Why is it important to care for raspberries in the fall?
Raspberries are unpretentious plants . It grows well and bears fruit, even if it is not looked after at all.
However, over time the bushes grow. In dense conditions, they lack sunlight, air circulation inside the bushes becomes difficult , and the plants begin to hurt.
All this leads to the fact that there are fewer berries and they grow small and not so sweet . Simple care measures in spring and autumn are a prerequisite for obtaining a stable harvest of vitamin-rich berries.
Stages of autumn care
Caring for raspberries in the autumn includes:
- thinning and pruning;
- weeding;
- loosening the earth;
- fertilizing;
- watering and mulching of plantings;
- shelter for the winter.
Processing bushes: basic rules
Sometimes situations happen when, even if all the rules of care are followed, the raspberry plant still does not produce a high-quality harvest. The problem may be that the bush is damaged by a fungal disease or harmful insects. Such procedures are carried out not only in spring and summer, but also in autumn, in order to rid the plant of disease for the winter.
To avoid this, it is necessary to periodically carry out preventive disinfection using special preparations.
From diseases
As a result of infection with pathogenic microflora, the plant may suffer from diseases such as mosaic, chlorosis, rust, rot , etc. Fungicides - chemical compounds for combating fungal plant diseases - help protect bushes. Since raspberries can be affected by a variety of ailments, you should first correctly determine the type of disease based on specific symptoms, and then choose a drug.
Find out in more detail why raspberry leaves turn yellow.
The most common diseases are:
- Late blight is determined by the presence of a brick-red coating on the rhizome. Treated with Paurin according to the instructions.
- Gray rot - young shoots become covered with ashy “dust”, then rot and die. Treatment - "Fitosporin-M" .
- Verticillium wilt is characterized by wilting of the tops of the stems and the appearance of bluish spots on the roots. “Previkur” and “Vitaros” help to cure
- Chlorosis - first the leaves turn yellow, then the shoots become thin, the bush withers and dies. “Topaz” and “Oxychom” can help
- Rust is determined by the appearance of yellow-orange bumps on the leaves. Next, reddish ulcers form on the stems, from which fungal spores are located, ready for wintering. “Forecast” and “Bayleton” help eliminate the disease .
A universal remedy for comprehensive protection of raspberries from any diseases is Bordeaux mixture , which, by the way, is used for most fruit and berry crops. You need to dilute 300 g of the purchased ready-made product in 10 liters of water, then strain through cheesecloth and spray.
Bordeaux mixture is a very toxic drug, so spraying is recommended in late autumn in dry, windless weather, preferably in a protective suit and respirator.
A good preventive measure in the fight against fungal and viral diseases of raspberries is copper sulfate. It is recommended to prepare a 1% solution: 100 g of the substance should be diluted in 10 liters of settled water at room temperature. The resulting product must be sprayed on the stems and watered on the roots. For spraying, 0.5 liters are needed per bush, and 1.5 liters for watering.
Processing times
The start time of autumn work depends on what type of shrub grows on the site.
Traditional varieties
These are unpretentious varieties that bear fruit in almost all types of soil and in any climate . They produce a harvest once per season.
Autumn activities for caring for such shrubs begin at the end of August . At this time, the fruiting period is already over, and the plant begins to prepare for winter.
The growth of the stems stops, the wood changes the green color of the bark to brown and thickens to protect it from the cold. The shrub enters the dormant stage, completing active processes. When the first snow falls, all metabolic processes stop.
Remontant varieties
The fruiting period of these varieties ends only with the onset of cold weather.
Need to know! Processing schemes for traditional and remontant raspberries differ. The remontant fruit bears fruit twice per season, so the timing of its pruning is shifted to late autumn.
Pruning of remontant varieties begins in late autumn , about two weeks before the expected frost. By this time, the second wave of fruiting is completed. Treatment begins after the leaves fall, since in the fall the remontant raspberries take nutrients from them for the root system.
How to spray grapes in autumn
In the fall, after harvesting, it is necessary to inspect the bushes for disease damage and the presence of pests. Autumn processing guarantees a good harvest next year. One of the diseases of grapes is mildew. Gray or yellow spots of an oily nature are signs of this disease. If you notice these signs, treat with the following drugs: Kartotsid, Efal, Amistar, Strobi . Oidium is another grape disease. If you smell rotten fish, it means that the grapes have contracted this disease. In this case, it is recommended to spray with colloidal sulfur. The solution is prepared as follows: take five grams of sulfur for 4 liters of water, another drug is potassium permanganate, and five grams of potassium for ten liters of water. You can also buy drugs in the store - Fundazol, Falcon . If there are no signs of damage, preventive treatment is carried out.
Of the pests, grapes are most often affected by grape budworm and mite. Rovekurt helps from her . For preventive spraying - Fundazol, Polychom.
The timing of spraying grapes depends on the varieties. Early varieties are sprayed already in September. Late ripening varieties - at the end of October. After processing, the grapes are pruned and covered for the winter.
Pruning technology
The first thing to do is to thin out the raspberry tree, removing all excess trunks and shoots . In this way, you will ensure good ventilation and illumination of the plantings, reducing the risk of disease and pest damage.
Required Tools
To work, you will need clothes made of thick fabric, gloves to protect your skin from thorny stems and sharp pruning shears . Don't forget to disinfect your tools before and after work. This way you will protect the bush from infection with diseases.
Schemes and instructions
Treatment of plantings begins with the removal of all diseased, broken, poorly developed and pest-infested shoots . The branches are cut down to the very roots, leaving no stump. Then all two-year-old shoots are removed.
Attention! The main purpose of the pruning procedure is to remove spent two-year-old shoots. They are distinguished from annuals by their brown, woody trunk.
Of the annuals, only well-developed branches are left . Be sure to shorten the tops by 10 cm. This part does not bear fruit and slows down the preparation of the main stem for winter.
The bushes are thinned out so that no more than 8-10 stems remain per 1 m² . All cut raspberries are taken out of the area and burned.
The nuances of pruning remontant raspberries
Remontant raspberries bear fruit both on two-year-old shoots and on annual shoots . Therefore, two-year-old trunks are not removed, but only the tops are pinched. The tops of annual shoots of remontant raspberries are not shortened, since this is where the berry crop is laid.
Having collected the first harvest, remove the fruit-bearing shoots to quickly obtain the second.
In regions with short summers, the second raspberry harvest does not have time to ripen . In such areas, remontant raspberries are grown as an annual plant. This means that the above-ground part is cut off completely in the fall. And next season new annual shoots will bear fruit.
Processing after trimming
After removing excess stems, the raspberry tree is carefully weeded and the soil is loosened . Weeds must be removed, as they use the nutrients and soil moisture necessary for cultivated plants.
Overgrown weeds shade the plantings and increase humidity in the root zone , promoting the development of rot and other raspberry diseases. They retain foci of infections and overwinter pests.
After weeding, the soil is loosened . If raspberries are planted in two or more rows, a ditch is made between them for autumn watering and fertilization.
Features of care depending on the region
In some cases, it is advisable to prune fruit-bearing shoots not in the fall, but in the early spring . It depends on the region where the crop is grown.
Spring pruning is more suitable for regions with mild winters . Indeed, in warm climates, raspberries continue to grow and accumulate nutrients even after the fruiting period.
And in areas with harsh winters and little snow, undetected fruit-bearing shoots contribute to better snow retention and successful wintering.
Treatment against diseases and pests
Most varieties bred by breeders have a fairly high level of immunity.
Varieties with high resistance to typical diseases:
- Polka;
- Firebird;
- Yellow Giant;
- Kuzmin News;
- Monomakh's hat;
- Sturdy;
- Giant;
- Beauty of Russia;
- Mirage.
Garden raspberries are resistant to common diseases and pests, but in cold, wet summers the risk of infection increases several times and preventive treatment is essential.
Most often appear:
- raspberry-strawberry weevil;
- bud moth;
- raspberry beetle;
- stem gall midge;
- raspberry fly.
Treatment: spray the bushes in spring and autumn with Bordeaux mixture and Karbofos emulsion.
At the end of August, they dig up the ground to a depth of 15-20 cm, so as not to create high humidity for the development of larvae, while adding tobacco dust or wood ash.
Prevention:
- It is not recommended to plant raspberries next to strawberries and blackberries; they have common diseases and pests.
- The proximity to calendula, nettle, red elderberry, dill, plum, pear, rose bushes, and barberry is considered favorable. And aromatic herbs work as repellents for insects that can spoil the raspberry harvest.
The leading diseases are:
- anthracnose;
- canker spotting;
- Dimidella;
- bacterial cancer;
- rust;
- white spotting;
- mosaic;
- curliness.
Diseases appear when care rules are violated, in cold summers with heavy rains, or when the recommended proximity is not observed. The source of the disease can be a fruit tree infected with black rot or another fungal disease that is spread by wind or insects.
Preventive measures include regular treatment of raspberries with HOM or Bordeaux mixture, regular thinning of bushes, timely loosening, and adherence to a watering schedule.
Additional care activities
In addition to pruning, weeding and loosening, raspberry plantings need fertilizing and protection from diseases and pests .
Fertilizer application
For successful wintering and full growth in the spring, fertilizers are added to the soil . Plants need nitrogen to develop their root system in spring. However, if you have already applied nitrogen fertilizers in the summer, there is no need to do this additionally in the fall.
is applied as the main phosphorus fertilizer in the fall , incorporating it into the soil. The shrub also needs potassium for successful wintering, so the soil is additionally fertilized with potassium magnesium or potassium monophosphate.
Follow the instructions when calculating the required amount of fertilizing. Remember that excess nutrients are just as harmful to plants as their deficiency.
As an alternative, complex phosphorus-potassium fertilizers for shrubs are used.
Protection from diseases and pests
Another important stage of autumn work with raspberries is processing the bushes to protect them from pests and diseases. Insect larvae and pathogens of fungal diseases overwinter in the bark. In the spring they wake up and harm young shoots.
Processing begins after pruning, but before mulching . The raspberry plant is cleared of leaves, cut branches, and mulch residues.
How to treat raspberries against pests? To protect against insects, bushes are sprayed with special products. Names of drugs that are most effective against wintering pests :
- “Fufanon” is an insectoacaricide for protection against a complex of pests;
- "Intavir" is an insecticide with enteric contact action against various types of pests.
To prevent the development of diseases, plantings are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture and copper sulfate solution.
Interesting things on the site:
Rules for feeding cherries in autumn
How to properly prune an apricot in the fall
Guide to preparing grapes for winter
Watering and mulching the soil
This is the final stage of autumn work . Raspberries are moisture-loving shrubs, so if the soil is dry, water it abundantly before wintering.
When the water has been absorbed, the soil surface is mulched . This will protect the root system from hypothermia, retain moisture in the soil and slow down the growth of weeds.
Important! The raspberry root system is afraid of frost, as it is located only 20-30 cm from the surface of the earth.
How to mulch raspberries in the fall and how to do it correctly? For autumn mulching, peat, straw, sawdust or rotted leaves are used . The selected material is poured around the stems in a layer of 8-10 cm.
Feeding with fertilizers
Year-round care and nutrition increase crop productivity, strengthen the immune system and protect against diseases and viruses.
Starter fertilizers
When planting in a trench or hole under raspberries, apply the following fertilizers:
- ammonium nitrate - up to 20 g per bush;
- azofoska or nitroammofoska - complex NPK complex (16:16:16) - 30-40 g per 1 seedling;
- additions of boron, zinc and copper are applied simultaneously with basic mineral fertilizers.
Feeding raspberries in winter
Already at the end of summer, in August, you need to pay attention to the raspberries. The nutrient supply in the soil is almost exhausted, the raspberry bushes have wasted a lot of energy. The main thing is not to skip the autumn feeding of raspberries, otherwise you may be left without a harvest.
In the first ten days of August 1-5 and 2 weeks later on August 15-20, it is important to feed raspberries
with mineral fertilizers:
- potassium sulfate - potassium (52%) and sulfur (18%) will protect plants from the upcoming cold weather and ensure the formation of fruit buds in the next season. The irrigation solution is prepared in the proportion of 1 tbsp. l. drug per 10 liters of water ;
- superphosphate extract - 10 tbsp. l. fertilizers per 10 liters of water ; if you fill it with hot water, the hood is ready in a day; if it’s cold, the solution is infused for at least 72 hours (3 days).
Preparing for cold weather
Caring for raspberries in the fall ends with bending the branches to the ground . After pruning, the stems are tied with ropes, a weight is attached and carefully tilted. It is better to do bending before the onset of frost, while the raspberry stems are still flexible.
When grown in the southern regions and central Russia, it is not necessary to cover raspberries . It is enough to mulch the soil well to protect the roots.
And in the Urals, Siberia and especially in the northern regions, shrubs need additional insulation.
One option is to wrap the bushes with spunbond or other suitable material . In this case, the free space between the branches is filled with straw. Shoots bent to the ground are also covered with leaves or spruce branches.
Need to know! An overly covered shrub will begin to rot during thaws and winter rains and will die as a result. Therefore, when choosing material for shelter, focus on the climate of your region.
The simplest and most effective way of insulation is to cover the bushes with snow . The snow blanket should cover them entirely.
For successful wintering, the condition of the plantings plays an important role. Resistance to cold is lower in bushes that are overfed with nitrogen, that have not completed the growing season in the fall, and in bushes that are dense, diseased, and growing in the shade.
Rules for caring for currants
Experienced gardeners use various chemicals to spray bushes:
- antifungal;
- growth accelerators;
- insecticidal substances.
Complex preparations help the summer resident not only treat the berry garden, but also improve the nutrition of the plant and accelerate its growth. When using chemical fertilizers, you should pay attention to the interaction of the ingredients that make up them.
The complex mixture is used for the following purposes:
- prevention of disease infection;
- destruction of the pathogen;
- treatment of individual parts of bushes infected with fungus.
Processing currant leaves. The illustration for the article is used under the standard license ©ofazende.ru
Rejuvenation of old bushes
Raspberry plantings successfully grow and bear fruit in the same place for many years . If you get a plot with an old raspberry tree, it is not necessary to uproot it and plant a new one.
Rejuvenation of old plantings carried out in the fall gives good results . The plantings are inspected and the oldest bushes that do not bear fruit are noted. Around each such bush they dig up the ground with a shovel, cutting off the roots, and remove it.
The resulting voids are filled with compost or humus and compacted . From the root shoots remaining in the ground, new shoots will appear in this place in the spring. After the procedure, the raspberry tree is well watered.
Removal of old roots is carried out in stages over 2-3 years , gradually completely renewing the plantings.
Cutting off the excess (video)
Raspberry is a plant whose branches live for two years and then die. True, shoots appear quite quickly, which will take on the function of the main ones in the next season. It is advisable to remove old shoots that have served their purpose even before the last berries are collected. If you did not do this on time, there is time in the fall. As for remontant raspberries, it is easier with them, since they bear fruit until the first frost, and they can be pruned in October and November. Cut off the shoots to the very base.
If we talk about currants and gooseberries, they have different pruning rules, depending on the variety, growing conditions and plant vigor.
Black currants usually have 10-15 shoots of different ages, two or three 5-6 year olds, 3-4 year olds and 1-2 year olds. The old ones need to be cut out so that there are no stumps left. Shoots called zero shoots also appear from the roots every year. 3-4 best shoots should be left. If you allow all the shoots to grow, the bush will become too dense and begin to lose vigor. If you prune new shoots a little, they will begin to bush vigorously. Annual branches grow on the older branches, which also need to be pruned a little. This will make the berries larger.
If you do not prune at all, the bush will become too dense, weaken and begin to produce a minimum yield of small berries.
Black currants need to be pruned every year.
The rules for pruning red and white currants are almost the same as for black currants. The only difference is that zero shoots are not cut off unless their tops are too weak or frozen. The side branches are not shortened, and branches older than six years can be left on the bush. More details with diagrams and tips.
Gooseberries can have branches that are 8 to 10 years old. They need to be rejuvenated. To do this, the old drying ends are cut off to the place where there is a strong lateral branching. This way you can increase your growth. There should be no more than 12-15 main branches. New shoots should be left if you plan to replace them.
Advice from experienced gardeners
Tips and recommendations from experienced gardeners will help you care for raspberries correctly and get a stable harvest every season :
- After completing all the autumn work in the raspberry garden, cut off the roots that spread beyond its borders. To do this, use a bayonet shovel to walk around the bushes at a distance of 30-40 cm. Carry out the procedure once a year in the fall to avoid the spread of raspberries throughout the entire area.
- When planting a new raspberry bed, dig the remains of slate or metal into the ground around the perimeter of the bed to a depth of 40-50 cm. This way you will limit the growth of roots.
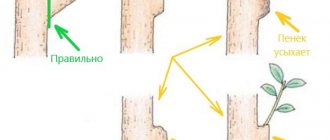
- Cut stems flush with the ground. Pathogens and pest larvae overwinter on protruding stumps.
- When thinning the bushes in the fall, also remove all small shoots. These stems will not have time to grow stronger before the cold weather arrives.
- When pruning, ruthlessly remove old shoots. The life cycle of the shrub is two-year; after the second year, the shoots stop growing and dry out.
When to spray trees and shrubs in the fall
It is recommended to start processing when the trees have shed their leaves. If you do not wait for them to fall, the leaves may get burned and this will lead to negative consequences - burns. The crops will be weakened and will not have time to receive the necessary nutrients. The best time for spraying is November. Before processing, lichens and old bark must be removed from old trees so that various pests do not hide there and avoid processing. It is better to do this procedure with a metal brush.
Raspberry diseases
Raspberry diseases are varied and are usually determined by the appearance of leaves, stems, shoots and berries, and less commonly, roots. The diagram shows some common diseases that can partially or completely ruin your harvest. Inspect your raspberry garden and rule out the following diseases.
Please note that curling and mosaic are viral diseases and cannot be treated. The leaves on bushes infected with leaf curl become small, and the berries become tasteless. When infected with mosaic, plants become smaller and lose their ability to bear abundant fruit. The leaves are covered with variegated spots of light yellow color. Bumps and drying areas may appear. The plant inevitably dies after wintering or too hot a summer. Since viruses spread quickly (usually when pruning healthy plants with an infected tool), it is better to immediately dig up and burn the affected bushes.
Gray mold, septoria, anthracnose, rust and other diseases can be successfully cured or reduced in activity. You can read more about some of them in our article.
- Raspberry diseases - how to detect and cure
How do you know if a raspberry is sick or if it simply lacks nutrients? You will find the answer in our material.
Bend down and cover for the winter
You can help raspberries survive the winter if you cover them properly. For this purpose it is recommended:
- cut off all unfallen leaves from the bush;
- when the previous stage is completely completed, at a level of 30 cm from the ground you need to pull the rope, carefully bend it and tie the branches to it;
- leave a fence made of boards or slate around the bush (it will protect against snow drifts);
- The top of the raspberries can be covered with spunbond (or other non-woven material); it is folded in several layers, placed on the ground and secured (the edges are pressed down or dug in).
Gooseberries after harvest
How to water
Gooseberries are one of the most drought-resistant berry bushes, however, in dry summers, gooseberries growing on light soils need watering, not only when the berries ripen, but also after harvesting, when the plants begin to prepare for winter and lay buds for the next fruiting.
In order to saturate the soil with moisture and prepare the bush for winter, moisture-recharging watering is carried out in two or three steps from late September to mid-October. The water consumption rate is from 40 to 60 liters for each bush. The depth of soil wetting should be at least 50 cm - this is the depth at which the gooseberry roots lie. The methods for watering gooseberries are the same as for currants.
How to fertilize
Caring for gooseberries involves regularly adding mineral and organic fertilizers to the soil. Gooseberries are not fertilized with nitrogen and organic matter after the gooseberry fruiting has completed, and phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are applied to the soil once every two years in the fall - this increases the winter hardiness of the plant. The approximate rate of fertilizer for each square meter of land is 50 g of superphosphate and 30 g of potassium, which can be replaced with 100 g of ash.
- Barberry Thunberg: cultivation, description of varieties
If the soil on the site is sandy or sandy loam, the dose of potassium should be increased by a quarter of the norm. Fertilizers are scattered over the area and, after watering, embedded in the soil to a depth of 10-12 cm.
How to trim
Growing gooseberries is complicated by the fact that every year it produces a huge number of young, thorny shoots, making it difficult to pick berries and care for gooseberries after harvest. Therefore, in the spring, and especially in the fall, it is so important to prune the bushes, freeing them from unnecessary, diseased, dried and broken shoots. Moreover, not only prickly, but also thornless varieties of gooseberries are pruned, since strong thickening harms any bush, and too many shoots weaken the plant and lead to disease or damage to the bush by insect pests. Autumn pruning allows you to thin out the gooseberries so much that the sunlight necessary for the plant penetrates into the very depths of the bush.
Gooseberries need to be pruned in mid-autumn, because if pruned earlier during the autumn thaws, shoots may begin to grow that do not have time to become woody before winter. Thin branches are cut almost to the ground, since there will be no fruit on them, and they will only waste nutrition from well-fruiting shoots. Remove old, darkened branches that, due to their age, are unlikely to bear fruit next year. If there are too many of these branches on the bush, remove only a third of them, and trim the rest in a year or two.
Just before frost, cut off those branches that interfere with the growth of others, leaving younger ones on the bush, and also remove the lower branches lying on the ground. Treat sections thicker than 7 mm with garden varnish. When pruning branches, try not to leave stumps.
Gooseberry propagation
In October, it is time to propagate gooseberries by layering. On a healthy five- to six-year-old bush, select several low-growing, well-developed branches, shorten annual growths on them by about a third of the length - this measure promotes more intensive germination of lateral buds, which in turn stimulates good root development and shoot growth. Bend the prepared cuttings to the ground, place them in pre-dug grooves and pin them with wire or wooden hooks. Then cover the cuttings with soil, water and mulch the soil around them. You can, of course, propagate gooseberries by layering in the spring, but you need to start early, before the buds open.
In autumn, gooseberries can be propagated by cuttings. Lignified cuttings 20 cm long are cut from the top of overgrowing or basal shoots - they take root better. Gooseberry cuttings are planted in beds at an angle of 45º, leaving one or two buds above the surface, the soil is compacted around them, the bed is mulched with peat or sawdust and covered with film.
How and with what to process
Pests and diseases of gooseberries can jeopardize both the quality and quantity of the future berry harvest. It is customary to deal with these problems as they arise, but it is better to prevent these problems from appearing in the first place. That is why it is necessary to treat gooseberry bushes with fungicides and insecticides several times during the growing season for preventive purposes.
In the fall, after cleaning and digging the area, as well as pruning the gooseberries, remove and burn all plant debris, and then treat the bushes and the soil under them with one percent Bordeaux mixture or preparations of a similar effect - copper oxychloride, captan.
How and with what to cover the bushes when preparing raspberries for winter?
In winter, the raspberry tree will be able to cover the snow, but it is important to promptly remove the ice crust, which does not allow the air needed by the roots to pass through.
When there is little snow, raspberries are covered with leaves. The layer of such a shelter should be about 30-35 cm. Also for this purpose, a special film is used, in which holes are made in advance for ventilation. Spunbond will also work.
When to cover raspberries?
Be sure to cover heat-loving and frost-resistant varieties, for which winter winds and drafts can be destructive. In the Primorsky Territory, for example, if there is a high probability of early frosts, raspberries are also covered.