How does the distance when planting between tomato bushes affect growth and fruiting?
The growth of the bushes and their fruiting will depend on how close to each other you plant the tomatoes.
Tomato bushes are growing quite strongly. If they do not have enough space, they will not be able to form shoots on which fruits will grow.
What happens when tomatoes are planted thickly?
Tomatoes are a crop that loves space. Unlike, for example, peppers, which, on the contrary, prefer a denser planting.
If you plant plants too close to each other, they will begin to interfere with each other. The fact is that tomatoes grow strongly and form new shoots. This is necessary for abundant fruiting and the formation of the fruits themselves.
When tomatoes sit too long, they have no room to grow. As a result, the harvest is meager, and the bushes themselves often get sick, since their immunity is weakened.
In addition, plants sitting nearby begin to compete with each other for sunlight, micronutrients in the soil, etc.
Also, dense plantings are dangerous due to the rapid spread of fungal diseases and massive pest damage.
If tomatoes are planted too far apart
If you plant tomatoes in open ground, leaving a lot of free space between the bushes, then nothing bad will happen. Plants will develop normally.
But the problem will be different. Namely, in the irrational use of site space. You shouldn’t expect tomatoes to grow to the size of berry bushes. Therefore, they need to be planted in the most optimal way.
In addition, by leaving a lot of space between the bushes, you doom yourself to weeding.
Also, the “empty” land will dry out, which in the future can lead to soil erosion.
The main mistakes when growing tomatoes
This is mainly the sin of novice gardeners. They do not yet know many secrets, so the plant may not live up to their expectations. The most common mistakes:
- Seeds for seedlings are sown at the wrong time;
- Growing a variety intended for a greenhouse in the ground;
- The gardener purchased the seedlings already with flower stalks. This is fraught with slow rooting and fruit formation;
- Frequent watering;
- Overfeeding, especially with nitrogen: this affects the taste;
- Planting in the ground ahead of schedule: the seedlings freeze and die.
Schemes for planting tomato seedlings
Exactly how to place tomatoes in your garden depends on how much space you can allocate to tomato beds, as well as other related factors.
For example, if the vegetable garden covers the garden on one side, then it is better to plant tomatoes in a row. If, on the contrary, the area is open, then it is better to place the tomatoes compactly and so that they are easy to care for.
The most popular schemes for planting tomatoes in open ground are below.
Parallel landing scheme
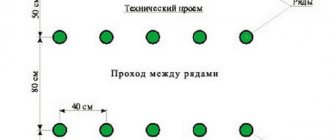
In fact, this is not one scheme, but a whole group of schemes for planting tomatoes in open ground, the essence of which is to plant plants in parallel in rows at an equal distance from each other.
Usually, 2 rows are made side by side with a distance of 50 cm between them, then a passage about a meter wide and again 2 rows. This paired arrangement is dictated by the need to care for tomato bushes.
ON A NOTE. The specific distance between tomato bushes in open ground is determined based on the size of the variety. Tall ones are planted less often, short ones more often.
By the way, when planting in parallel, it is better to plant the bushes from west to east, so that the sun evenly illuminates the plant throughout the day.
Checkerboard landing pattern
The checkerboard method is used for planting low-growing and low-growing varieties in open ground. It is also good for limited space or when you are planting in a specific area due to crop rotation.
With this scheme, you first determine the size of the area where you will plant tomatoes and dig holes so that there is 40-50 cm between adjacent holes.
The advantage of this scheme is the compact arrangement of tomato bushes.
Planting in raised beds
Some summer residents make high, warm beds for the convenience of caring for tomatoes in the open ground. In one bed, 2 rows of seedlings are placed with a distance of 50 cm between the bushes. Leave 70 cm between rows.
The advantage of this scheme is the ease of caring for tomato bushes.
How to choose a place for a tomato bed
Tomatoes are sensitive to growing conditions - this is due to the subtropical origin of nightshade crops. On the site for the tomato bed, you should allocate a well-drained sunny area, protected from the wind.
It is extremely undesirable to plant tomatoes in the same place again, as after any nightshades - potatoes, peppers, eggplants. It is necessary to wait 2-3 years to reduce the likelihood of an outbreak of infections whose spores remain in the garden.
The best predecessors for tomato culture are onions, garlic, carrots, cucumbers, all legumes or green manure, which improve the health of the soil.
When choosing a place for a tomato garden, you should also take into account nearby neighbors in the garden.
- Do not place tomatoes next to potatoes. In addition to diseases, they have a common pest - the Colorado potato beetle.
- Experienced summer residents know that marigolds and calendula not only decorate the site. Planted along the edges of the beds, flowers repel insect pests. Phytoncides of fragrant plants resist outbreaks of late blight and other fungal diseases of tomatoes.
At what distance from each other to plant tomatoes in open ground, popular schemes
When planting tomatoes in open ground, it is important to choose the correct distance between plants so that the bushes do not interfere with each other.
ON A NOTE. On average, the optimal distance between individual tomatoes is about 50 cm, and between rows 70-80 cm. More precise values depend on the characteristics of the particular tomato variety.
The choice of a specific landing scheme depends on several factors:
- Dimensions and shape of the site.
- Number of seedlings.
- Varietal characteristics of planted tomatoes.
There are several schemes. Let's look at the 2 most popular and effective ones.
Parallel landing
If you plant tomatoes in open ground in even rows using the strip method, then it is better to form beds 1 m wide. Leave 50-60 cm between rows in one bed, and maintain a distance of 100 cm between rows.
This method of planting will allow you to care for tomatoes very conveniently.
Leave at least 50 cm between individual bushes.
Chess scheme
On square plots, a checkerboard planting pattern is practiced. In this case, maintain 40 cm between individual bushes.
This model is good if you have few seedlings or are limited in space.
Also, planting using the checkerboard method is chosen if the area of open ground is poorly located, or, conversely, only it has a suitable type of soil.
Protection of young seedlings from return frosts
Despite the fact that tomato seedlings are transferred to the ground only after stable warming, there is always a risk of return frosts. Even a slight drop in temperature is dangerous for seedlings.
- If the forecast predicts colder weather, beds with young plants are covered with spunbond or other similar material.
- If the seedlings are already frozen, then all damaged leaves are removed from them, and healthy tissues are treated with a warm solution of boron or iodine. You can also treat the bushes with Epin or Zircon. This is a way to stimulate the growth of new vegetative mass.
- After 10 days, they are sprayed again with anti-stress drugs (“Epin”, “Zircon”), after which after another 4 days urea is applied under the bushes.
- If, as a result of frost, the leaves have only withered, they are revived by spraying with warm water (+25...+30°C).
At what distance from each other should different varieties be planted?
Summer residents often plant several varieties in their gardens. Some will be used for preparing light summer salads, others for pickling, others for preparing tomato juice, etc.
Each variety of tomatoes growing in open ground needs its own conditions for normal development.
Tall tomatoes
Tall tomatoes need a lot of space to grow, so the distance when planting is at least 70 cm between individual bushes and at least 1 m between rows.
Planting “standard” tomatoes
Medium-sized bushes need less distance to grow and bear fruit normally.
On average, about half a meter is left between individual bushes (a little more is possible), and a distance of 80 cm is made between the rows to make it convenient to care for tomatoes in the open ground.
At what distance to plant low-growing tomatoes?
Low-growing tomato varieties form low, compact bushes. Some gardeners leave only 30 cm between them. But still, it is better not to make the distance between tomatoes less than 40 cm and between rows less than 50 cm.
It is advisable to maintain such a distance to make it convenient to collect fruits, as well as to prevent fungal infections.
What determines the distance between tomatoes?
Tomato varieties have different structures and bush heights. This is the main factor determining the placement of tomato seedlings. In total, two types of varieties of this plant can be distinguished.
Indeterminate varieties are distinguished by a powerful, tall bush (the stems of individual tomatoes can reach up to 3 m). At the same time, the above-ground part is compact, but the root system is highly developed in the horizontal direction. Indeterminate tomatoes require a large feeding area. Crowded planting leads to competition for nutrients, which reduces yields.
Determinate varieties of tomatoes can also be tall - individual bushes reach a height of 1.5 m. These plants require pinching, after which two main stems remain. They usually require tying up, but even in this state they can be spreading. Thickening of plantings of determinate varieties leads to deterioration of pollination and premature shedding of ovaries.
In addition to the type of tomatoes, the planting pattern is also influenced by the method of cultivation: there is a different approach to placement in open and closed ground.
At what depth to plant tomato seeds?
It is very important to choose the correct seeding depth when planting tomatoes.
The optimal value is considered to be 1 - 1.5 cm. This depth is enough for the tomatoes to quickly germinate and sprout.
Deeper planting does not make sense, since the tomatoes will take a long time to sprout. In this case, the seeds will spend a lot of energy on germination. In addition, because the seedlings will form lateral roots, which are not really needed.
But when planting seedlings in open ground, they are planted to a depth slightly greater than the container in which they grew.
Beds for tomatoes - what and why?
Tomato bushes do not get sick and produce a good harvest on fertilized structured soil without stagnant water. Excess soil moisture provokes epidemics of fungal diseases. Lack of water stimulates the development of the root system. In search of water, tomato roots penetrate to a depth of 1.5 m.
If the groundwater level is high, it is necessary to drain the water. Land reclamation is a labor-intensive and expensive undertaking, which is mandatory when planting perennial plants.
In the case of growing annuals, including tomatoes, it is much easier to organize raised beds.
“Tall” is a relative concept. To drain excess water, it is enough to raise the bed by 15-20 cm. To give a neat look, the edges can be strengthened with scraps of slate, boards, etc.
Gardening Tips and Tricks
When growing tomatoes in open ground, gardeners often resort to a variety of tricks to increase tomato yields.
- Tall seedlings are not planted directly into the hole, but are laid horizontally with the crown facing north. This is done so that lateral roots form on the buried stem.
- The soil under the bushes is mulched with sawdust. This improves the soil structure and retains moisture from evaporation.
- Before planting, pour a handful of ash into the bottom of the hole.
- After planting in open ground, the bushes are covered on the south side from the scorching sun. They use broken tree branches with leaves, cardboard boxes, etc.
- Near large-fruited varieties, a support for tying is immediately placed.
- Low-growing tomatoes are planted on the south side, and tall ones on the north side so that they do not block the sun.
- Plant early-ripening varieties next to early-ripening varieties, and late-ripening varieties next to late-ripening ones. This will make caring for the bushes much easier.
- Be sure to use stands and supports for tall varieties.
- Carry out stepsoning. This way you will reduce the area occupied by the tomato bush and also increase the overall yield.
Planting methods
There are 2 main methods of planting in the ground: seed and seedlings. The first case is rarely used, only in cases where the climate is warm enough and the summer is long, and there is no need to harvest quickly.
Seeds
The seed material is spread directly into the soil and mulched.
Positive aspects of the method
- hardening of future plants: increasing their cold resistance and tolerance to dry periods;
- late fruit ripening: if you rationally combine seedlings and seed sowing, the tomato season can be extended by 2-3 weeks.
Not all tomato seeds can germinate normally in all regions, so you need to choose your seed carefully. This article will tell you about the Agata tomato variety.
Negative aspects
- possible only in southern latitudes, for example, in Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, since sowing is expected in mid-March-early April;
- large % of unripe tomatoes at the end of the season;
- the seed material must be clean, so it is especially carefully treated against diseases;
- it has been proven that seed germination required is more than 85%;
- the bushes grow slowly, so they can be suppressed by weeds - constant weeding is required;
To avoid getting a large number of unripe tomatoes, you need to choose early-ripening varieties.
To control weeds, seeds planted in tomatoes are often treated with herbicides during the growth and ripening process, which has a detrimental effect on the purity of the product.
Seedlings
Planting tomatoes with seedlings is a traditional method of cultivation. Planting is done when the first inflorescence has already appeared and the bush has grown to about 25 cm in height. In this case, the root bag is placed in the hole along with a lump of earth and the plant is slightly deepened.
Seedlings that have grown to a height of more than 40 cm do not need to be deepened much, as they may stop growing further. This link will tell you about planting and caring for the Benito tomato variety.
You can water the seedlings only after 12-15 days, after the adaptation period.
Common mistakes
Novice gardeners often make mistakes when planting tomatoes in open ground.
Let's sort them out.
- Planting next to nightshades. Tomatoes are relatives of potatoes, peppers and eggplants, so it is advisable to plant them away from each other so that they do not get sick.
- It is also a mistake to grow tomatoes where potatoes, peppers or eggplants grew last year.
- Planting too often. In an attempt to save space, gardeners often plant seedlings in open ground too close to each other. But you can’t do that. Tomatoes need room to grow, and neighbors will compete with each other for micronutrients and sun.
In addition, in dense plantings there is no air movement. All this leads to the rapid spread of diseases.
- Supports for tall tomatoes are not used. Because of this, they grow crooked under the weight of the fruit and often lie on the ground, which provokes various rots.
- Varieties of tomatoes are planted interspersed. This significantly complicates care and also reduces the yield of low-growing tomatoes growing in open ground.
Preparing seedlings
Transplantation is stressful for seedlings, so a week before the intended transfer to the ground, seedlings begin to be prepared for new conditions. Preparing seedlings involves hardening the seedlings, which allows plants to adapt to growth at lower temperatures than in the room.
Hardening begins 2 weeks before transplantation. To do this, cups with seedlings are taken out onto the balcony or into the greenhouse. First for 15-30 minutes, then every day the time is increased and in a week it is brought to a full day. The air temperature should not fall below +10…+12°С.
Answers to frequently asked questions
How to choose the distance for planting tomatoes if I don’t know what variety I’m planting?
In this case, focus on the average value of half a meter between individual bushes. If the seedling is large, step back a little more (55 - 60 cm).
Is any additional tool needed?
A garden marker will be a great help to use to mark the rows for planting.
Do I need to cover tomatoes after planting in open ground?
Not required, but recommended. Shelter will help plants take root faster and better adapt to open ground conditions.
Do I need to put something in the hole when planting?
You can sprinkle a tablespoon of wood ash on the bottom, but then it must be covered with a layer of soil so that the roots of the tomato do not touch the fertilizer. In general, fertilizing is carried out approximately two weeks after planting in a permanent place.
What to do before boarding?
Be sure to harden the seedlings. This will help her settle in better in her new place.
What tomatoes love - soil preparation
After choosing the right location, soil preparation is the second most important stage of agricultural technology for open-ground tomatoes. The soil in the garden bed for growing tomatoes begins to be prepared in advance - in the fall.
Autumn work
After the end of the season, the area must be dug deep for the winter - wintering insects and the roots of perennial weeds freeze out when raised to the surface. Before plowing (digging), poor soil is fertilized. Choose one of the methods:
- organic matter - 5 kg of humus or compost (partial bucket) per 1 sq. m;
- mineral fertilizers - 50 g of superphosphate (1/4 cup) and 20 g of potassium salts per 1 sq. m.
Spring work
As soon as the soil in the garden bed matures, it must be dug up and harrowed. For digging they bring in:
- bird droppings - 1 kg per 1 sq. m;
- hardwood ash - 1 kg per sq. m;
- ammonium sulfate - 25 g (1 heaped tablespoon) per 1 sq. m.
Tomatoes do not tolerate acidic soils. The easiest way to normalize the pH is with lime (about 500 g per 1 sq. m). When planting, wood ash (under a bush - 2 tablespoons) not only deoxidizes the soil, but also contains all the necessary microelements.