mutually beneficial “cooperation”. The presence of an apple tree will prevent the formation of gray rot on raspberry bushes. In turn, this fruit tree will be protected from scab.
We plant currants, blackberries, honeysuckle or tomatoes next to raspberries - all these plants contribute to the active development of the plant
Another important point that any gardener should take into account is the nutritional value of the substrate. Of course, to saturate the soil with useful components, there are mineral and nitrogen fertilizers, as well as various complex preparations
However, you can improve the result with the help of suitable raspberry “neighbors”.