Most experienced gardeners prefer to transplant raspberries in the autumn. The summer heat is no longer there, and the thermometer remains in the low positive range. In addition, long autumn rains come, maintaining constant soil moisture. All this contributes to better rooting of the transplanted bushes.
- 2 When is the best time to replant raspberry bushes?
- 3 How to choose the right place for a raspberry garden
3.1 Video: choosing a place and neighbors to organize a raspberry garden
- 4.1 Video: preparing a place for transplanting raspberries
- 5.1 Video: methods of planting raspberries
5.2.1 Video: propagating raspberries by seeds
Timing for autumn transplantation of raspberries
Plan it according to weather conditions and crop variety. Plant early ripening raspberries in September; seedlings of late and remontant varieties are ready for transplanting in October.
The timing of planting raspberries in the fall, depending on the climatic characteristics of the area:
- Southern regions with warm autumn - October–first ten days of November. In spring, replanting is undesirable, since raspberries do not take root well at high temperatures and lack of moisture.
- Volga region, central regions - September–mid-October. Follow the weather forecast. The main condition for rooting the crop is replanting no later than a month before persistent frosts.
- Northern territories (Siberia, Ural) - from early to mid-September. If August is cool and damp, postpone the event until May. The onset of winter earlier than the average is disastrous for young seedlings.
Transfer non-frost-resistant and late varieties to a new location in the spring.
Why replant raspberries to a new place?
Changing the place of growth is a mandatory procedure for some perennial plants. This also applies to fruit and berry bushes, which include raspberries. There are three reasons why she needs periodic transplantation:
- It depletes the soil, which leads to a lack of nutrients in it. The bush gradually fades and produces fewer and fewer new shoots.
- Raspberry yields are decreasing.
- The grown berries are small and tasteless.
- Dense plantings are a source of many diseases.
Advantages of autumn transplantation
Gardeners move raspberries in any season except winter. This approach is fraught with risks: in summer the bushes can die from the heat, and at the beginning of spring the earth is not yet warmed up enough. Transplanting raspberries to a new location in the fall has several advantages:
- Cool temperatures, high humidity.
- Rainy season. Such water is healthier for raspberries than from a well or pipeline.
- The fruiting period is coming to an end. This means that the plant spends more energy on adaptation and rooting. Such bushes are stronger than those transplanted in the spring - the latter will have to take root and bear fruit.
Advantages of autumn transplantation
Experienced gardeners believe that planting raspberry seedlings in the fall has more advantages than in the spring.
They support their opinion with the following facts:
- High humidity and comfortable autumn temperatures are favorable for the rooting of the crop. The survival rate of seedlings in the cool season is higher than in the spring with dry periods and temperature changes.
- There is no shortage of high-quality planting material. The plant goes into a dormant state, replacement buds form on the root collar.
- Plant biorhythms are taken into account. In spring, nutrients are spent on the development of the aboveground part. In autumn, due to them, the rhizome grows, which ensures the health of raspberry bushes and increases productivity.
- Summer residents and gardeners have more time free from caring for other crops. Use it to prepare the site in advance and fertilize the soil.
If the timing of transplantation is met, the seedlings have time to take root before winter, withstand frosts and produce a harvest next summer.
Preparing for landing
The new place for raspberries should be sufficiently lit
This plant is quite unpretentious, which allows it to grow everywhere and delight the gardener with a harvest. Transplanting raspberries in the fall should be done in a place that suits the shrub in all respects. It must be remembered that the berry crop is heat-loving. Sufficiently sunny areas should be selected.
Selection of material for transplantation
When transferring a raspberry tree to a new site in the fall, shoots from the first year of life are used. Dense fibrous roots should be at least 12–15 cm. Flexible shoots with a diameter of 1 cm at the base, without cracks, swelling, and no signs of putrefactive infection on the rhizome are considered suitable.
In spring, raspberries are propagated by dividing the bush, root, and green cuttings. Lignified suckers formed from adventitious root buds are suitable for autumn transplantation. The shoots are carefully separated from the mother bush at a distance of no closer than 30 cm.
Seedlings with signs of root canker, swellings at the base with stem gall midge and blue spots characteristic of purple spot are discarded.
Technology for successful transplantation - step-by-step instructions
Before planting, the seedlings are shortened to a height of 30...40 cm. Planting is carried out without deepening - to the usual depth for the raspberry root.
- prepare holes or trenches in the marked area - 25...35 cm deep;
- arrange the seedlings at the required intervals;
- Spread each root in the hole and sprinkle it halfway with dry soil.
- water well - at least 10 liters. for 3 seedlings.
- Fill the hole to the top with dry soil and lightly compact the soil.
In order not to remember about the seedlings until spring, it is necessary to cover the bed with mulch - compost, dry leaves, any crumbly organic matter with a layer of at least 7...10 cm.
This concludes the preparation for winter of the newly planted area.
Preparing the site and soil
Place the raspberry tree in a sunny place, protected from cold winds. Farmers recommend planting the crop in one row on the western or eastern border with the neighboring plot, retreating 1 meter from the fence. It is unacceptable to grow raspberries in the garden between fruit trees. Shadow from the crowns and the struggle for food lead to a decrease in yield and a deterioration in the taste of berries.
Choose a flat area with groundwater no higher than one and a half meters, which prevents root rotting. Avoid frequently flooded, poorly lit lowlands and hills with insufficient moisture for use as a crop.
When determining a place for a raspberry plant, take into account the favorable proximity and predecessors.
The berry subshrub develops well and bears fruit next to apple trees, currants, blackberries, and dill. Bad neighbors that are affected by the same diseases and compete for nutrients - cherries, strawberries, tomatoes, grapes, corn, sea buckthorn. Garlic and sorrel grown around the perimeter of the garden bed stop the development of roots and the migration of raspberries throughout the garden.
The best predecessors of subshrubs of the Rosaceae family are cereals, legumes, and vegetables, with the exception of nightshades. Green manure enriches the soil with nitrogen, to which raspberries are sensitive.
The crop loves drained, sandy or loamy soil, fertilized with minerals and organic matter. Highly acidic soil requires alkalization. To obtain a neutral or slightly acidic pH, use wood ash, dolomite flour, and fluff. A popular recipe is a glass of slaked lime per 1 square meter. m.
A month and a half before transplanting, prepare the soil. Start by cleaning the area allocated for the berry garden, digging the soil onto the bayonet of a shovel.
Depending on the fertility of the soil, apply fertilizer per 1 square meter. m:
- 10–30 kg of organic matter (compost, manure);
- 40–50 g of potassium sulfate;
- 60–80 g superphosphate.
If the soil pH is more acidic than normal (5.8–6.2), the raspberries will experience a nitrogen deficiency. In addition to alkalizing agents, use nitrates - carbonate nitrophoska, sodium nitrate, calcium nitrate. Acidify alkaline soil with ammonia forms of minerals - ammonium sulfate, montanium nitrate, ammonium chloride.
To increase the viscosity of sandy soil, more manure will be needed; dilute peat soil with sand.
Where do raspberries grow?
Transplanted raspberries should not be adjacent to garden trees
Professionals, as an example of a suitable place, call planting shrubs along the fence on the south or southwest side of the garden. In this case, care should be taken to ensure that no fruit trees grow nearby. Also, there should be no potatoes, strawberries or tomatoes near the seedlings. These crops have similar pests and diseases to this plant. Gardeners with experience name gooseberries and chokeberries as the best predecessors for berry seedlings.
When choosing a place for transplantation, you must remember that the shrub does not tolerate low wetlands. It is better to give preference to slightly raised and flat areas . Sandy soils are suitable only with constant watering in the summer. Raspberries should not be transplanted near dirt roads, as they generate a lot of dust.
Methods for transplanting raspberries
4–5 years after planting the seedlings, raspberry bushes reduce the number of fruit shoots and ovaries, and the volume of unproductive shoots increases. If the yield does not decrease after 5 years, postpone replanting for 1–2 years. Raspberries with remontant varieties can be transferred to a new bed after 10 years.
The trench, strip, bush or hole transplantation method is used. The choice depends on personal preferences and the capabilities of the owner of the site.
Trench
Use this method if you plan to plant raspberries along a fence or in a row on a trellis.
Algorithm for preparing a trench:
- A month before the event, dig a ditch 60 cm deep and -50 cm wide. If one row is not enough, make other trenches, keeping a distance between rows of 1.5–2.5 m.
- Lay a 10 cm thick drainage layer of sand and gravel on the bottom.
- The next stage is creating a nutritional cushion. Place branches, fallen forest leaves, dry and green grass on the drainage, and water. Sprinkle fertile, fertilized soil mixture on top. When rotting, plant residues will not only nourish the plants, but also generate heat.
- After the soil has settled, place the seedlings at the bottom of the trench at a distance of 40–60 cm from each other. Straighten the roots so that there are no creases. The spacing between seedlings depends on the size of adult bushes. For tall varieties, maximum intervals are used.
- Cover the shoots with fertile soil and tamp lightly.
- Pour in plenty of water in several additions. To retain moisture, mulch the surface with peat, compost or humus.
- At the ends of the trench, dig posts onto which stretch two rows of wire at a distance of 30 cm and 1 m from the ground. When the seedlings grow, tie them to a trellis.
The popularity of the trench method is due to uniform illumination, food supply, ease of weeding and shelter for the winter.
Tape
The belt method is more often used on farms when planting large plantations. When caring for the crop, you can use mechanized means, since the raspberry field is an even row with free access on both sides. It differs from the trench method in the absence of a nutrient cushion and in size. The width and depth of the dug ditch are 40 cm each, the distance between the tapes is 1.8–2 m. The scheme and algorithm for planting seedlings are similar to the trench method.
To save space, seedlings are planted in a 1 m wide ribbon in two rows. The distance between bushes and rows is 40–50 cm.
Bush or pit
Use this method if you need to plant several shoots in different places on the site or in a humid climate, since the pitting method ensures good ventilation of the plants.
Instructions for preparing planting holes:
- dig holes at a distance from each other 60–100 cm deep and 40 cm in diameter;
- maintain an interval between rows of 1–1.5 m;
- pour half a bucket of rotted manure, 50 g of potassium sulfate, superphosphate into the hole;
- sprinkle fertilizers with garden soil;
- place the seedling in the prepared hole, straighten the roots and cover with soil;
- water, mulch.
In order for the root system to remain healthy and for the above-ground part of the crop to develop normally, the root collar of the planting material must be flush with the surface of the earth after compaction and watering.
Distance between seedlings when planting raspberries
The bed and seedlings are prepared. The area needs to be marked so that next year there are no difficulties: most often, row spacing is too narrow.
In 1 row
- Medium-sized varieties (120...180 cm): 50...70 cm;
- Tall varieties (150...250 cm): 70...100 cm.
Ribbon in 2 rows
- Medium-sized varieties (120...180 cm): in a row 40...60 cm, row width - 50 cm, row spacing - 120...150 cm;
- Tall varieties (150...250 cm): in a row 60...80 cm, row width - 70 cm, row spacing - 150...200 cm.
For growing on a trellis (tape method)
- Medium-sized varieties (120...180 cm): in a row 30...50 cm, row width - 50 cm, row spacing - 150...200 cm;
- Tall varieties (150...250 cm): in a row 40...50 cm, row width - 60 cm, row spacing - 200...250 cm.
Selection of seedlings
Seedlings must be exclusively healthy
High-quality seedlings can be bought in specialized garden centers and nurseries that have a well-deserved reputation. Plants that grew in containers are often sold.
To perform autumn work related to transplantation, agronomists recommend choosing small seedlings. They must have developed roots. Amateur gardeners recommend adhering to the following aspects, which involve choosing annual seedlings for transplanting. It is worth considering that the ground root must be at least 8 mm. It is important to inspect seedlings to identify diseases. Before transplanting a shrub, you need to find out its varietal characteristics and conduct a soil analysis.
When it is necessary to propagate a crop, preference should be given to adult seedlings. Such seedlings are capable of forming adventitious buds on the root system, which can become full-fledged shoots. Shoots that are one year old are suitable for this work. You can grow raspberries by purchasing strong seedlings. This can be determined by the trunk diameter exceeding 1 centimeter at the bottom.
Particular attention should be paid to inspecting the root system
You also need to make sure that the root system of the plant is completely healthy. It must be well developed. The height of the seedlings should not exceed 40 cm. After planting, they can be pruned. It is required to leave only fifteen centimeters of shoot relative to ground level.
Aftercare
In order for the transplanted raspberries to recover faster and not wither, they are properly cared for: watered, loosened the soil, and fertilized.
Experienced gardeners reveal the secrets of proper care:
- After transplantation, the plant is immediately prepared for winter. Some use covering material, others believe that it is better to bend the branches to the ground, first placing spruce paws under them so that there is no contact with the frozen soil surface. Raspberries are a winter-hardy crop; covering them with snow is sufficient.
- In the northern regions, bushes are additionally insulated with dense covering material, wooden slabs, and slate. The main thing is that air continues to circulate inside.
- After the spring snow melts, the crop is fed with a mineral complex, ash, and organic matter.
- In the summer, standard care measures are carried out: water, remove weeds, feed.
Caring for remontant raspberries in autumn
Autumn care is very important for obtaining a good harvest. Remontant raspberries require pruning, fertilizing, and treatment against various pests.
Watering and fertilizing
To support raspberry bushes after harvesting, they are watered. This is most relevant for the southern regions, where autumn weather is often dry and warm, and little snow falls in winter. In this area, water quickly evaporates or freezes, so watering is important.
In the middle zone, autumn is usually rainy. Because of this, the last watering is carried out at the end of September. It is important to shed the soil to a depth of at least 40 cm.
Autumn watering is controlled depending on weather conditions. Due to wet soil and warm weather, there is a chance of new shoots forming . This will lead to the depletion of the earth. New branches will not have time to get stronger before winter, so they will die. Watering is accompanied by pruning of bushes.
In autumn, raspberries require fertilizing to support them after the growing season and fruiting. To do this, add humus to the soil at the rate of 1 bucket per bush and mineral fertilizers. Potassium salt and superphosphates are added 1 tsp each. per plant. If the soil is sandy, the amount of fertilizer is doubled.
Pest treatment
Insecticides are used against weevils, raspberry beetles, spider mites and other insects. The most popular of them:
- "Aktellik";
- "Intavir";
- "Fufanon."
Solutions are made according to the instructions on the package.
Folk remedies are also suitable in the fight against raspberry beetles. For example, an infusion of wormwood and marigold is often used. Take 100 g of these plants and pour 1 liter of water, leave in different containers for 2 days. After this, the infusions are combined and mixed thoroughly. This product is used to treat the plant and the soil around it.
Kidney moths are combated using the following drugs:
- "Spark";
- "Decis";
- "Confidor".
Before using these products, be sure to remove all dry leaves.
For caterpillars and glassware, “Karbofos” and “Nitrafen” are used . Mustard solution is also used against these pests. 100 g of powder is dissolved in 5 liters of water. Then the resulting product is sprayed on the plants.
Raspberry gall midge is one of the most dangerous pests . It resembles a mosquito and lays eggs on branches. Caterpillars emerge from them and eat young shoots. To get rid of this pest, mix 1.5 tbsp. l. "Karbofos" and 1 tbsp. l. chlorophos, diluted in 10 liters of water. The resulting product is sprayed onto the bushes.
There is also a folk method for destroying gall midges. 0.5 kg of chopped garlic is infused in 8 liters of water for 24 hours. After this, 20 laundry soap is added there. Mix everything thoroughly. Spray twice with an interval of 4 days.
Trimming
Autumn care for remontant raspberries necessarily includes pruning. This procedure helps:
- Prevention of excessive thickening of bushes, which significantly reduces fruiting rates.
- Formation of a beautiful plant.
- Increased resistance to diseases and pests.
- Penetration of sunlight and fresh air.
If raspberries are planted this season, then only gentle pruning is carried out. In this case, only the tips of the shoots are cut off, leaving approximately 20 cm in length.
A maximum of 8 branches are left on each bush. Before carrying out the procedure, it is important to choose the right moment. The first frost should already be here. When pruning is done in warm and sunny weather, new shoots and buds will begin to form. If it suddenly gets colder after this, the branches will freeze, which will lead to the death of the entire bush.
Some gardeners grow remontant raspberries as an annual. To stimulate fruiting next season, all branches are removed. No more than 3 cm of their length is left above the ground. Pruning is carried out with a sharp and disinfected instrument.
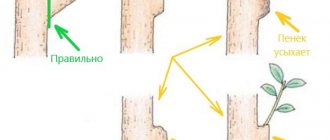
Two-year-old shoots that have already produced crops several times are cut off completely. The stumps are made slightly below ground level, otherwise pathogenic microflora will begin to multiply on them.
Important. In the case of the Yellow Giant variety, two-year-old shoots are not pruned, since they are the ones that show the greatest fruiting. For such raspberries, only the ends are shortened.
Damaged and weak branches must be cut off. If they show signs of disease or the presence of insects, they are immediately burned.
Damaged shoots are removed not only in autumn, but also in spring. This will significantly increase the quantity and improve the quality of the fruit.